July
... continued to chase the car A with uniform velocity of 20 m/sec . Find the time taken ,in which the car B will overtake the car A. ...
... continued to chase the car A with uniform velocity of 20 m/sec . Find the time taken ,in which the car B will overtake the car A. ...
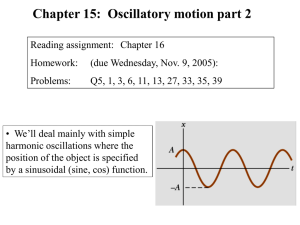
Chapter 15b
... An mass oscillates with an amplitude of 4.00 m, a frequency of 0.5 Hz and a phase angle of p/4. (a) What is the period T? (b) Write an equation for the displacement of the particle. (c) Calculate the velocity and acceleration of the object at any time t. (d) Determine the position, velocity and acce ...
... An mass oscillates with an amplitude of 4.00 m, a frequency of 0.5 Hz and a phase angle of p/4. (a) What is the period T? (b) Write an equation for the displacement of the particle. (c) Calculate the velocity and acceleration of the object at any time t. (d) Determine the position, velocity and acce ...
8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics
... (a) [5 pts] How much work does the contact force apply to the system as a function of angle? (b) [5 pts] What is the angular speed of the bar as a function of angle? (c) [5 pts] What is the angular acceleration of the bar as a function of angle? (d) [10 pts] What are the vertical and horizontal forc ...
... (a) [5 pts] How much work does the contact force apply to the system as a function of angle? (b) [5 pts] What is the angular speed of the bar as a function of angle? (c) [5 pts] What is the angular acceleration of the bar as a function of angle? (d) [10 pts] What are the vertical and horizontal forc ...
File
... ____ 10. Two perpendicular forces, one of 45.0 N directed upward and the second of 60.0 N directed to the right, act simultaneously on an object with a mass of 35.0 kg. What is the magnitude of the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 2.14 m/s2 b. 3.00 m/s2 c. 5.25 m/s2 d. 1.41 m/s2 ____ 11. An ...
... ____ 10. Two perpendicular forces, one of 45.0 N directed upward and the second of 60.0 N directed to the right, act simultaneously on an object with a mass of 35.0 kg. What is the magnitude of the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 2.14 m/s2 b. 3.00 m/s2 c. 5.25 m/s2 d. 1.41 m/s2 ____ 11. An ...
TEST
... C. a/2 D. a/4 42. If the force of gravity on a balloon is 3000 N, and the lift force provided by the atmosphere is 3300 N, in which direction is the net force acting? ______________________________ 43. A child’s toy is suspended from the ceiling by means of a string. The earth pulls downward on the ...
... C. a/2 D. a/4 42. If the force of gravity on a balloon is 3000 N, and the lift force provided by the atmosphere is 3300 N, in which direction is the net force acting? ______________________________ 43. A child’s toy is suspended from the ceiling by means of a string. The earth pulls downward on the ...
APRotMotionHW2010.29.. - Jaclyn Kuspiel Murray
... A spinning wheel on a fireworks display is initially rotating in a counterclockwise direction. The wheel has an angular acceleration of -4.60 rad/s2. Because of this acceleration, the angular velocity of the wheel changes from its initial value to a final value of -24.0 rad/s. While this change occu ...
... A spinning wheel on a fireworks display is initially rotating in a counterclockwise direction. The wheel has an angular acceleration of -4.60 rad/s2. Because of this acceleration, the angular velocity of the wheel changes from its initial value to a final value of -24.0 rad/s. While this change occu ...
AP Physics - eLearning
... 10. A skater extends her arms horizontally, holding a 5-kg mass in each hand. She is rotating about a vertical axis with an angular velocity of one revolution per second. If she drops her hands to her sides, what will the final angular velocity (in rev sec ) be if her moment of inertia remains appr ...
... 10. A skater extends her arms horizontally, holding a 5-kg mass in each hand. She is rotating about a vertical axis with an angular velocity of one revolution per second. If she drops her hands to her sides, what will the final angular velocity (in rev sec ) be if her moment of inertia remains appr ...
Integrated Physical Science: Semester 2 Exam Review
... c. In a spaceship orbiting the Earth The earth 3. If you are riding in a bus and drop a pen, describe what happens to the pen. What is your frame of reference? Moving with the bus 4. What is the formula for speed? What are the units for distance, time, and speed? s=d/t ...
... c. In a spaceship orbiting the Earth The earth 3. If you are riding in a bus and drop a pen, describe what happens to the pen. What is your frame of reference? Moving with the bus 4. What is the formula for speed? What are the units for distance, time, and speed? s=d/t ...
6.2 Newton`s Second Law
... Force causes an object to accelerate, while the object’s mass resists the acceleration. The larger the object (the more mass it has), the harder it is to accelerate. ...
... Force causes an object to accelerate, while the object’s mass resists the acceleration. The larger the object (the more mass it has), the harder it is to accelerate. ...
acceleration
... Reading Graphs of Acceleration • You can represent the acceleration of an object with a speed-time graph • speed is plotted on the ...
... Reading Graphs of Acceleration • You can represent the acceleration of an object with a speed-time graph • speed is plotted on the ...
NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOTION
... • . A gun recoils when it is fired. The recoil is the result of action-reaction force pairs. As the gases from the gunpowder explosion expand, the gun pushes the bullet forwards and the bullet pushes the gun backwards. The acceleration of the recoiling gun is ... A-greater than the acceleration of ...
... • . A gun recoils when it is fired. The recoil is the result of action-reaction force pairs. As the gases from the gunpowder explosion expand, the gun pushes the bullet forwards and the bullet pushes the gun backwards. The acceleration of the recoiling gun is ... A-greater than the acceleration of ...