rotation
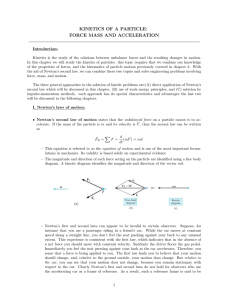
... From Newton’s 2nd law we know that forces cause accelerations. We might ask what particular quantity, obviously related to force, will cause angular accelerations. Consider a 10 N force applied to a rod pivoted about the left end. We can apply the force in a variety of ways, not all causing the same ...
... From Newton’s 2nd law we know that forces cause accelerations. We might ask what particular quantity, obviously related to force, will cause angular accelerations. Consider a 10 N force applied to a rod pivoted about the left end. We can apply the force in a variety of ways, not all causing the same ...
Physics trivia
... roller coaster A has a 300 ft high hill with a descent angle of 80°, and roller coaster B has a 310 ft high hill with an angle of 70°, which roller coaster will have the faster speed at the bottom of the hill? Roller coaster B. If non-conservative forces (such as friction and air resistance) are neg ...
... roller coaster A has a 300 ft high hill with a descent angle of 80°, and roller coaster B has a 310 ft high hill with an angle of 70°, which roller coaster will have the faster speed at the bottom of the hill? Roller coaster B. If non-conservative forces (such as friction and air resistance) are neg ...
Chapter 4 Kinetics of a particle
... P.E. between two points is equal to the work done by an external force against the field of a conservative force for bringing the particle from the starting point to the end point, any path (- Fc ) dr , with the ...
... P.E. between two points is equal to the work done by an external force against the field of a conservative force for bringing the particle from the starting point to the end point, any path (- Fc ) dr , with the ...
Document
... Newton’s “Laws” of Motion “An object in uniform motion remains in uniform motion unless it is acted upon by an external force.” [In this context, uniform motion means moving with constant velocity.] “The change in motion of an object is directly proportional to the net external force.” ...
... Newton’s “Laws” of Motion “An object in uniform motion remains in uniform motion unless it is acted upon by an external force.” [In this context, uniform motion means moving with constant velocity.] “The change in motion of an object is directly proportional to the net external force.” ...
MS Word
... was present (GE 1: 8) but what happens if we increase the force that was used in GE 1: 1? Let's try to double the force used in that case. Push the cart/person with twice the force that it took to move the cart at a constant velocity. You may have to try several times to get it right. Try to keep th ...
... was present (GE 1: 8) but what happens if we increase the force that was used in GE 1: 1? Let's try to double the force used in that case. Push the cart/person with twice the force that it took to move the cart at a constant velocity. You may have to try several times to get it right. Try to keep th ...
PHYSICS UNIT 3 Motion
... Kinetic Energy is the energy an object has due its motion. It is calculated from the definition: KE = ½ mv2. The mass must be in kilograms, and the velocity in metres per second, and KE is measured in joules. Gravitational Potential Energy is the energy an object has due to its position, as with all ...
... Kinetic Energy is the energy an object has due its motion. It is calculated from the definition: KE = ½ mv2. The mass must be in kilograms, and the velocity in metres per second, and KE is measured in joules. Gravitational Potential Energy is the energy an object has due to its position, as with all ...
Torque Torque is defined as the measure of tendency of a force to
... Can you draw the elbow angle along with associated lever parameters with the elbow in full extension? At different elbow angles? What happens to the moment arm of the muscle force when the elbow is fully extended compared to when the elbow is at 90 degrees? Does the elbow angle have anything to do w ...
... Can you draw the elbow angle along with associated lever parameters with the elbow in full extension? At different elbow angles? What happens to the moment arm of the muscle force when the elbow is fully extended compared to when the elbow is at 90 degrees? Does the elbow angle have anything to do w ...
Lights-Camera-Action!-Contract
... furniture, and snow and rain on the roof). Internal Forces: Are stresses within materials from which a structure is made. These stresses occur from external forces and can change the shape or size of a structure. Tension forces: Stretch a material by pulling its ends apart. Tensile strength measures ...
... furniture, and snow and rain on the roof). Internal Forces: Are stresses within materials from which a structure is made. These stresses occur from external forces and can change the shape or size of a structure. Tension forces: Stretch a material by pulling its ends apart. Tensile strength measures ...
Physics Regents Review Sheet
... _____ Newton’s 1st Law of Motion _____ what inertia is and what affects it _____ Newton’s 2nd Law _____ how to find the net force _____ how and when to use F = ma _____ when the net force is 0 _____ the net force on an object when it is moving at a constant velocity _____ Newton’s 3rd Law _____ what ...
... _____ Newton’s 1st Law of Motion _____ what inertia is and what affects it _____ Newton’s 2nd Law _____ how to find the net force _____ how and when to use F = ma _____ when the net force is 0 _____ the net force on an object when it is moving at a constant velocity _____ Newton’s 3rd Law _____ what ...
Foundation of Newtonian Mechanics
... velocity as it loses height. This means that gravity is applying a force to that object, and since the object’s displacement is parallel to the force of gravity, gravity is doing work on the object. This leads to the following: From equation (11) v 2f vi2 2 gy , where “g” is the acceleration du ...
... velocity as it loses height. This means that gravity is applying a force to that object, and since the object’s displacement is parallel to the force of gravity, gravity is doing work on the object. This leads to the following: From equation (11) v 2f vi2 2 gy , where “g” is the acceleration du ...
ID_newton4_060706 - Swift Education and Public Outreach
... This tells us two things. One is that again, the speed at which an object falls doesn’t depend on its mass. The second is that if the acceleration due to gravity were different (say, on another planet) you’d weigh a different amount. These two concepts are the basis of this exercise. Additional Back ...
... This tells us two things. One is that again, the speed at which an object falls doesn’t depend on its mass. The second is that if the acceleration due to gravity were different (say, on another planet) you’d weigh a different amount. These two concepts are the basis of this exercise. Additional Back ...