Gravity and circular motion review
... 10. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be According to Kepler's laws, how many days are required for the planet to travel from the starting point to p ...
... 10. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be According to Kepler's laws, how many days are required for the planet to travel from the starting point to p ...
4.1_simple_harmonic_motion_
... (b) the velocity and acceleration when the particle has displacement 1.5 cm and moves towards the equilibrium position from its initial position at x = 3.0 cm; (c) the total energy of motion. 11. Show explicitly that, if x = A cos (ωt +Ф), the period of motion is given by T = 2π/ω, independently of ...
... (b) the velocity and acceleration when the particle has displacement 1.5 cm and moves towards the equilibrium position from its initial position at x = 3.0 cm; (c) the total energy of motion. 11. Show explicitly that, if x = A cos (ωt +Ф), the period of motion is given by T = 2π/ω, independently of ...
Physics Force Worksheet
... moving upward at 5.00 m/s; (c) they accelerate upward at 2.00 m/s 2; (d) they accelerate downward at 2.00 m/s2. (e) If the maximum allowable tension is 10.0 N, what is the maximum possible upward acceleration? Assume m1 is the upper mass and m2 is the lower mass. ...
... moving upward at 5.00 m/s; (c) they accelerate upward at 2.00 m/s 2; (d) they accelerate downward at 2.00 m/s2. (e) If the maximum allowable tension is 10.0 N, what is the maximum possible upward acceleration? Assume m1 is the upper mass and m2 is the lower mass. ...
Exam 1 Solutions Kinematics and Newton’s laws of motion
... Can you feel gravity? We previously determined that you can’t. 1) Hanging from a 100 m high diving board – your arms feel stretched by the bending of the board. 2) Standing on a bed – your legs feel compressed by the springs in the mattress. The bent diving board or the compressed springs provide th ...
... Can you feel gravity? We previously determined that you can’t. 1) Hanging from a 100 m high diving board – your arms feel stretched by the bending of the board. 2) Standing on a bed – your legs feel compressed by the springs in the mattress. The bent diving board or the compressed springs provide th ...
Physical Science Motion and Forces Worksheet
... acceleration is ____ 24. Which of the following best illustrates balanced forces? a) a rock falling to the ground b) a stretched rubber band being held between two hands c) a person lifting a heavy box off of the ground d) a crash between a large truck and a train 25. _____ forces acting on an objec ...
... acceleration is ____ 24. Which of the following best illustrates balanced forces? a) a rock falling to the ground b) a stretched rubber band being held between two hands c) a person lifting a heavy box off of the ground d) a crash between a large truck and a train 25. _____ forces acting on an objec ...
Lecture 04 - WebPhysics
... • Suppose the water travels downstream at 2 m/s carrying the swimmer with it. • The swimmer pushes himself or herself from one shore to another. • The result is that they will have a downstream motion as well as a motion towards/away from the shore. ...
... • Suppose the water travels downstream at 2 m/s carrying the swimmer with it. • The swimmer pushes himself or herself from one shore to another. • The result is that they will have a downstream motion as well as a motion towards/away from the shore. ...
8th Grade Science
... 1. A 300-N force acts on a 25-kg object. The acceleration of the object is ____. 2. A 3,000-N force acts on a 200-kg object. The acceleration of the object is____. 3. A 105.0 kg boxer has his first match in Panama (g=9.782 m/s2) and his second match at the North Pole (g=9.832 m/s2). a. What is his m ...
... 1. A 300-N force acts on a 25-kg object. The acceleration of the object is ____. 2. A 3,000-N force acts on a 200-kg object. The acceleration of the object is____. 3. A 105.0 kg boxer has his first match in Panama (g=9.782 m/s2) and his second match at the North Pole (g=9.832 m/s2). a. What is his m ...
Motion - Riverside Prep PAC Middle School
... is when its distance from another stationary object is changing ...
... is when its distance from another stationary object is changing ...
Name Quiz #3 — Spring 2006 Phys 2110 1. A plane has an
... 3. You are in a car which going over the top of a hill at a constant speed of 13.0 ms . The hill has a radius of curvature of 55.0 m. Suppose you have a mass of 75 kg. Find your apparent weight at the top of the hill. (Recall that your apparent weight is the force that the seat exerts upward on you. ...
... 3. You are in a car which going over the top of a hill at a constant speed of 13.0 ms . The hill has a radius of curvature of 55.0 m. Suppose you have a mass of 75 kg. Find your apparent weight at the top of the hill. (Recall that your apparent weight is the force that the seat exerts upward on you. ...
Newton`s 2nd Law Note
... a variety of laws which explain why objects move (or don't move) as they do. These three laws have become known as Newton's three laws of motion ...
... a variety of laws which explain why objects move (or don't move) as they do. These three laws have become known as Newton's three laws of motion ...
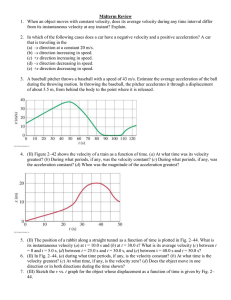
AP 1 Midterm Review
... 43. You are making a circular turn in your car on a horizontal road when you hit a big patch of ice, causing the force of friction between the tires and the road to become zero. While the car is on the ice, it (a) moves along a straight-line path away from the center of the circle. (b) moves along a ...
... 43. You are making a circular turn in your car on a horizontal road when you hit a big patch of ice, causing the force of friction between the tires and the road to become zero. While the car is on the ice, it (a) moves along a straight-line path away from the center of the circle. (b) moves along a ...
Example
... on a stool that can rotate freely about a vertical axis. The student, who has been set into rotation at an initial angular speed i , holds two dumbbells in his outstretched hands. His angular momentum vector L lies along the rotation axis, pointing upward. The student then pulls in his hands as sho ...
... on a stool that can rotate freely about a vertical axis. The student, who has been set into rotation at an initial angular speed i , holds two dumbbells in his outstretched hands. His angular momentum vector L lies along the rotation axis, pointing upward. The student then pulls in his hands as sho ...