Unit 4 - Youngstown City Schools
... 7. Forces and fluids: use Cartesian Diver as an example of forces in fluids; students can experience this in small groups; they conclude that any time something moves, a force is involved and they analyze how the movement occurs. Conservation of Matter is also brought back into this discussion as no ...
... 7. Forces and fluids: use Cartesian Diver as an example of forces in fluids; students can experience this in small groups; they conclude that any time something moves, a force is involved and they analyze how the movement occurs. Conservation of Matter is also brought back into this discussion as no ...
NEWTON`S LESSON 12
... 2. How much upward force would be needed to accelerate the 5.0-kg mass up this incline at 3.0 m/sec2? 3. How much upward force would be needed to restrict the 5.0-kg mass' downward acceleration to 1.0 m/sec2? 4. If the 5.0-kg mass were allowed to slide down this incline without any additional applie ...
... 2. How much upward force would be needed to accelerate the 5.0-kg mass up this incline at 3.0 m/sec2? 3. How much upward force would be needed to restrict the 5.0-kg mass' downward acceleration to 1.0 m/sec2? 4. If the 5.0-kg mass were allowed to slide down this incline without any additional applie ...
Model of a Bicycle from Handling Qualities Considerations
... Figure 1 shows the bicycle with the variable names used in the handling qualities model of the bicycle, also referred to as the Patterson Control Model. Note that almost all of these are different from the variable names used in the dynamic model of the bike. The axes shown are similar to those used ...
... Figure 1 shows the bicycle with the variable names used in the handling qualities model of the bicycle, also referred to as the Patterson Control Model. Note that almost all of these are different from the variable names used in the dynamic model of the bike. The axes shown are similar to those used ...
KEY - NNHS Tigerscience
... 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, wo ...
... 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, wo ...
AP Physics Pacing Curriculum
... the free-body diagram to the algebraic representation. 3.B.2.1 The student is able to create and use free-body diagrams to analyze physical situations to solve problems with motion qualitatively and quantitatively. 3.C.4 Contact forces result from the interaction of one object touching another objec ...
... the free-body diagram to the algebraic representation. 3.B.2.1 The student is able to create and use free-body diagrams to analyze physical situations to solve problems with motion qualitatively and quantitatively. 3.C.4 Contact forces result from the interaction of one object touching another objec ...
Force and Motion
... , tells you that if you double the force, you will double the object’s acceleration. If you apply the same force to several different objects, the one with the most mass will have the smallest acceleration and the one with the least mass will have the greatest acceleration. If you apply the same for ...
... , tells you that if you double the force, you will double the object’s acceleration. If you apply the same force to several different objects, the one with the most mass will have the smallest acceleration and the one with the least mass will have the greatest acceleration. If you apply the same for ...
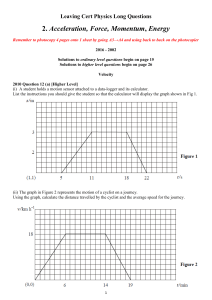
2. Acceleration, Force, Momentum, Energy
... (i) What is meant by the term ‘acceleration due to gravity’? (ii) A spacecraft of mass 800 kg is on the surface of the moon, where the acceleration due to gravity is 1.6 m s−2. Compare the weight of the spacecraft on the surface of the moon with its weight on earth, where the acceleration due to gra ...
... (i) What is meant by the term ‘acceleration due to gravity’? (ii) A spacecraft of mass 800 kg is on the surface of the moon, where the acceleration due to gravity is 1.6 m s−2. Compare the weight of the spacecraft on the surface of the moon with its weight on earth, where the acceleration due to gra ...
NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOT ION, FRICTION
... A person sitting in an accelerated frame (non-inertial frame) experiences pseudo forces. Eg. when you take sharp turn while riding on bike, you feel an outward force which is called centrifugal force - a typical example of pseudo force. Pseudo forces exist only in non-inertial (accelerated) frames. ...
... A person sitting in an accelerated frame (non-inertial frame) experiences pseudo forces. Eg. when you take sharp turn while riding on bike, you feel an outward force which is called centrifugal force - a typical example of pseudo force. Pseudo forces exist only in non-inertial (accelerated) frames. ...
Packet 8: Impulse Momentum
... by which gravity attracts the stuff to Earth B) acceleration the rate at which stuffdirection changesit's itsstuff velocity d. velocity - how fast andthe in what is moving C) weight -e.the force by whichthe gravity the stuff to Earth position - where stuff isattracts at ...
... by which gravity attracts the stuff to Earth B) acceleration the rate at which stuffdirection changesit's itsstuff velocity d. velocity - how fast andthe in what is moving C) weight -e.the force by whichthe gravity the stuff to Earth position - where stuff isattracts at ...
Newton`s Laws and Momentum - science
... There are many misconceptions about Newton’s First Law. Read: "How many ways can you state Newton's First Law?" and "Thoughts on force..."to try and understand how it fits to many situations. Newton’s first law states that an object will remain stationary or continue at a constant velocity unless ac ...
... There are many misconceptions about Newton’s First Law. Read: "How many ways can you state Newton's First Law?" and "Thoughts on force..."to try and understand how it fits to many situations. Newton’s first law states that an object will remain stationary or continue at a constant velocity unless ac ...
Chapter 6 Circular Motion and Other Applications of Newton`s Laws
... can categorize this as a uniform circular motion problem, complicated by the fact that the gravitational force acts at all times on the aircraft. (A) Analyze the situation by drawing a free-body diagram for the pilot at the bottom of the loop, as shown in Figure 6.7b. The only forces acting on him a ...
... can categorize this as a uniform circular motion problem, complicated by the fact that the gravitational force acts at all times on the aircraft. (A) Analyze the situation by drawing a free-body diagram for the pilot at the bottom of the loop, as shown in Figure 6.7b. The only forces acting on him a ...
Ch03_Lecture_Outline - Saint Leo University Faculty
... • Action and reaction on different masses If the same force is applied to two objects of different masses, Greater mass object small acceleration ...
... • Action and reaction on different masses If the same force is applied to two objects of different masses, Greater mass object small acceleration ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Physics 121. Lecture 16.
... Collisions in two or three dimensions. • Collisions in two or three dimensions are approached in the same way as collisions in one dimension. • The x, y, and z components of the linear momentum must be conserved if there are no external forces acting on the system. • The collisions can be elastic or ...
... Collisions in two or three dimensions. • Collisions in two or three dimensions are approached in the same way as collisions in one dimension. • The x, y, and z components of the linear momentum must be conserved if there are no external forces acting on the system. • The collisions can be elastic or ...