
forces and the laws of motion - PAMS-Doyle
... that they would both hit the ground at the same time. He was right. • When the only force acting on a falling object is gravity, they are in free fall. • Acceleration of a falling object is due to the force of gravity is 9.8 m/sec/sec. • 1 meter = 9.8 m/sec/sec • 2 meters = 19.6 m/sec/sec • 3 meters ...
... that they would both hit the ground at the same time. He was right. • When the only force acting on a falling object is gravity, they are in free fall. • Acceleration of a falling object is due to the force of gravity is 9.8 m/sec/sec. • 1 meter = 9.8 m/sec/sec • 2 meters = 19.6 m/sec/sec • 3 meters ...
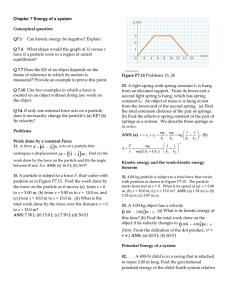
Chapter 7 Energy of a system Conceptual question Q7.1 Can kinetic
... A single conservative force acts on a 5.00-kg particle within a system due to its intteaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = (2x + 4) N describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00 m, calculate (a) the work done by this ...
... A single conservative force acts on a 5.00-kg particle within a system due to its intteaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = (2x + 4) N describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00 m, calculate (a) the work done by this ...
Exam Review - Dublin Schools
... face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the firefly or the force on the bus? ...
... face of the driver. This is a clear case of Newton's third law of motion. The firefly hit the bus and the bus hits the firefly. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the firefly or the force on the bus? ...
Vectors & Scalars - The Grange School Blogs
... Final Time Constant Only work when the acceleration is constant! ...
... Final Time Constant Only work when the acceleration is constant! ...
P2a Forces and Their Effects
... Stopping distance Total stopping distance = Thinking distance + Braking distance ...
... Stopping distance Total stopping distance = Thinking distance + Braking distance ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 12: Keeping momentum
... The football player A football player throws a ball with an initial velocity of 40 m/s and an angle of 40o with respect to the field. At what distance from the player will the ball hit the field? Assume that the player’s length is negligible (i.e. the ball is thrown from a vertical height of 0.0 m) ...
... The football player A football player throws a ball with an initial velocity of 40 m/s and an angle of 40o with respect to the field. At what distance from the player will the ball hit the field? Assume that the player’s length is negligible (i.e. the ball is thrown from a vertical height of 0.0 m) ...
8th 2014 midterm
... c) The rate of change of position in which the same distance is traveled each second. Constant speed d) A change in the velocity during a time interval divided by the time interval during which the velocity changes. Acceleration e) The speed and the direction of a moving object. Velocity f) The tota ...
... c) The rate of change of position in which the same distance is traveled each second. Constant speed d) A change in the velocity during a time interval divided by the time interval during which the velocity changes. Acceleration e) The speed and the direction of a moving object. Velocity f) The tota ...
Lecture 18
... of where we’ve put the axis of rotation, though we haven’t actually changed the masses! But what if we don’t have point masses to deal with? What if we have solid objects? It actually requires calculus to do this, so we’ve given you a table of objects to deal with (p.278). If you needed one of these ...
... of where we’ve put the axis of rotation, though we haven’t actually changed the masses! But what if we don’t have point masses to deal with? What if we have solid objects? It actually requires calculus to do this, so we’ve given you a table of objects to deal with (p.278). If you needed one of these ...
Simple Machines Objectives - Kirkwood Community College
... 1. Define angular displacements, angular velocity, and angular acceleration, and apply these concepts to the solution of physical problems. 2. Draw analogies relating rotational-motion parameters (θ, ω, α)to linear-motion parameters, and solve angular acceleration problems in a manner similar to tha ...
... 1. Define angular displacements, angular velocity, and angular acceleration, and apply these concepts to the solution of physical problems. 2. Draw analogies relating rotational-motion parameters (θ, ω, α)to linear-motion parameters, and solve angular acceleration problems in a manner similar to tha ...
Course Syllabus
... everyday life with scientific mind, ethic, moral, desired values. Expected Learning Outcome ...
... everyday life with scientific mind, ethic, moral, desired values. Expected Learning Outcome ...















![PhysRozz Midterm 2012 [via06-07] Version 18](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014722455_1-33f5b15b25beb94441904fea997b655c-300x300.png)




