Magnetic fields
... E and E B fields. Some electronic devices and experiments need a beam of charged particles all moving at nearly the same velocity. This can be achieved using both a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field, arranged so they are at right angles to each other. Particles of charge q pass thr ...
... E and E B fields. Some electronic devices and experiments need a beam of charged particles all moving at nearly the same velocity. This can be achieved using both a uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field, arranged so they are at right angles to each other. Particles of charge q pass thr ...
File - IMSS Biology 2014
... In this section we will investigate the relationship between the acceleration of a cart and the applied force. You will now apply a constant force to the cart and observe the resultant acceleration. You will do this for several different forces to find out exactly how acceleration depends on applied ...
... In this section we will investigate the relationship between the acceleration of a cart and the applied force. You will now apply a constant force to the cart and observe the resultant acceleration. You will do this for several different forces to find out exactly how acceleration depends on applied ...
Definition of linear momentum
... the forces acting between the particles are internal ones. From Newton’s third law the vector sum of internal forces = 0 Forces acting from objects that are outside from the system are external ones. In order to know if a force is external or internal one we must clearly define what is the system! ...
... the forces acting between the particles are internal ones. From Newton’s third law the vector sum of internal forces = 0 Forces acting from objects that are outside from the system are external ones. In order to know if a force is external or internal one we must clearly define what is the system! ...
Bottle Flip/ Angular Momentum
... • Straight line motion – mass • Spinning = mr2 (depends on r) • ω – angular velocity • Angular force = Torque • Pull the string on a top -> applying a torque to make it speed up -> angular momentum increases. • It slows down after being released due to frictional torque ...
... • Straight line motion – mass • Spinning = mr2 (depends on r) • ω – angular velocity • Angular force = Torque • Pull the string on a top -> applying a torque to make it speed up -> angular momentum increases. • It slows down after being released due to frictional torque ...
3, 4, 6, 9, 14 / 5, 8, 13, 18, 23, 27, 32, 52
... acceleration must be zero. On the other hand, if the speed of the object is constant, the object could be accelerating if the direction of the velocity is changing. ...
... acceleration must be zero. On the other hand, if the speed of the object is constant, the object could be accelerating if the direction of the velocity is changing. ...
Slides
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backwards) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wh ...
... When the fly hit the truck, it exerted a force on the truck (only for a fraction of a second). So, in this time period, the truck accelerated (backwards) up to some speed. After the fly was squashed, it no longer exerted a force, and the truck simply continued moving at constant speed. Follow-up: Wh ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy
... The truck is accelerating at a rate of +1.50 m/s2. The mass of the crate is 120-kg and it does not slip. The magnitude of the displacement is 65 m. What is the total work done on the crate by all of the forces acting on it? (normal force) W = ( FN cos90° ) Δx = 0 ...
... The truck is accelerating at a rate of +1.50 m/s2. The mass of the crate is 120-kg and it does not slip. The magnitude of the displacement is 65 m. What is the total work done on the crate by all of the forces acting on it? (normal force) W = ( FN cos90° ) Δx = 0 ...
AAAAA
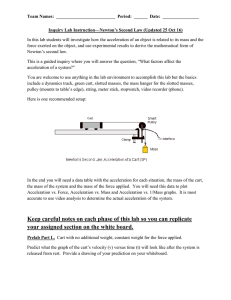
... This is a guided inquiry where you will answer the question, “What factors affect the acceleration of a system?” You are welcome to use anything in the lab environment to accomplish this lab but the basics include a dynamics track, green cart, slotted masses, the mass hanger for the slotted masses, ...
... This is a guided inquiry where you will answer the question, “What factors affect the acceleration of a system?” You are welcome to use anything in the lab environment to accomplish this lab but the basics include a dynamics track, green cart, slotted masses, the mass hanger for the slotted masses, ...
Chapter 7
... A pulsar is a celestial object that emits light in short bursts. A pulsar in the Crab Nebula flashes at a rate of 30 times/s. Suppose the light pulses are caused by the rotation of a spherical object that emits light from a pair of ...
... A pulsar is a celestial object that emits light in short bursts. A pulsar in the Crab Nebula flashes at a rate of 30 times/s. Suppose the light pulses are caused by the rotation of a spherical object that emits light from a pair of ...