Momentum
... possibly lead to collision with the Earth in 2036 after passing close by in 2029. Assuming an ion engine of thrust 0.5N is attached to the asteroid in 2029, what change in velocity could be given to the asteroid after a year of firing the engine? Would it be enough to move the asteroid out of a coll ...
... possibly lead to collision with the Earth in 2036 after passing close by in 2029. Assuming an ion engine of thrust 0.5N is attached to the asteroid in 2029, what change in velocity could be given to the asteroid after a year of firing the engine? Would it be enough to move the asteroid out of a coll ...
POP4e: Ch. 1 Problems
... 5. Two forces are acting on an object. Which of the following statements is correct? (a) The object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. (b) The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. (c) The object is in equilibrium if the forc ...
... 5. Two forces are acting on an object. Which of the following statements is correct? (a) The object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. (b) The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. (c) The object is in equilibrium if the forc ...
Exam II Difficult Problems
... • A rock is dropped from a high tower and falls freely under the influence of gravity. Which one of the following statements concerning the rock as it falls is true? Neglect the effects of air resistance. Momentum changed by Impulse ...
... • A rock is dropped from a high tower and falls freely under the influence of gravity. Which one of the following statements concerning the rock as it falls is true? Neglect the effects of air resistance. Momentum changed by Impulse ...
Work, Kinetic Energy
... Why do we need a concept of energy? The energy approach to describing motion is particularly useful when Newton’s Laws are difficult or impossible to use Energy is a scalar quantity. It does not have a direction associated with it ...
... Why do we need a concept of energy? The energy approach to describing motion is particularly useful when Newton’s Laws are difficult or impossible to use Energy is a scalar quantity. It does not have a direction associated with it ...
KEY
... They have the same momenta but in opposite directions before they collided So the total momenta was zero before they collided (0 = p + -p) It still must be zero after the collision so they must stop (or bounce back with the same speed). ...
... They have the same momenta but in opposite directions before they collided So the total momenta was zero before they collided (0 = p + -p) It still must be zero after the collision so they must stop (or bounce back with the same speed). ...
Rotational Kinetic Energy
... Angular momentum-the product of the angular velocity of a body and its moment of inertia about the axis of rotation. Depends on the mass of the object and how it is distributed ...
... Angular momentum-the product of the angular velocity of a body and its moment of inertia about the axis of rotation. Depends on the mass of the object and how it is distributed ...
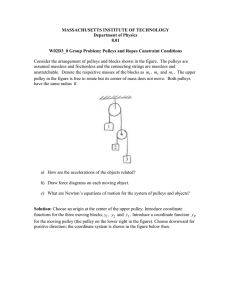
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
... Consider the arrangement of pulleys and blocks shown in the figure. The pulleys are assumed massless and frictionless and the connecting strings are massless and unstretchable. Denote the respective masses of the blocks as m1 , m2 and m3 . The upper pulley in the figure is free to rotate but its cen ...
... Consider the arrangement of pulleys and blocks shown in the figure. The pulleys are assumed massless and frictionless and the connecting strings are massless and unstretchable. Denote the respective masses of the blocks as m1 , m2 and m3 . The upper pulley in the figure is free to rotate but its cen ...
Science of Golf: Newton`s Third Law of Motion
... HUBBELL: A force is really any push or pull on an object. It has a direction and it has a magnitude. HICKS: Force is measured in units called newtons. Say the collision applies 8000 newtons, or 1800 pounds of force, to the ball in this direction. The ball applies the same 8000 newtons of force back ...
... HUBBELL: A force is really any push or pull on an object. It has a direction and it has a magnitude. HICKS: Force is measured in units called newtons. Say the collision applies 8000 newtons, or 1800 pounds of force, to the ball in this direction. The ball applies the same 8000 newtons of force back ...
ch6 momentum
... The time rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the ____________ acting on the object Net Force ...
... The time rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the ____________ acting on the object Net Force ...
Universal Gravitation
... Field lines represent the gravitational field about the Earth. Where the field lines are closer together, the field is stronger. Farther away, where the field lines are farther apart, the field is weaker. ...
... Field lines represent the gravitational field about the Earth. Where the field lines are closer together, the field is stronger. Farther away, where the field lines are farther apart, the field is weaker. ...
Ph211_CH5_worksheet-f06
... Since the masses are attached their accelerations are equal: a1y = a2x = asystem Solving for asystem: m2gsin – m1asystem - m1g = m2asystem asystem = (m2gsin – m1g)/(m1 + m2) = -1.03 m/s2 (i.e. up the incline!) e. What are the tension forces acting on each mass? Express the tension vectors in compo ...
... Since the masses are attached their accelerations are equal: a1y = a2x = asystem Solving for asystem: m2gsin – m1asystem - m1g = m2asystem asystem = (m2gsin – m1g)/(m1 + m2) = -1.03 m/s2 (i.e. up the incline!) e. What are the tension forces acting on each mass? Express the tension vectors in compo ...
UNIT 4 Lab
... Each part of the rope exerts a force on the part of the rope next to it. This type of force is called a tensile force. If the mass of the rope is negligible, the tensile forces on each little piece of rope are equal. This will be shown in Unit 4 Reading A. The rope also exerts a normal force on the ...
... Each part of the rope exerts a force on the part of the rope next to it. This type of force is called a tensile force. If the mass of the rope is negligible, the tensile forces on each little piece of rope are equal. This will be shown in Unit 4 Reading A. The rope also exerts a normal force on the ...