Review test # 2
... ____ 22. Matter is defined as anything that a. can be seen and touched. c. can be weighed. b. has mass and takes up space. d. contains kinetic or potential energy. ____ 23. The science of what matter is made of and how it changes is called a. chemistry. c. kinetics. b. physics. d. engineering. ____ ...
... ____ 22. Matter is defined as anything that a. can be seen and touched. c. can be weighed. b. has mass and takes up space. d. contains kinetic or potential energy. ____ 23. The science of what matter is made of and how it changes is called a. chemistry. c. kinetics. b. physics. d. engineering. ____ ...
Dynamics and mechanics of motor
... constants do not fulfill the Einstein relation. In contrast, unbound motors are assumed to simply diffuse thermally with diffusion constant Du . The translational and the rotational filament currents, Ja and Jr , as well as the motor current Jb are generated by active interactions between motors and ...
... constants do not fulfill the Einstein relation. In contrast, unbound motors are assumed to simply diffuse thermally with diffusion constant Du . The translational and the rotational filament currents, Ja and Jr , as well as the motor current Jb are generated by active interactions between motors and ...
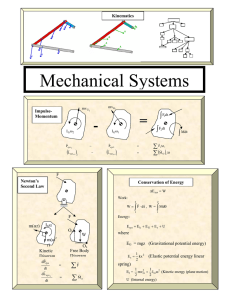
Mechanical Vibrations
... A mechanical vibration is the motion of a particle or a body which oscillates about a position of equilibrium. Most vibrations in machines and structures are undesirable because of the increased stresses and energy losses which accompany them. They should therefore be eliminated or reduced as much a ...
... A mechanical vibration is the motion of a particle or a body which oscillates about a position of equilibrium. Most vibrations in machines and structures are undesirable because of the increased stresses and energy losses which accompany them. They should therefore be eliminated or reduced as much a ...
Physics 120 Lab 3: Modeling Motion of Cart on Track: no force
... of the cart running off the end of the track, without falling, to explain how the programmer needs to account for ALL relevant physical constraints to make sure the simulation is realistic. 3. Discuss your predicted graph of momentum vs. time and what VPython showed and discuss how the computer code ...
... of the cart running off the end of the track, without falling, to explain how the programmer needs to account for ALL relevant physical constraints to make sure the simulation is realistic. 3. Discuss your predicted graph of momentum vs. time and what VPython showed and discuss how the computer code ...
pdf file
... ‘Moving force is the product of the mass value of a body with the acceleration induced in that body.’ [Mach, 1942], p. 304 ...
... ‘Moving force is the product of the mass value of a body with the acceleration induced in that body.’ [Mach, 1942], p. 304 ...
APPARENT MASSES AND INERTIA MOMENTS OF THE PARAFOIL
... motion is unstable – large moving objects generate motion of certain fluid mass. When the object motion is unstable and motion parameters change, motion of the fluid is disturbed. To calculate forces acting on a moving solid body and its acceleration, it is necessary to know pressure distribution in ...
... motion is unstable – large moving objects generate motion of certain fluid mass. When the object motion is unstable and motion parameters change, motion of the fluid is disturbed. To calculate forces acting on a moving solid body and its acceleration, it is necessary to know pressure distribution in ...