Newton`s Laws of Motion Practice Test 1. Which of Newton`s Three
... force on the ball at rest. This causes the ball at rest to accelerate. However, the ball at rest also exerts the same magnitude of force (in the opposite direction) of the moving ball. This will cause the moving ball to decelerate or even move in another direction. A. Newton’s First Law B. Newton’s ...
... force on the ball at rest. This causes the ball at rest to accelerate. However, the ball at rest also exerts the same magnitude of force (in the opposite direction) of the moving ball. This will cause the moving ball to decelerate or even move in another direction. A. Newton’s First Law B. Newton’s ...
The Centripetal Force Requirement
... A person's sensation of weight is due to the presence of a normal force upon their body. Usually, this normal force is of the same magnitude as the force of gravity. So a 600 Newton person typically feels 600 N of normal force to provide a sensation of how much they weigh. When the normal force beco ...
... A person's sensation of weight is due to the presence of a normal force upon their body. Usually, this normal force is of the same magnitude as the force of gravity. So a 600 Newton person typically feels 600 N of normal force to provide a sensation of how much they weigh. When the normal force beco ...
Newton`s Universal Law of Gravitation- any
... If there are more than 2 objects, you can find the net force on one object by finding its gravitational attraction to each of the masses surrounding it and then performing a vector summation of those forces. Here it could be helpful to write the forces as unit vectors ( i and j). In the equation, th ...
... If there are more than 2 objects, you can find the net force on one object by finding its gravitational attraction to each of the masses surrounding it and then performing a vector summation of those forces. Here it could be helpful to write the forces as unit vectors ( i and j). In the equation, th ...
Document
... • The acceleration produced by a net force acting on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force and in the same direction as the net force, and the acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. • Acceleration = net force/mass • a=Fnet/m Physics 3050: Lec ...
... • The acceleration produced by a net force acting on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force and in the same direction as the net force, and the acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. • Acceleration = net force/mass • a=Fnet/m Physics 3050: Lec ...
The Force! - Cobb Learning
... INERTIA the tendency of an object to resist changes in acceleration ...
... INERTIA the tendency of an object to resist changes in acceleration ...
Solutions for class #1 from Yosunism website Problem 4.
... the test- taker with two of them. Since the symmetric mode frequency is not listed, choose choice it!---as in (A). ...
... the test- taker with two of them. Since the symmetric mode frequency is not listed, choose choice it!---as in (A). ...
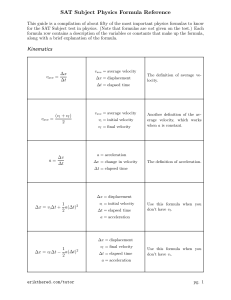
SAT Subject Physics Formula Reference
... the kinetic coefficient of friction µk or the static coefficient of friction µs . ...
... the kinetic coefficient of friction µk or the static coefficient of friction µs . ...
AP C UNIT 4 - student handout
... Example 2: A cylinder of mass M and radius R has a string wrapped around it, with the string coming off the cylinder above the cylinder. If the string is pulled to the right with a force F, what is the acceleration of the cylinder if the cylinder rolls without slipping? What is the frictional force ...
... Example 2: A cylinder of mass M and radius R has a string wrapped around it, with the string coming off the cylinder above the cylinder. If the string is pulled to the right with a force F, what is the acceleration of the cylinder if the cylinder rolls without slipping? What is the frictional force ...
Momentum and Impulse
... If the force exerted on an object is NOT a constant force, finding the impulse/change in momentum is a little more difficult. As the saying goes, “If the forces varies… You must integrate!” ...
... If the force exerted on an object is NOT a constant force, finding the impulse/change in momentum is a little more difficult. As the saying goes, “If the forces varies… You must integrate!” ...
Physics 04-Statics, Torque, Rotational Motion
... discover the little brother has let all the air out of one of your tires. Not knowing the reason for the flat tire, you decide to change it. You have a 50-cm long lug-wrench attached to a lugnut as shown. If 900 Nm of torque is needed, how much force is needed? F = 2078 N Less force required if ...
... discover the little brother has let all the air out of one of your tires. Not knowing the reason for the flat tire, you decide to change it. You have a 50-cm long lug-wrench attached to a lugnut as shown. If 900 Nm of torque is needed, how much force is needed? F = 2078 N Less force required if ...
1. A skydiver of mass 80 kg falls vertically with a constant speed of
... On the diagram above, draw and label arrows to represent the forces on the ball in the position shown. ...
... On the diagram above, draw and label arrows to represent the forces on the ball in the position shown. ...
Dynamics Powerpoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... has a constant velocity of 3.0 m/s. A) What other horizontal force is acting on the carriage and what is the magnitude and direction of that force? B) What value of applied horizontal force would be required to accelerate the carriage from rest to 7.0 m/s in 2.0 s? ...
... has a constant velocity of 3.0 m/s. A) What other horizontal force is acting on the carriage and what is the magnitude and direction of that force? B) What value of applied horizontal force would be required to accelerate the carriage from rest to 7.0 m/s in 2.0 s? ...
Physics Fall Exam Study Guide
... A window cleaner is on a scaffold supported by two ropes at its ends. If he weighs 160 lbs and is positioned in the middle of the scaffold, how much weight is being supported by each rope? _____________________________________________________________________________ ...
... A window cleaner is on a scaffold supported by two ropes at its ends. If he weighs 160 lbs and is positioned in the middle of the scaffold, how much weight is being supported by each rope? _____________________________________________________________________________ ...
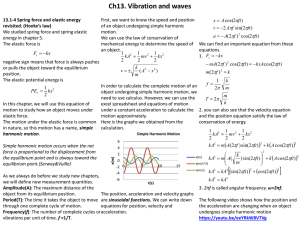
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... Calculate the total energy of the system and A wave traveling in the positive x-direction is the maximum speed of the object if the pictured in Figure below. Find the amplitude of the motion is 0.0300m.(b) amplitude, wave length, speed and period What is the velocity of the object when the of the wa ...
... Calculate the total energy of the system and A wave traveling in the positive x-direction is the maximum speed of the object if the pictured in Figure below. Find the amplitude of the motion is 0.0300m.(b) amplitude, wave length, speed and period What is the velocity of the object when the of the wa ...
How Biomechanics Can Improve Sports Performance
... only quantifies the active component of muscle, passive component is not recorded levels are relative to a particular muscle and particular person therefore need method to compare muscle/muscle or person/person not all subjects can perform maximal voluntary contractions (MVCs) to permit ...
... only quantifies the active component of muscle, passive component is not recorded levels are relative to a particular muscle and particular person therefore need method to compare muscle/muscle or person/person not all subjects can perform maximal voluntary contractions (MVCs) to permit ...