Forces and Motion Study Guide
... 37. What is Newton’s 1st Law of Motion? Give an example. An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an outside force, also known as law of inertia, deals with balanced forces. Ex: table cloth trick 38. What is Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion? Give an example. The acceleration of an object ...
... 37. What is Newton’s 1st Law of Motion? Give an example. An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an outside force, also known as law of inertia, deals with balanced forces. Ex: table cloth trick 38. What is Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion? Give an example. The acceleration of an object ...
Lecture 9 Force and Motion Newton`s Third Law We can all accept
... Fnet = F2on1 - friction This tells us that when friction < F2on1, the team will move into the center and lose. because Fnet ≠ 0, so there would be an acceleration! This is a second law relationship, not third! Just remember that in a third law pair the forces have to act on different objects. Also, ...
... Fnet = F2on1 - friction This tells us that when friction < F2on1, the team will move into the center and lose. because Fnet ≠ 0, so there would be an acceleration! This is a second law relationship, not third! Just remember that in a third law pair the forces have to act on different objects. Also, ...
Assignment of Laws of Motion
... Q5. A 50gm bullet is fired from 10kg gun with velocity of 500m/s what is the speed of recoil of gun? Q6. A force of 98 N just required to move a mass of 45 kg on a rough surface find the coefficient of friction and angle of friction? Q7.For the next several questions, consider the velocity-time plot ...
... Q5. A 50gm bullet is fired from 10kg gun with velocity of 500m/s what is the speed of recoil of gun? Q6. A force of 98 N just required to move a mass of 45 kg on a rough surface find the coefficient of friction and angle of friction? Q7.For the next several questions, consider the velocity-time plot ...
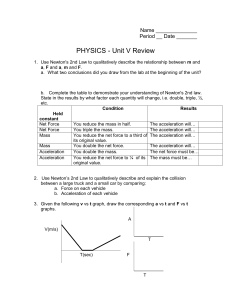
Unit V review
... b. resolving forces into x and y components, then finding the vector sum of the forces. c. analysis of the kinematic behavior of the object. 4. Solve quantitative problems involving forces, mass and acceleration using Newton's 2nd Law. a. Having determined the net force (as in #3), and given the mas ...
... b. resolving forces into x and y components, then finding the vector sum of the forces. c. analysis of the kinematic behavior of the object. 4. Solve quantitative problems involving forces, mass and acceleration using Newton's 2nd Law. a. Having determined the net force (as in #3), and given the mas ...
File
... 3. The “reaction” force does not cancel the “action” force because: (A) The action force is greater than the reaction force. (B) The action force is less than the reaction force. (C) They act on different bodies. (D) They are in the same direction. (E) The reaction exists only after the action force ...
... 3. The “reaction” force does not cancel the “action” force because: (A) The action force is greater than the reaction force. (B) The action force is less than the reaction force. (C) They act on different bodies. (D) They are in the same direction. (E) The reaction exists only after the action force ...
Newton`s Laws First Law --an object at rest tends to stay at rest AND
... *Speed is a combination of the two: m/s, ...
... *Speed is a combination of the two: m/s, ...
Newton Second Law OK
... on it: the normal force, gravity, and the frictional force. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. • The friction force is parallel to it. • The gravitational force points down. If the object is at rest, the forces are the same except that we use the static frictional force, and ...
... on it: the normal force, gravity, and the frictional force. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. • The friction force is parallel to it. • The gravitational force points down. If the object is at rest, the forces are the same except that we use the static frictional force, and ...
A baseball is thrown vertically upward
... A baseball is thrown vertically upward. It then goes upward until it reaches its highest point and then comes back down to the thrower. 1) Make a system schema for the situation above. ...
... A baseball is thrown vertically upward. It then goes upward until it reaches its highest point and then comes back down to the thrower. 1) Make a system schema for the situation above. ...
Situation Diagram Free-body diagram
... The object does not necessarily have to moving in one direction or another, but the directions of the force vectors will change accordingly. ...
... The object does not necessarily have to moving in one direction or another, but the directions of the force vectors will change accordingly. ...
Name - North Salem Schools Teachers Module
... If additional objects are involved, draw separate free body diagrams for each object ...
... If additional objects are involved, draw separate free body diagrams for each object ...
Forces in One Direction
... Acceleration, or the change In an object’s motion. Force is a VECTOR quantity! The SI unit of force is the Newton, Labeled with an, N. ...
... Acceleration, or the change In an object’s motion. Force is a VECTOR quantity! The SI unit of force is the Newton, Labeled with an, N. ...
Unit 2 Study Guide Answer Key
... If two or more forces are acting on an object in the same direction, you find the net force by adding the forces together. If two or more forces are acting on an object in opposite directions, you find the net force by subtracting the forces. The object will move in the direction of the greater forc ...
... If two or more forces are acting on an object in the same direction, you find the net force by adding the forces together. If two or more forces are acting on an object in opposite directions, you find the net force by subtracting the forces. The object will move in the direction of the greater forc ...