Sample problems
... 18. A Hooke’s law spring is compressed a distance d and is used to launch a mass m vertically to a height h above its starting position. Next, the spring is compressed by 2d and is used to launch the same mass. How high does the mass now rise above its starting position? ANS: 4h 19. Alex throws a 0 ...
... 18. A Hooke’s law spring is compressed a distance d and is used to launch a mass m vertically to a height h above its starting position. Next, the spring is compressed by 2d and is used to launch the same mass. How high does the mass now rise above its starting position? ANS: 4h 19. Alex throws a 0 ...
Getting mathematical - Teaching Advanced Physics
... x = A sin 2ft or x = A sin t f is the frequency of the oscillation, and is related to the period T by f = 1/T. The amplitude of the oscillation is A. Velocity: v = 2f A cos 2ft = A cos t Acceleration: a = - (2f)2 A sin 2ft = -2 A sin t Depending on your students’ mathematical knowledge, y ...
... x = A sin 2ft or x = A sin t f is the frequency of the oscillation, and is related to the period T by f = 1/T. The amplitude of the oscillation is A. Velocity: v = 2f A cos 2ft = A cos t Acceleration: a = - (2f)2 A sin 2ft = -2 A sin t Depending on your students’ mathematical knowledge, y ...
to see a detailed table of contents outlining all chapter lessons in
... Application of the Principle of Impulse and Momentum to the Three-Dimensional Motion of a Rigid Body 18.4 Kinetic Energy of a Rigid Body in Three Dimensions 18.5 Motion of a Rigid Body in Three Dimensions 18.6 Euler’s Equations of Motion. Extension of d’Alembert’s Principle to the Motion of a Rigid ...
... Application of the Principle of Impulse and Momentum to the Three-Dimensional Motion of a Rigid Body 18.4 Kinetic Energy of a Rigid Body in Three Dimensions 18.5 Motion of a Rigid Body in Three Dimensions 18.6 Euler’s Equations of Motion. Extension of d’Alembert’s Principle to the Motion of a Rigid ...
Circular Motion
... Sometimes it is at the exact center of the object Sometimes it may not be in the object at all ...
... Sometimes it is at the exact center of the object Sometimes it may not be in the object at all ...
No Slide Title
... components. • Be sure of your coordinate system; is the motion of the object you want to study relative to another object? • Write down the equations of motion for each direction separately. • If you cannot understand the problem, draw motion diagrams for each of the directions separately. • Make su ...
... components. • Be sure of your coordinate system; is the motion of the object you want to study relative to another object? • Write down the equations of motion for each direction separately. • If you cannot understand the problem, draw motion diagrams for each of the directions separately. • Make su ...
1 Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Centripetal Force and Centripetal Acceleration An accelerating object is an object that is changing its velocity. And since velocity is a vector that has both magnitude and direction, a change in either the magnitude or the direction results in a change in the velocity. An object moving in a cir ...
... Centripetal Force and Centripetal Acceleration An accelerating object is an object that is changing its velocity. And since velocity is a vector that has both magnitude and direction, a change in either the magnitude or the direction results in a change in the velocity. An object moving in a cir ...
Refresher - UF Physics
... complete summary of introductory math and physics. It is only meant to be a refresher of some of the concepts used in this course. Please report any inaccuracies to the ...
... complete summary of introductory math and physics. It is only meant to be a refresher of some of the concepts used in this course. Please report any inaccuracies to the ...
rotary motion - GEOCITIES.ws
... A 7.5 kg bowling ball (Irolling = 7/5 m R2 ) with a radius of 12 cm is at the top of a ramp 5.0 m long and inclined at 30.00. a) Find the torque acting on the ball. b) Find its rotational inertia. ...
... A 7.5 kg bowling ball (Irolling = 7/5 m R2 ) with a radius of 12 cm is at the top of a ramp 5.0 m long and inclined at 30.00. a) Find the torque acting on the ball. b) Find its rotational inertia. ...
The Two Body Problem
... decompositions are not valid if it is not for the CM values and values relative to the CM. ...
... decompositions are not valid if it is not for the CM values and values relative to the CM. ...
Physics Level Force and Motion Review 2010
... Matching: Match the term to the correct definition. 1. Normal Force (FN) a. When all forces are balanced and acceleration is zero 2. Net Force (Fnet) b. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force 3. g c. Objects remain at rest or moving at a constant velocity unless acted ...
... Matching: Match the term to the correct definition. 1. Normal Force (FN) a. When all forces are balanced and acceleration is zero 2. Net Force (Fnet) b. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force 3. g c. Objects remain at rest or moving at a constant velocity unless acted ...
Lecture2_Freefall
... comes to a stop, and so its velocity is zero. However, since the ball is in free fall, its acceleration is g = 9.8 m/s2 (at every moment). ...
... comes to a stop, and so its velocity is zero. However, since the ball is in free fall, its acceleration is g = 9.8 m/s2 (at every moment). ...
Scalar A scalar quantity is a physical quantity which is completely
... : The speed of an object is the rate at which distance is increasing. : velocity is the rate at which displacement is changing. Velocity should always be quoted with a direction. The combined effect of a number of vectors can be found by adding the vectors together. The result of the addition is the ...
... : The speed of an object is the rate at which distance is increasing. : velocity is the rate at which displacement is changing. Velocity should always be quoted with a direction. The combined effect of a number of vectors can be found by adding the vectors together. The result of the addition is the ...
Newton`s Laws Notes
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • Things are LAZY…they keep doing what they’re already doing unless an UNBALANCED force causes a change! ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • Things are LAZY…they keep doing what they’re already doing unless an UNBALANCED force causes a change! ...
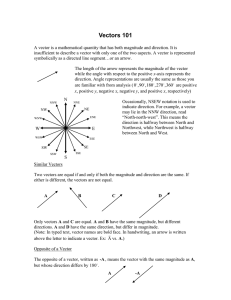
Vectors 101
... Unit vector notation There are three unit vectors, ˆi , ˆj, and kˆ . (Read “i-hat”, “j-hat”, and “k-hat”) î is the vector whose magnitude is one and is directed along the positive x axis. ĵ is the vector whose magnitude is one and is directed along the positive y axis. k̂ has a magnitude of one an ...
... Unit vector notation There are three unit vectors, ˆi , ˆj, and kˆ . (Read “i-hat”, “j-hat”, and “k-hat”) î is the vector whose magnitude is one and is directed along the positive x axis. ĵ is the vector whose magnitude is one and is directed along the positive y axis. k̂ has a magnitude of one an ...
ESS 303 -- Biomechanics
... Concurrent forces: forces that act on the same point at the same time Colinear forces: forces in a straight line (calculate the sum) 5N + 7N – 10N = 2N Coplanar forces: forces in a plane (connect the vectors and calculate the displacement ...
... Concurrent forces: forces that act on the same point at the same time Colinear forces: forces in a straight line (calculate the sum) 5N + 7N – 10N = 2N Coplanar forces: forces in a plane (connect the vectors and calculate the displacement ...