3.Momentum
... • When we apply a net force to an object over a period of time, we are applying an impulse to the object: Impulse applied = Net Force × time during which net force is applied. ...
... • When we apply a net force to an object over a period of time, we are applying an impulse to the object: Impulse applied = Net Force × time during which net force is applied. ...
POP4e: Ch. 1 Problems
... necessarily true because the angle of the incline is unknown. (e) None of these statements is necessarily true because the mass of one block is not given. Since the rollers on the ramp used by David were frictionless, he did not do any work overcoming nonconservative forces as he slid the block up t ...
... necessarily true because the angle of the incline is unknown. (e) None of these statements is necessarily true because the mass of one block is not given. Since the rollers on the ramp used by David were frictionless, he did not do any work overcoming nonconservative forces as he slid the block up t ...
ch13_lecture
... At x = 0, F and a are zero, but v is a maximum The object’s momentum causes it to overshoot the equilibrium position The force and acceleration start to increase in the opposite direction and velocity decreases The motion continues indefinitely ...
... At x = 0, F and a are zero, but v is a maximum The object’s momentum causes it to overshoot the equilibrium position The force and acceleration start to increase in the opposite direction and velocity decreases The motion continues indefinitely ...
Circular
... (a) Derive an expression for the force experienced by an object of mass m which is rotating with angular velocity w around a circular path of radius r, in the absence of any gravitational field. (4 marks) (b) In a laboratory a small weight is attached by a piece of string of length l to a fixed poin ...
... (a) Derive an expression for the force experienced by an object of mass m which is rotating with angular velocity w around a circular path of radius r, in the absence of any gravitational field. (4 marks) (b) In a laboratory a small weight is attached by a piece of string of length l to a fixed poin ...
Ball launcher
... The world record for running 100 m is about 10 seconds. What is the average speed? Red 5 m/sec Yellow 0 m/sec Green 10 m/sec Blue 0.1 m/sec When is the runner accelerating? Red Mostly at the very beginning of the race Yellow The acceleration is constant Green All the time, but more at the beginning ...
... The world record for running 100 m is about 10 seconds. What is the average speed? Red 5 m/sec Yellow 0 m/sec Green 10 m/sec Blue 0.1 m/sec When is the runner accelerating? Red Mostly at the very beginning of the race Yellow The acceleration is constant Green All the time, but more at the beginning ...
Force and Motion
... Drag Force and Terminal Velocity When an object moves through any fluid, such as air or water, the fluid exerts a drag force on the moving object in the direction opposite to its motion. A drag force is the force exerted by a fluid on the object moving through the fluid. This force is dependent on t ...
... Drag Force and Terminal Velocity When an object moves through any fluid, such as air or water, the fluid exerts a drag force on the moving object in the direction opposite to its motion. A drag force is the force exerted by a fluid on the object moving through the fluid. This force is dependent on t ...
Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
... Centripetal Acceleration • Centripetal means center-seeking. • Centripetal acceleration is always directed toward the center of the circle of motion. • It is this centripetal acceleration that is responsible for the change in the direction of the velocity; the magnitude of the velocity remains cons ...
... Centripetal Acceleration • Centripetal means center-seeking. • Centripetal acceleration is always directed toward the center of the circle of motion. • It is this centripetal acceleration that is responsible for the change in the direction of the velocity; the magnitude of the velocity remains cons ...
Systems of Particles
... • Suppose you are standing on the edge of a dock and jump straight down. If you land on sand your stopping time is much shorter than if you land on water. Using the impulse–momentum theorem as a guide, determine which one of the following statements is correct. a.In bringing you to a halt, the sand ...
... • Suppose you are standing on the edge of a dock and jump straight down. If you land on sand your stopping time is much shorter than if you land on water. Using the impulse–momentum theorem as a guide, determine which one of the following statements is correct. a.In bringing you to a halt, the sand ...
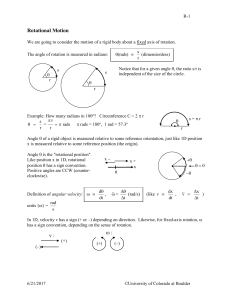
RotationalMotion - University of Colorado Boulder
... As the mass descends, PE is converted into KE. With a rolling object, KEtot = KEtrans + KErot , so some of the PE is converted into KErot and less energy is left over for KEtrans. A smaller KEtrans means slower speed (since KEtrans = (1/2) M v2 ). So rolling object goes slower than sliding object, b ...
... As the mass descends, PE is converted into KE. With a rolling object, KEtot = KEtrans + KErot , so some of the PE is converted into KErot and less energy is left over for KEtrans. A smaller KEtrans means slower speed (since KEtrans = (1/2) M v2 ). So rolling object goes slower than sliding object, b ...
ISNS3371_012307_bw
... The total momentum of an isolated system is conserved, I.e., it remains constant. An outside or external force is required to change the momentum of an isolated system. The Law of Conservation of Momentum is an alternate way of stating Newton’s laws: 1. An object’s momentum will not change if left a ...
... The total momentum of an isolated system is conserved, I.e., it remains constant. An outside or external force is required to change the momentum of an isolated system. The Law of Conservation of Momentum is an alternate way of stating Newton’s laws: 1. An object’s momentum will not change if left a ...




![Newton`s 1st Law Chapter 4 [ Edit ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014791822_1-2c861cb90e155a9bec8e50db1f7a973a-300x300.png)