332 Unit 7 Momentum student handout
... • Jack and Leon are fishing in their boat when they decide to jump into the water. Jack, 45-kg, jumps off the front of the boat with a speed of 2m/s. While at the exact same moment, Leon, 90-kg, jumps out of the back of the boat at a speed of 4m/s. If the boat has a mass of 100 kg and was at rest pr ...
... • Jack and Leon are fishing in their boat when they decide to jump into the water. Jack, 45-kg, jumps off the front of the boat with a speed of 2m/s. While at the exact same moment, Leon, 90-kg, jumps out of the back of the boat at a speed of 4m/s. If the boat has a mass of 100 kg and was at rest pr ...
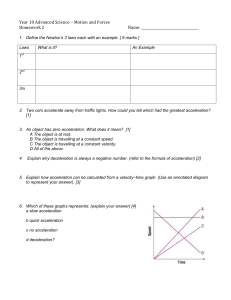
lab 3: newton`s second law of motion
... 4. Learn to use the average of a number of small measurements in order estimate a single, small, difficult measurement. Background Scientific Principles Newton’s Second Law of Motion predicts that a force acting on an object will cause that object to move at ever faster and faster velocities. Veloci ...
... 4. Learn to use the average of a number of small measurements in order estimate a single, small, difficult measurement. Background Scientific Principles Newton’s Second Law of Motion predicts that a force acting on an object will cause that object to move at ever faster and faster velocities. Veloci ...
Chapter #5 energy-multiple
... 26. What happens to the total energy of a moving object if all the applied forces are conserved? A. It increases B. It decreases C. It remains constant D. The velocity is required to answer this question E. The altitude is required to answer this question 27. A machine does 2500 J of work in 1 min. ...
... 26. What happens to the total energy of a moving object if all the applied forces are conserved? A. It increases B. It decreases C. It remains constant D. The velocity is required to answer this question E. The altitude is required to answer this question 27. A machine does 2500 J of work in 1 min. ...
Newton`s 3 Laws
... 25. Lisa has a mass of 55 kg. What would be her mass and her weight on: a Earth (g = 9.8 m/s2) b the Moon (g = 1.63 m/s2) c Mars (g = 3.7 m/s2)? 26. Dylan lands on the Planet Cochon. His mass is 70 kg on Earth. a What would be his mass on Cochon? b If his weight on Cochon is 350 N, what is the accel ...
... 25. Lisa has a mass of 55 kg. What would be her mass and her weight on: a Earth (g = 9.8 m/s2) b the Moon (g = 1.63 m/s2) c Mars (g = 3.7 m/s2)? 26. Dylan lands on the Planet Cochon. His mass is 70 kg on Earth. a What would be his mass on Cochon? b If his weight on Cochon is 350 N, what is the accel ...
Chapter 7 Notes - Valdosta State University
... Once again, this is a vector equation since all of the velocities have both magnitude and direction. This leads to the principle of conservation of linear momentum which states: ...
... Once again, this is a vector equation since all of the velocities have both magnitude and direction. This leads to the principle of conservation of linear momentum which states: ...
Rotational Dynamics
... Torque obeys superposition principle. If there are several forces acting on the body, one can find torques for each of those forces and calculate the net torque with respect to the chosen rotational axis. The body can rotate around this axis with nonzero angular acceleration if the net torque is not ...
... Torque obeys superposition principle. If there are several forces acting on the body, one can find torques for each of those forces and calculate the net torque with respect to the chosen rotational axis. The body can rotate around this axis with nonzero angular acceleration if the net torque is not ...
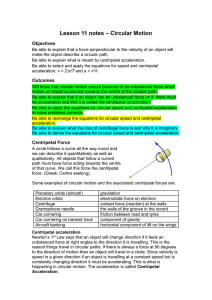
Lesson 22 notes – Circular Motion - science
... centripetal force that is proportional to a centripetal acceleration. If there is no more centripetal force the object does not fly out of the circle away from the centre of the circle it just carries along in a straight line out of the circle. Think of the following examples: Sitting in the back se ...
... centripetal force that is proportional to a centripetal acceleration. If there is no more centripetal force the object does not fly out of the circle away from the centre of the circle it just carries along in a straight line out of the circle. Think of the following examples: Sitting in the back se ...
Types of Forces
... Other situations could be imagined in which two of the individual vector forces cancel each other ("balance"), yet a third individual force exists that is not balanced by another force. For example, imagine a book sliding across the rough surface of a table from left to right. The downward force of ...
... Other situations could be imagined in which two of the individual vector forces cancel each other ("balance"), yet a third individual force exists that is not balanced by another force. For example, imagine a book sliding across the rough surface of a table from left to right. The downward force of ...
AP Physics – The Physics Little AP Test Review Helper
... velocity or acceleration, initial displacement, &tc. Use these values with motion equations to solve problem. Forces: Forces involve Newton’s three laws of motion. You will not have them (the laws) available to you, so you should commit them to memory. Force questions can show up in any concept area ...
... velocity or acceleration, initial displacement, &tc. Use these values with motion equations to solve problem. Forces: Forces involve Newton’s three laws of motion. You will not have them (the laws) available to you, so you should commit them to memory. Force questions can show up in any concept area ...