Chapter 5: Applying Newton`s Laws
... length. Be sure to include the body’s weight, except in cases where the body has negligible mass (and hence negligible weight). If the mass is given, use w=mg to find the weight. Label each force with a symbol representing the magnitude of the force. ...
... length. Be sure to include the body’s weight, except in cases where the body has negligible mass (and hence negligible weight). If the mass is given, use w=mg to find the weight. Label each force with a symbol representing the magnitude of the force. ...
Chapter 4 Making Sense of the Universe: Understanding Motion
... • All falling objects accelerate at the same rate (not counting friction of air resistance). • On Earth, g ≈ 10 m/s2: speed increases 10 m/s with each second of falling. ...
... • All falling objects accelerate at the same rate (not counting friction of air resistance). • On Earth, g ≈ 10 m/s2: speed increases 10 m/s with each second of falling. ...
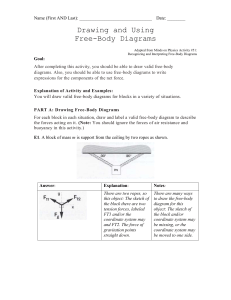
Drawing and Using
... First of all, you should make sure that the directions of all your forces are accurately drawn. This will help you find the components of the forces, which will help you find the net force, and ultimately, the acceleration of the object. Then, if the sizes of the force vectors are also drawn accurat ...
... First of all, you should make sure that the directions of all your forces are accurately drawn. This will help you find the components of the forces, which will help you find the net force, and ultimately, the acceleration of the object. Then, if the sizes of the force vectors are also drawn accurat ...
Slide 1
... V(x, y, z) be the velocity vector at a point (x, y, z). ◦ Then, V assigns a vector to each point (x, y, z) in a certain domain E (the interior of the pipe). ◦ So, V is a vector field on 3 called a velocity field. ...
... V(x, y, z) be the velocity vector at a point (x, y, z). ◦ Then, V assigns a vector to each point (x, y, z) in a certain domain E (the interior of the pipe). ◦ So, V is a vector field on 3 called a velocity field. ...
Cornell Notes 3.3 Newton`s Laws November 29, 2011 Pages 91
... Newton’s third law tells us that any time two objects hit each other, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other. However, the effect of the force is not always the same. When a large truck hits a small car, the forces are equal. However, the small car experiences a much greater change in ve ...
... Newton’s third law tells us that any time two objects hit each other, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other. However, the effect of the force is not always the same. When a large truck hits a small car, the forces are equal. However, the small car experiences a much greater change in ve ...
Physics 235 Chapter 10 Motion in a Non-Inertial Reference Frame
... The laws of physics are only valid in inertial reference frames. However, it is not always easy to express the motion of interest in an inertial reference frame. Consider for example the motion of a book laying on top of a table. In a reference frame that is fixed with respect to the Earth, the moti ...
... The laws of physics are only valid in inertial reference frames. However, it is not always easy to express the motion of interest in an inertial reference frame. Consider for example the motion of a book laying on top of a table. In a reference frame that is fixed with respect to the Earth, the moti ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Select x and y coordinate axes. The positive x axis direction is the 0° direction. Vector equations require accurate vector directions. For more information read the Guidelines for Coordinate Axes. Example: acceleration 0°, gravity force -90°, support force +90°, and pull force 0° 5) Rewrite the 2nd ...
... Select x and y coordinate axes. The positive x axis direction is the 0° direction. Vector equations require accurate vector directions. For more information read the Guidelines for Coordinate Axes. Example: acceleration 0°, gravity force -90°, support force +90°, and pull force 0° 5) Rewrite the 2nd ...
Physics 131 Review Translational Kinematics: Position ( ): location relative to an origin
... Position ( r ): location relative to an origin Unit: m Displacement: change in position r r r ∆r = r1 − r2 Unit: m Velocity: rate r of change of the position r dr v= dt Unit: m/s Acceleration: rate of change of the velocity r r dv a= dt Unit: m/s2 Equation of Motion: When the acceleration vector is ...
... Position ( r ): location relative to an origin Unit: m Displacement: change in position r r r ∆r = r1 − r2 Unit: m Velocity: rate r of change of the position r dr v= dt Unit: m/s Acceleration: rate of change of the velocity r r dv a= dt Unit: m/s2 Equation of Motion: When the acceleration vector is ...