Linear Momentum
... moving at 45 mph than to stop a car moving at 45 mph, even though they both have the same speed. • Both mass and velocity are important factors when considering the force needed to change the motion of an object. ...
... moving at 45 mph than to stop a car moving at 45 mph, even though they both have the same speed. • Both mass and velocity are important factors when considering the force needed to change the motion of an object. ...
EOC_chapter8 - AppServ Open Project 2.4.9
... the pallet is negligible. Initially, the momentum of the system is zero. When the heart beats, it expels a mass m of blood into the aorta with speed v, and the body and platform move in the opposite direction with speed V. The blood velocity can be determined independently (e.g., by observing the Do ...
... the pallet is negligible. Initially, the momentum of the system is zero. When the heart beats, it expels a mass m of blood into the aorta with speed v, and the body and platform move in the opposite direction with speed V. The blood velocity can be determined independently (e.g., by observing the Do ...
No Slide Title
... Introduction The Concept of a Vector Forces, Couples, and Moments Equilibrium and Free-body Diagrams ...
... Introduction The Concept of a Vector Forces, Couples, and Moments Equilibrium and Free-body Diagrams ...
Updated Center of Mass
... moves as though all the system's mass were concentrated there, and that the vector sum of all the external forces were applied there. A dramatic example is given in the figure. In a fireworks display a rocket is launched and moves under the influence of gravity on a parabolic path (projectile motion ...
... moves as though all the system's mass were concentrated there, and that the vector sum of all the external forces were applied there. A dramatic example is given in the figure. In a fireworks display a rocket is launched and moves under the influence of gravity on a parabolic path (projectile motion ...
SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND RAOTATIONAL DYNAMICS Various
... velocity. For this, the net external torque or the vector sum of all the torques acting on the body is zero. A body is in rotational equilibrium, when algebraic sum of moments of all the forces acting on the body about a fixed point is zero. Example − In case of beam balance or see-saw, the system w ...
... velocity. For this, the net external torque or the vector sum of all the torques acting on the body is zero. A body is in rotational equilibrium, when algebraic sum of moments of all the forces acting on the body about a fixed point is zero. Example − In case of beam balance or see-saw, the system w ...
VU3Motion2009
... resist changes to their motion. It is associated with an object’s mass – more mass, more inertia. Inertia is NOT a force. ...
... resist changes to their motion. It is associated with an object’s mass – more mass, more inertia. Inertia is NOT a force. ...
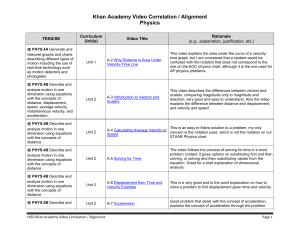
Khan Academy Video Correlation / Alignment Physics
... between objects. Ⓡ PHYS.4D Calculate the effect of forces on objects including the law of inertia, the relationship between force and acceleration, and the nature of force pairs between objects. ...
... between objects. Ⓡ PHYS.4D Calculate the effect of forces on objects including the law of inertia, the relationship between force and acceleration, and the nature of force pairs between objects. ...
General Instructions
... The engines of a rocket taking off produced a constant force. It was observed that this produced an acceleration, which increased as the rocket gained altitude. Propose a reason why this happened. ...
... The engines of a rocket taking off produced a constant force. It was observed that this produced an acceleration, which increased as the rocket gained altitude. Propose a reason why this happened. ...
Measurement and Interpretation of Ground Reaction Forces, Center
... the differences? Repeat this process for 20 equal time intervals. Show your work. Is this calculated impulse closer to the value obtained from the APAS system than the one calculated from the 10 time intervals? Explain. Divide the total time (start to end) into 10 equal time intervals and calculate ...
... the differences? Repeat this process for 20 equal time intervals. Show your work. Is this calculated impulse closer to the value obtained from the APAS system than the one calculated from the 10 time intervals? Explain. Divide the total time (start to end) into 10 equal time intervals and calculate ...
Momentum Problems (From Merrill Principles and Problems with
... a. If the balls stick together, what is their combined speed and direction after the collision? b. If the balls rebound, with the 3 kg ball moving westward at 1 m/s after the collision, what is the speed and direction of the 1 kg ball after the collision? 23. One way of measuring the muzzle velocity ...
... a. If the balls stick together, what is their combined speed and direction after the collision? b. If the balls rebound, with the 3 kg ball moving westward at 1 m/s after the collision, what is the speed and direction of the 1 kg ball after the collision? 23. One way of measuring the muzzle velocity ...
Lesson 1 – Stationary Point Charges and Their Forces
... object isn’t interacting with anything else in the universe, its velocity remains constant. 2. Momentum is defined as the product of mass and velocity. Force is defined as the rate momentum changes: ...
... object isn’t interacting with anything else in the universe, its velocity remains constant. 2. Momentum is defined as the product of mass and velocity. Force is defined as the rate momentum changes: ...
Chapter 9 PPT
... Write expressions for the x- and y-components of the momentum of each object before and after the collision Remember to include the appropriate signs for the components of the velocity vectors Write expressions for the total momentum of the system in the x-direction before and after the collision ...
... Write expressions for the x- and y-components of the momentum of each object before and after the collision Remember to include the appropriate signs for the components of the velocity vectors Write expressions for the total momentum of the system in the x-direction before and after the collision ...
Jeopardy
... Speedy the snail accelerates from 2 m/s to 15 m/s at a constant acceleration of 5 m/s2. This is the distance Speedy covers as he accelerates. ...
... Speedy the snail accelerates from 2 m/s to 15 m/s at a constant acceleration of 5 m/s2. This is the distance Speedy covers as he accelerates. ...
Magnetic Force on a current Element
... Had we instead been seeking F21, the magnetic force acting on line 1 from the field of line 2, we would have found F21 = -F12. Conclusion: 1) Two parallel lines with current in opposite directions experience a force of repulsion. 2) For a pair of parallel lines with current in the same direction, a ...
... Had we instead been seeking F21, the magnetic force acting on line 1 from the field of line 2, we would have found F21 = -F12. Conclusion: 1) Two parallel lines with current in opposite directions experience a force of repulsion. 2) For a pair of parallel lines with current in the same direction, a ...