D. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
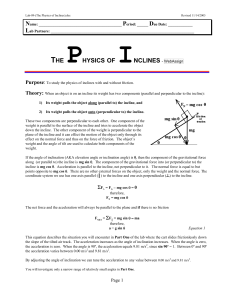
... The spring has a constant k = 20 kN/m and is held by cables so that it is initially • Apply the principle of work and energy for the rebound of the package. The compressed 120 mm. The package has a only unknown in the relation is the velocity of 2.5 m/s in the position shown and the maximum deflecti ...
... The spring has a constant k = 20 kN/m and is held by cables so that it is initially • Apply the principle of work and energy for the rebound of the package. The compressed 120 mm. The package has a only unknown in the relation is the velocity of 2.5 m/s in the position shown and the maximum deflecti ...
Newton`s Laws - Ipod Physics
... The classic way of saying this is, “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction”. Newton’s third law simply says that forces come in pairs. You push on a wall and the wall pushes on you. We call these action/reaction force pairs. One of the skills most people master is walking. We rarel ...
... The classic way of saying this is, “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction”. Newton’s third law simply says that forces come in pairs. You push on a wall and the wall pushes on you. We call these action/reaction force pairs. One of the skills most people master is walking. We rarel ...
ISNS3371_012307_bw
... end of the rope is not in contact with the block, and cannot exert a direct force on the block. Rather a force is exerted on the rope, which transmits that force to the block. The force experienced by the block from the rope is called the stretching force, commonly referred to as tension. Tension is ...
... end of the rope is not in contact with the block, and cannot exert a direct force on the block. Rather a force is exerted on the rope, which transmits that force to the block. The force experienced by the block from the rope is called the stretching force, commonly referred to as tension. Tension is ...
Noah Newton`s 2nd Law on Hills Class Exercises
... i. Jimmy’s truck and boat trailer are parked on the boat ramp, 10 m uphill from the water. He gets in the truck, eases off the brake, and allows the trailer to accelerate all the way down the ramp until it reaches the water going 2 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the trailer and the ramp is ...
... i. Jimmy’s truck and boat trailer are parked on the boat ramp, 10 m uphill from the water. He gets in the truck, eases off the brake, and allows the trailer to accelerate all the way down the ramp until it reaches the water going 2 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the trailer and the ramp is ...
Seesaws 9 Balanced Seesaw
... Ang. Position – an object’s orientation Ang. Velocity – change in ang. position w/ time Torque – a twist or spin Ang. Accel. – change in ang. velocity with time Rotational Mass – measure of rotational inertia ...
... Ang. Position – an object’s orientation Ang. Velocity – change in ang. position w/ time Torque – a twist or spin Ang. Accel. – change in ang. velocity with time Rotational Mass – measure of rotational inertia ...
Earth Orientation: - Binary Research Institute
... hardly “precesses” at all relative to objects within the SS: 365.24219878 × 86,400s = 366.24219878x 8,6164.0905382s = 31,556,925.97s This equation describes Earth’s complete 360 degree period of revolution of 31,556,925.97s relative to a fixed frame of reference, implying that the position of the ve ...
... hardly “precesses” at all relative to objects within the SS: 365.24219878 × 86,400s = 366.24219878x 8,6164.0905382s = 31,556,925.97s This equation describes Earth’s complete 360 degree period of revolution of 31,556,925.97s relative to a fixed frame of reference, implying that the position of the ve ...
PPT File - HCC Learning Web
... Usually, the choice between using a vertical or horizontal strip is equally good, but in some cases, one choice is much better than the other. For example, for the area shown below, is a vertical or horizontal strip a better choice, and why? Think about this and discuss your choice with a neighbor. ...
... Usually, the choice between using a vertical or horizontal strip is equally good, but in some cases, one choice is much better than the other. For example, for the area shown below, is a vertical or horizontal strip a better choice, and why? Think about this and discuss your choice with a neighbor. ...
AP Newton practice
... a. There is an residual upward force from the hand on each ball. b. There is a greater residual force from the hand on A than there is on B. c. Only gravity acts on B but there is an additional residual force from the hand on A. d. There is an additional downwards force besides gravity on each ball. ...
... a. There is an residual upward force from the hand on each ball. b. There is a greater residual force from the hand on A than there is on B. c. Only gravity acts on B but there is an additional residual force from the hand on A. d. There is an additional downwards force besides gravity on each ball. ...
438K pdf
... Instead, therefore, let me indicate why the notion of a manifold is important in robotics. The reader is surely familiar with the fact that the configurations of a rigid body fixed at a point in some inertial frame are in 1–1 correspondence with the set SO(3) of 3 × 3 orthogonal matrices with determ ...
... Instead, therefore, let me indicate why the notion of a manifold is important in robotics. The reader is surely familiar with the fact that the configurations of a rigid body fixed at a point in some inertial frame are in 1–1 correspondence with the set SO(3) of 3 × 3 orthogonal matrices with determ ...
Engineering Mechanics
... Continuum mechanics is concerned with motion and deformation of material objects, called bodies, under the action of forces. If these objects are solid bodies, the respective subject area is termed solid mechanics, if they are fluids, it is fluid mechanics or fluid dynamics. The mathematical equatio ...
... Continuum mechanics is concerned with motion and deformation of material objects, called bodies, under the action of forces. If these objects are solid bodies, the respective subject area is termed solid mechanics, if they are fluids, it is fluid mechanics or fluid dynamics. The mathematical equatio ...
NEWTON`S LESSON 12
... 2. How much upward force would be needed to accelerate the 5.0-kg mass up this incline at 3.0 m/sec2? 3. How much upward force would be needed to restrict the 5.0-kg mass' downward acceleration to 1.0 m/sec2? 4. If the 5.0-kg mass were allowed to slide down this incline without any additional applie ...
... 2. How much upward force would be needed to accelerate the 5.0-kg mass up this incline at 3.0 m/sec2? 3. How much upward force would be needed to restrict the 5.0-kg mass' downward acceleration to 1.0 m/sec2? 4. If the 5.0-kg mass were allowed to slide down this incline without any additional applie ...