Quiz on Motion under gravity
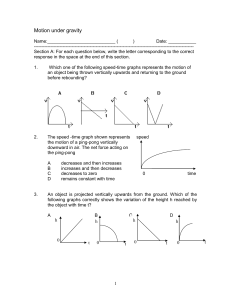
... The acceleration of the object decreases as the object rises up; The acceleration is positive for the upward motion and negative for the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for th ...
... The acceleration of the object decreases as the object rises up; The acceleration is positive for the upward motion and negative for the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for th ...
Unit 5 Review
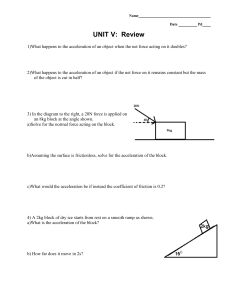
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
Physics – Inclines Worksheet 2 Name: Please make a special note
... Physics – Inclines Worksheet 2 ...
... Physics – Inclines Worksheet 2 ...
Physics Tested Targets
... 2.2 Draw and explain how balanced forces affect an object's motion in the space… ...
... 2.2 Draw and explain how balanced forces affect an object's motion in the space… ...
Circular Motion - strikerphysics11
... operational speed of 500 rpm in 3.0 sec. What is the angular acceleration of the CD during this time? If the CD comes to a stop in 4.0 sec, what is the angular acceleration during that part of the motion? A microwave oven has a 30 cm rotating plate. The plate accelerates from rest to a uniform rate ...
... operational speed of 500 rpm in 3.0 sec. What is the angular acceleration of the CD during this time? If the CD comes to a stop in 4.0 sec, what is the angular acceleration during that part of the motion? A microwave oven has a 30 cm rotating plate. The plate accelerates from rest to a uniform rate ...
Chapter 18 Test Review
... reference point. • Gravity: The force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass. • Friction: a force that always acts to oppose motion. ...
... reference point. • Gravity: The force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass. • Friction: a force that always acts to oppose motion. ...
P2.2_-_Speeding_up_and_slowing_down_answ... 309KB Jun 06
... four forces are balanced. At which points during a flight are the forces unbalanced? Take off, climbing to cruising altitude, descending to land, landing. 13. Define Newton's First Law of Motion. An object will stay at rest or continue at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external unbalanc ...
... four forces are balanced. At which points during a flight are the forces unbalanced? Take off, climbing to cruising altitude, descending to land, landing. 13. Define Newton's First Law of Motion. An object will stay at rest or continue at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external unbalanc ...
Lecture Notes for Section 13.4 (Equation of Motion)
... The second law only provides solutions for forces and accelerations. If velocity or position have to be found, kinematics equations are used once the acceleration is found from the equation of motion. Any of the tools learned in Chapter 12 may be needed to solve a problem. Make sure you use consiste ...
... The second law only provides solutions for forces and accelerations. If velocity or position have to be found, kinematics equations are used once the acceleration is found from the equation of motion. Any of the tools learned in Chapter 12 may be needed to solve a problem. Make sure you use consiste ...
R - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... if e > 1. The constants C and h can be determined from the initial conditions; if the particle is projected from point A with an initial velocity v0 perpendicular to OA, we have h = r0v0. O ...
... if e > 1. The constants C and h can be determined from the initial conditions; if the particle is projected from point A with an initial velocity v0 perpendicular to OA, we have h = r0v0. O ...
Properties of Uniform Circular Motion
... quantity. Velocity, being a vector, has both a magnitude and a direction. Since an object is moving in a circle, its direction is ...
... quantity. Velocity, being a vector, has both a magnitude and a direction. Since an object is moving in a circle, its direction is ...