Document
... Gravitational force: an attractive force that exists between all objects with mass; an object with mass attracts another object with mass; the magnitude of the force is directly proportional to the masses of the two objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two obj ...
... Gravitational force: an attractive force that exists between all objects with mass; an object with mass attracts another object with mass; the magnitude of the force is directly proportional to the masses of the two objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two obj ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... Conservation of Linear Momentum in a Two Particle System Consider an isolated system with two particles that do not have any external forces exerting on it. What is the impact of Newton’s 3rd Law? If particle#1 exerts force on particle #2, there must be another force that the particle #2 exerts on ...
... Conservation of Linear Momentum in a Two Particle System Consider an isolated system with two particles that do not have any external forces exerting on it. What is the impact of Newton’s 3rd Law? If particle#1 exerts force on particle #2, there must be another force that the particle #2 exerts on ...
Dynamics Pupil Notes Name
... Be able to state Newton’s three laws and describe their implications. Be able to calculate the resultant force on an object when more than one force acts on ...
... Be able to state Newton’s three laws and describe their implications. Be able to calculate the resultant force on an object when more than one force acts on ...
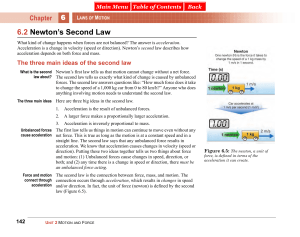
Newtons` second law is customarily presented to beginning students
... 1. Introduction. Center of gravity, center of mass, this concept seems very familiar. Indeed, many people including students of science have used the phrase in daily conversation. Yet, “what is the center of mass?”, and of more concern, what are its properties? We explore these ideas in the attempt ...
... 1. Introduction. Center of gravity, center of mass, this concept seems very familiar. Indeed, many people including students of science have used the phrase in daily conversation. Yet, “what is the center of mass?”, and of more concern, what are its properties? We explore these ideas in the attempt ...
Multiple-Choice Questions
... ___ 27. The distance traveled by an object in a unit of time is called speed. ___ 28. The slowing down of a car in a given time is called velocity. ___ 29. Newton has 4 laws of motions. ___ 30. One of the first scientists to study the rate of gravitational acceleration was Newton. ___ 31. In the met ...
... ___ 27. The distance traveled by an object in a unit of time is called speed. ___ 28. The slowing down of a car in a given time is called velocity. ___ 29. Newton has 4 laws of motions. ___ 30. One of the first scientists to study the rate of gravitational acceleration was Newton. ___ 31. In the met ...
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (1)
... An oscillating mass may lose its mechanical energy to a force such as air resistance that is proportional to the speed of the mass r and r opposite in direction, which can be defined as F = −bv The damping constant is b and is a measure of the strength of the damping force (kg/s) If the damping cons ...
... An oscillating mass may lose its mechanical energy to a force such as air resistance that is proportional to the speed of the mass r and r opposite in direction, which can be defined as F = −bv The damping constant is b and is a measure of the strength of the damping force (kg/s) If the damping cons ...
sums, differences and products of vectors
... 2d. Subtraction. Subtraction is performed by using the rules for vector addition. That is, the subtraction of one vector from another is accomplished by adding the negative of the vector being “subtracted.” The negative of a vector is most easily seen from its geometrical representation where the he ...
... 2d. Subtraction. Subtraction is performed by using the rules for vector addition. That is, the subtraction of one vector from another is accomplished by adding the negative of the vector being “subtracted.” The negative of a vector is most easily seen from its geometrical representation where the he ...
Student Word - Nuffield Foundation
... her suitcase in her hand. The mass of the hotel guest is 70 kg and the mass of the suitcase is 20 kg. The lift accelerates at 0.5 m s–2 as it sets off from the ground floor, and decelerates at 0.4 m s–2 as it nears the 4th floor. a Draw force diagrams showing the forces acting on: i the suitcase ii ...
... her suitcase in her hand. The mass of the hotel guest is 70 kg and the mass of the suitcase is 20 kg. The lift accelerates at 0.5 m s–2 as it sets off from the ground floor, and decelerates at 0.4 m s–2 as it nears the 4th floor. a Draw force diagrams showing the forces acting on: i the suitcase ii ...
Chapter 13 - AP Physics Vibrations and Waves Power Point-
... A 1300 kg car is constructed on a frame supported by four springs. Each spring has a spring constant of 20,000 N/m. If two people riding in the car have a combined mass of 160 kg, find the frequency of vibration of the car when it is driven over a pothole in the road. Find also the period and the an ...
... A 1300 kg car is constructed on a frame supported by four springs. Each spring has a spring constant of 20,000 N/m. If two people riding in the car have a combined mass of 160 kg, find the frequency of vibration of the car when it is driven over a pothole in the road. Find also the period and the an ...
Slide 1
... total mass of 40.0 kg. What is the acceleration of the cart if the net force on the cart is 60.0 N? • a = F/m = 60 N / 40kg=1.5 m/s2 • What is the upward acceleration of a helicopter with a mass of 5,000 kg if a force of 10,000 N acts on it in an upward direction? • a= F/m = 10,000 N / 5,000 kg = 2 ...
... total mass of 40.0 kg. What is the acceleration of the cart if the net force on the cart is 60.0 N? • a = F/m = 60 N / 40kg=1.5 m/s2 • What is the upward acceleration of a helicopter with a mass of 5,000 kg if a force of 10,000 N acts on it in an upward direction? • a= F/m = 10,000 N / 5,000 kg = 2 ...
Momentum Problems (From Merrill Principles and Problems with
... 9. A stationary life raft of mass 180 kg carries two swimmers of mass 50 kg (on the right) and 80 kg (on the left), who jump off in opposite directions, each with a horizontal speed of 3 m/s. What speed and direction does the raft have afterward? 10. A car moving at 10 m/s crashes into a barrier and ...
... 9. A stationary life raft of mass 180 kg carries two swimmers of mass 50 kg (on the right) and 80 kg (on the left), who jump off in opposite directions, each with a horizontal speed of 3 m/s. What speed and direction does the raft have afterward? 10. A car moving at 10 m/s crashes into a barrier and ...
Newton`s Laws and Momentum – Script Draft Introduction One value
... • Velocity measures the rate of positional change of an object. We described velocity by talking about speed and direction. This soccer ball currently has a velocity of zero. But when it is kicked we can measure its speed in m/sec and determine its direction. ...
... • Velocity measures the rate of positional change of an object. We described velocity by talking about speed and direction. This soccer ball currently has a velocity of zero. But when it is kicked we can measure its speed in m/sec and determine its direction. ...