3 - CSUN.edu
... In a collision, the impulse encountered by an object is equal to its momentum change A. TRUE B.FALSE 5. In a collision, an object experiences an impulse. This impulse causes and is equal to ___ of the object. A. Force B. momentum C. Acceleration D. Velocity E. Energy Change F. Kinematics Change G. M ...
... In a collision, the impulse encountered by an object is equal to its momentum change A. TRUE B.FALSE 5. In a collision, an object experiences an impulse. This impulse causes and is equal to ___ of the object. A. Force B. momentum C. Acceleration D. Velocity E. Energy Change F. Kinematics Change G. M ...
Newton's Third Law - Fulton County Schools
... Newton’s Third Law – cont’d For every action, there is an equal but opposite ...
... Newton’s Third Law – cont’d For every action, there is an equal but opposite ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... • A baseball accelerates downward at 9.8 m/s2. If the gravitational force is the only force acting on the baseball and is 1.4 N, what is the baseball’s mass? • Known: F = 1.4 N Equation: m=F/a a = 9.8 m/s2 ...
... • A baseball accelerates downward at 9.8 m/s2. If the gravitational force is the only force acting on the baseball and is 1.4 N, what is the baseball’s mass? • Known: F = 1.4 N Equation: m=F/a a = 9.8 m/s2 ...
AP Physics-1 Forces HW-2 Read Textbook Chapter 5, sections 5.1
... example. If your answer is no, explain why not. A friend tells you that since his car is at rest, there are no forces acting on it. How would you reply? You drop two objects from the same height at the same time. Object 1 has a greater mass than object 2. If the upward force due to air resistance is ...
... example. If your answer is no, explain why not. A friend tells you that since his car is at rest, there are no forces acting on it. How would you reply? You drop two objects from the same height at the same time. Object 1 has a greater mass than object 2. If the upward force due to air resistance is ...
Chapter 3 Summary
... • Set up the problem as usual, including the force of friction • For example, as seen in fig. 3.11: • ΣF = Ffriction = -μk N = m a • From the y-direction, Fgrav = N = m g • Therefore, -μk m g = m a and a = - μk g • Once you have found the acceleration, other quantities involved with motion can also ...
... • Set up the problem as usual, including the force of friction • For example, as seen in fig. 3.11: • ΣF = Ffriction = -μk N = m a • From the y-direction, Fgrav = N = m g • Therefore, -μk m g = m a and a = - μk g • Once you have found the acceleration, other quantities involved with motion can also ...
Free Body Diagrams - Mr. Romero
... <+450. N + F> = (35.0kg)(+9.0 m/s/s) 450. N + F = 315 N F = 315 N - 450. N = -135 N (to the ...
... <+450. N + F> = (35.0kg)(+9.0 m/s/s) 450. N + F = 315 N F = 315 N - 450. N = -135 N (to the ...
Widely separated binary systems of very low mass stars Phan Bao
... If an external force acts on the system but does no work, i.e. no energy transfer to the system, the force can change the KE or PE of the system. Her KE increases due to internal transfers from the biochemical energy in her muscles ...
... If an external force acts on the system but does no work, i.e. no energy transfer to the system, the force can change the KE or PE of the system. Her KE increases due to internal transfers from the biochemical energy in her muscles ...
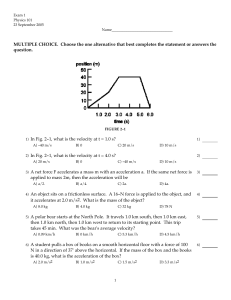
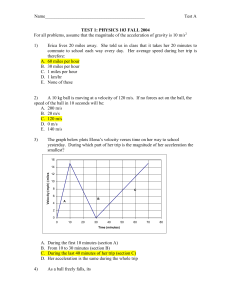
SAMPLE TEST 1: PHYSICS 103
... magnitude 200 N. The elephant moves with a constant forward acceleration. Which statement is most true about the magnitude of the force of kinetic friction acting on the elephant? A. It is greater than 200 N B. It is less than 200 N C. It is equal to 200 N D. None of the above are necessarily true ...
... magnitude 200 N. The elephant moves with a constant forward acceleration. Which statement is most true about the magnitude of the force of kinetic friction acting on the elephant? A. It is greater than 200 N B. It is less than 200 N C. It is equal to 200 N D. None of the above are necessarily true ...