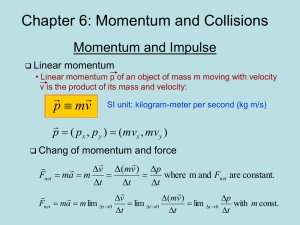
8. LINEAR MOMENTUM. Key words: Linear Momentum, Law of
... collisions between atoms elementary particles. At the subatomic level, physicists learn about the structure of nuclei and their constituents, and about the nature of the forces involved, by careful study of collisions between nuclei and / or elementary particles. It should be stressed that actually ...
... collisions between atoms elementary particles. At the subatomic level, physicists learn about the structure of nuclei and their constituents, and about the nature of the forces involved, by careful study of collisions between nuclei and / or elementary particles. It should be stressed that actually ...
Springs & Strings
... When forces are exerted on connected objects, their accelerations are the same. In the situation below, if we know the force and the masses, we can find the acceleration and the tension ...
... When forces are exerted on connected objects, their accelerations are the same. In the situation below, if we know the force and the masses, we can find the acceleration and the tension ...
9-1 Momentum and Its Relation to Force Example 9
... Example 9-8: Unequal masses, target at rest. A very common practical situation is for a moving object (mA) to strike a second object (mB, the “target”) at rest (vB = 0). Assume the objects have unequal masses, and that the collision is elastic and occurs along a line (head-on). (a) Derive equations ...
... Example 9-8: Unequal masses, target at rest. A very common practical situation is for a moving object (mA) to strike a second object (mB, the “target”) at rest (vB = 0). Assume the objects have unequal masses, and that the collision is elastic and occurs along a line (head-on). (a) Derive equations ...
Unit III: Worksheet 1a
... b. Resolve forces into x and y components, then find the vector sum of the forces. c. State whether the velocity of the object is constant or changing. 3. Given a diagram or description of an object in equilibrium, including the forces acting on the object, determine the magnitude and direction of t ...
... b. Resolve forces into x and y components, then find the vector sum of the forces. c. State whether the velocity of the object is constant or changing. 3. Given a diagram or description of an object in equilibrium, including the forces acting on the object, determine the magnitude and direction of t ...
[ Problem View ]
... Hint C.1 Use Newton's law If the velocity is "wrong" the forces won't balance and the resulting transverse force will cause a transverse acceleration. Use to determine how this acceleration will depend on and . You want particles with the incorrect velocity to have the maximum possible deviation in ...
... Hint C.1 Use Newton's law If the velocity is "wrong" the forces won't balance and the resulting transverse force will cause a transverse acceleration. Use to determine how this acceleration will depend on and . You want particles with the incorrect velocity to have the maximum possible deviation in ...
MS Physical Science: Forces-Collision Safety
... ii. All changes in motion comes from the result of a force, or a type of push or pull Explore 2. Students given round objects with various masses, a golf ball, tennis ball, medicine ball, ping pong ball (stand ins for these materials can be used from t4t materials) etc, and are asked to record the m ...
... ii. All changes in motion comes from the result of a force, or a type of push or pull Explore 2. Students given round objects with various masses, a golf ball, tennis ball, medicine ball, ping pong ball (stand ins for these materials can be used from t4t materials) etc, and are asked to record the m ...
Lecture6
... • The driving force of motion of ordinary vehicles such as cars and locomotives is friction. A car moves because a reaction to the force exerted by the tire produces a force by the road on the wheel. • What is then driving force of a rocket? When an explosion occurs in a spherical chamber with fue ...
... • The driving force of motion of ordinary vehicles such as cars and locomotives is friction. A car moves because a reaction to the force exerted by the tire produces a force by the road on the wheel. • What is then driving force of a rocket? When an explosion occurs in a spherical chamber with fue ...
Notes: Vectors
... A. Frame of reference is a point (origin) that an object's motion can be compared to. B. The origin can be moving (inertial frame of reference) as long as it is not accelerating. C. Motion can be measured relative to the origin using an x, y, z coordinate system (we will only work with the x and y a ...
... A. Frame of reference is a point (origin) that an object's motion can be compared to. B. The origin can be moving (inertial frame of reference) as long as it is not accelerating. C. Motion can be measured relative to the origin using an x, y, z coordinate system (we will only work with the x and y a ...
3.Momentum
... • When we apply a net force to an object over a period of time, we are applying an impulse to the object: Impulse applied = Net Force × time during which net force is applied. ...
... • When we apply a net force to an object over a period of time, we are applying an impulse to the object: Impulse applied = Net Force × time during which net force is applied. ...














![[ Problem View ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009194971_1-46a1d77561d5c03a41e4de32d5b76d8f-300x300.png)