106 final exam
... 1) A motorcycle accelerates from 10 m/s to 25 m/s in 5 seconds. the average acceleration of the bike is a) 3m/s2 b)5m/s2 c)15m/s2 d)25m/s2 2) A boy walks 150 meters due east and then turns around and walks 30 meters due west. The boy's displacement is a. 30 meters east ...
... 1) A motorcycle accelerates from 10 m/s to 25 m/s in 5 seconds. the average acceleration of the bike is a) 3m/s2 b)5m/s2 c)15m/s2 d)25m/s2 2) A boy walks 150 meters due east and then turns around and walks 30 meters due west. The boy's displacement is a. 30 meters east ...
Worksheet - 2
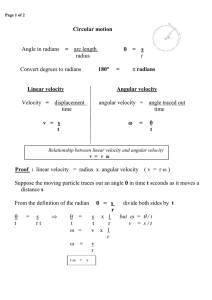
... a) Speed and velocity b) Uniform and Non-uniform speed c) Uniform and Non-uniform velocity d) Uniform acceleration and non-uniform acceleration 3. Define Uniform circular motion 4. What do you mean by the term retardation? Give an example 5. Describe the distance-time graph for a) Body at rest b) Bo ...
... a) Speed and velocity b) Uniform and Non-uniform speed c) Uniform and Non-uniform velocity d) Uniform acceleration and non-uniform acceleration 3. Define Uniform circular motion 4. What do you mean by the term retardation? Give an example 5. Describe the distance-time graph for a) Body at rest b) Bo ...
3. (a) The force on the electron is Thus, the magnitude of FB is 6.2
... (b) This amounts to repeating the above computation with a change in the sign in the charge. Thus, FB has the same magnitude but points in the negative z direction, namely, ...
... (b) This amounts to repeating the above computation with a change in the sign in the charge. Thus, FB has the same magnitude but points in the negative z direction, namely, ...
1PP Examination Autumn 2002_postMod_2
... If a nucleus is represented by an object the size of a 1p coin, indicate the distance between two 1p coins that would best correspond to the distance between two nuclei in a crystal. Assume size of nucleus is 10-15m and typical spacing of nuclei in a crystal is 10-10m. ...
... If a nucleus is represented by an object the size of a 1p coin, indicate the distance between two 1p coins that would best correspond to the distance between two nuclei in a crystal. Assume size of nucleus is 10-15m and typical spacing of nuclei in a crystal is 10-10m. ...
Midterm Exam No. 02 (Fall 2014) PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I
... Find the effective charge density by calculating −∇ · P. In particular, you should obtain two terms, one containing θ(R − r) that is interpreted as a volume charge density, and another containing δ(R − r) that can be interpreted as a surface charge density. 4. (25 points.) A particle of mass m and c ...
... Find the effective charge density by calculating −∇ · P. In particular, you should obtain two terms, one containing θ(R − r) that is interpreted as a volume charge density, and another containing δ(R − r) that can be interpreted as a surface charge density. 4. (25 points.) A particle of mass m and c ...
Regents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know
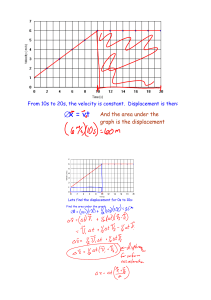
... direction from its velocity vector. ( ) 7. Speed, distance, and time are scalar quantities. ('11: 1) 8. The slope of the velocity-time graph is acceleration. () 9. The slope of the distance-time graph is velocity. () 10. The area under the velocity-time graph is distance. ('11: 37) 11. An accelerati ...
... direction from its velocity vector. ( ) 7. Speed, distance, and time are scalar quantities. ('11: 1) 8. The slope of the velocity-time graph is acceleration. () 9. The slope of the distance-time graph is velocity. () 10. The area under the velocity-time graph is distance. ('11: 37) 11. An accelerati ...
Document
... 7. A car, initially at rest , travels 20 m in 4 s along a straight line with constant acceleration. The acceleration of the car (in m/s2) is: 8. An object is thrown straight up from ground level with a speed of 50 m/s. If g = 10 m/s 2 its distance above ground level 1.0 sec later is: 9 - 12 A ball i ...
... 7. A car, initially at rest , travels 20 m in 4 s along a straight line with constant acceleration. The acceleration of the car (in m/s2) is: 8. An object is thrown straight up from ground level with a speed of 50 m/s. If g = 10 m/s 2 its distance above ground level 1.0 sec later is: 9 - 12 A ball i ...
PHYS4330 Theoretical Mechanics HW #1 Due 6 Sept 2011
... where τ is a positive constant, and starts from rest at x = 0 and t = 0. Find the velocity v(t) = ẋ(t) and position x(t) as functions of time. Also find the velocity v(t) for times t � τ . (2) A particle of mass m moves in two dimensions according to plane polar coordinates r and φ. It is acted on ...
... where τ is a positive constant, and starts from rest at x = 0 and t = 0. Find the velocity v(t) = ẋ(t) and position x(t) as functions of time. Also find the velocity v(t) for times t � τ . (2) A particle of mass m moves in two dimensions according to plane polar coordinates r and φ. It is acted on ...
Phy221 E1Review
... d. Draw motion graphs from lab data or other representations of motion and interpret the meaning of coordinates, intercepts, slope and area. e. Given an equation describing the motion of an object, utilize differentiation and/or integration to represent the other kinematic variables as functions of ...
... d. Draw motion graphs from lab data or other representations of motion and interpret the meaning of coordinates, intercepts, slope and area. e. Given an equation describing the motion of an object, utilize differentiation and/or integration to represent the other kinematic variables as functions of ...
Section 14.4 Motion in Space: Velocity and Acceleration
... In Calc 1 and 2, we saw that derivatives and integrals were closely related to the concept of speed, distance traveled and acceleration. In this section, we shall generalize these ideas to vectors, tracking the motion of a body in 3-dimensional space (rather than the rather fake 2-d space developed ...
... In Calc 1 and 2, we saw that derivatives and integrals were closely related to the concept of speed, distance traveled and acceleration. In this section, we shall generalize these ideas to vectors, tracking the motion of a body in 3-dimensional space (rather than the rather fake 2-d space developed ...
Lesson 25 – PowerPoint
... A car is travelling with a starting velocity of 90m/s and then after 10s its velocity changes to a final velocity of 50m/s. ...
... A car is travelling with a starting velocity of 90m/s and then after 10s its velocity changes to a final velocity of 50m/s. ...