Developer Notes - University of Hawaii System
... How about an object that is moving? Can it be in equilibrium? By Newton's 1st Law, if the object is going in a straight line at a constant speed, there must be no net force on it, or else it would speed up, slow down, or turn. For a car going at a steady speed on a straight highway, the force of the ...
... How about an object that is moving? Can it be in equilibrium? By Newton's 1st Law, if the object is going in a straight line at a constant speed, there must be no net force on it, or else it would speed up, slow down, or turn. For a car going at a steady speed on a straight highway, the force of the ...
Unit B Practice Unit Exam
... 15. The distance between the Earth and Sun is approximately 149 600 000 km, or 1 astronomical unit (1 au). The force of gravity acting on the Earth due to the Sun is F. If the Sun were 3 times more massive than it is now and the Earth-Sun distance increased to 7 au, the new force of gravity acting o ...
... 15. The distance between the Earth and Sun is approximately 149 600 000 km, or 1 astronomical unit (1 au). The force of gravity acting on the Earth due to the Sun is F. If the Sun were 3 times more massive than it is now and the Earth-Sun distance increased to 7 au, the new force of gravity acting o ...
Name of Model
... c. Is the car accelerating? What direction is the car's acceleration? (Explain how you know.) ...
... c. Is the car accelerating? What direction is the car's acceleration? (Explain how you know.) ...
Unbalanced Forces & Acceleration
... Unbalanced Forces and Velocity (cont.) • An unbalanced force applied to a moving object in the same direction as the motion speeds the object up. • An unbalanced force applied to a moving object in the opposite direction as the motion slows the object down. • Friction is applied in the opposite dire ...
... Unbalanced Forces and Velocity (cont.) • An unbalanced force applied to a moving object in the same direction as the motion speeds the object up. • An unbalanced force applied to a moving object in the opposite direction as the motion slows the object down. • Friction is applied in the opposite dire ...
Document
... (e) d, and (f) W if they, instead, slow at 4.0 m/s2? ANSWER: (a) 1.7 102 N; (b) 3.4 102 m; (c) -5.8 104 J; (d) 3.4 I02 N; (e) 1.7 102m; (f) -5.8 104 J 5. A helicopter lifts a72 kg astronaut 15 m vertically from the ocean by means of a cable. The acceleration of the astronaut is g/10. How ...
... (e) d, and (f) W if they, instead, slow at 4.0 m/s2? ANSWER: (a) 1.7 102 N; (b) 3.4 102 m; (c) -5.8 104 J; (d) 3.4 I02 N; (e) 1.7 102m; (f) -5.8 104 J 5. A helicopter lifts a72 kg astronaut 15 m vertically from the ocean by means of a cable. The acceleration of the astronaut is g/10. How ...
chapter05
... For µs, use the angle where the block just slips For µk, use the angle where the block slides down at a constant speed ...
... For µs, use the angle where the block just slips For µk, use the angle where the block slides down at a constant speed ...
Physics 111
... Linear and Rotational Mechanics: Logical Structure NEWTONIAN MECHANICS forces & torques cause changes in the motion TRANSLATIONAL DYNAMICS movement from one place to another ...
... Linear and Rotational Mechanics: Logical Structure NEWTONIAN MECHANICS forces & torques cause changes in the motion TRANSLATIONAL DYNAMICS movement from one place to another ...
J S U N I L T U... Force Created by Jsunil Tutorial Panjabi colony Gali no. 01
... Balanced And Unbalanced Forces : --- Forces which do not cause any change in state of rest or of uniform motion along a straight line are called balanced forces. The resultant of balanced forces is always equal to zero (because the forces are equal and opposite) The forces acting on a body produce a ...
... Balanced And Unbalanced Forces : --- Forces which do not cause any change in state of rest or of uniform motion along a straight line are called balanced forces. The resultant of balanced forces is always equal to zero (because the forces are equal and opposite) The forces acting on a body produce a ...
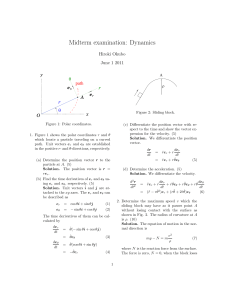
Midterm examination: Dynamics
... C2 are constants, and v is the velocity. If the particle has an initial velocity v0 , derive an expression for the distance D required for it to a stop. (10) Solution. Integration of the acceleration gives the distance ...
... C2 are constants, and v is the velocity. If the particle has an initial velocity v0 , derive an expression for the distance D required for it to a stop. (10) Solution. Integration of the acceleration gives the distance ...
Physics Final - cloudfront.net
... 6. T: At any instant, an orbiting moon has a velocity that is not in the direction of its acceleration. 7. F: Two satellites orbit a common planet with the same average orbital radius. The more massive satellite will have a greater speed than the less massive one. 8. T: The force of gravity exerted ...
... 6. T: At any instant, an orbiting moon has a velocity that is not in the direction of its acceleration. 7. F: Two satellites orbit a common planet with the same average orbital radius. The more massive satellite will have a greater speed than the less massive one. 8. T: The force of gravity exerted ...
Our Place in the Cosmos Elective Course
... • Objects at rest stay at rest, objects in motion stay in motion • “Newton’s First Law” is actually due to Galileo Galilei (1564 -1642) • The Greek philosopher Aristotle, around 2000 years earlier, believed that the natural state of objects was to be at rest - an object in motion would tend toward t ...
... • Objects at rest stay at rest, objects in motion stay in motion • “Newton’s First Law” is actually due to Galileo Galilei (1564 -1642) • The Greek philosopher Aristotle, around 2000 years earlier, believed that the natural state of objects was to be at rest - an object in motion would tend toward t ...