Principle of Impulse and momentum
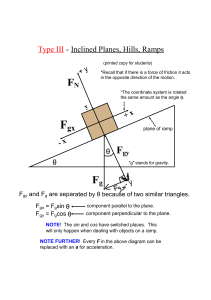
... The 250 N crate is acted upon by a force having a variable magnitude P = 100t, where t is in seconds. Determine the crate’s velocity 2 s after P has been applied. The initial velocity is v1 = 1 m/s down the plane, and mk = 0.3. ...
... The 250 N crate is acted upon by a force having a variable magnitude P = 100t, where t is in seconds. Determine the crate’s velocity 2 s after P has been applied. The initial velocity is v1 = 1 m/s down the plane, and mk = 0.3. ...
During the Program - Biomechanics - science21
... 31. List at least two factors that effect balance and stability: (i) (ii) (iii) Others:32. The larger the base of support, the greater/less the stability of the object. (delete incorrect) 33. Briefly discuss what happens to stability if the line of gravity falls outside the base of support. ...
... 31. List at least two factors that effect balance and stability: (i) (ii) (iii) Others:32. The larger the base of support, the greater/less the stability of the object. (delete incorrect) 33. Briefly discuss what happens to stability if the line of gravity falls outside the base of support. ...
Document
... In problems dealing with several connected rigid bodies each body may be considered separately or, if no more than three unknowns are involved, the principles of impulse and momentum may be applied to the entire system, considering the impulses of the external forces only. When the lines of action o ...
... In problems dealing with several connected rigid bodies each body may be considered separately or, if no more than three unknowns are involved, the principles of impulse and momentum may be applied to the entire system, considering the impulses of the external forces only. When the lines of action o ...
Lecture 4
... • Just like for motion in 1D, we can let Δt get smaller and smaller…. • Gives instantaneous velocity vector: ...
... • Just like for motion in 1D, we can let Δt get smaller and smaller…. • Gives instantaneous velocity vector: ...
Drag
... have to use the momentum formalism, rather than F=ma. It is also the first example of non-uniform acceleration that we will deal with using the Force Approach. On the mathematical side, it gives us more experience with differential equations than we get from simple UAM (uniformly accelerated motion) ...
... have to use the momentum formalism, rather than F=ma. It is also the first example of non-uniform acceleration that we will deal with using the Force Approach. On the mathematical side, it gives us more experience with differential equations than we get from simple UAM (uniformly accelerated motion) ...
rotational motion & law of gravity
... with an average angular speed of 4.0 rads/sec. In what time interval will the child’s feet have an angular displacement of 8.0 rad? ...
... with an average angular speed of 4.0 rads/sec. In what time interval will the child’s feet have an angular displacement of 8.0 rad? ...
Learning Objectives – Textbook Correlation
... 3.2 Determine both the displacement and distance traveled in a numerical problem given sufficient information 3.3 Define average speed and average velocity 3.4 Distinguish between average speed and average velocity 3.5 Determine both the average speed and average velocity in a numerical problem give ...
... 3.2 Determine both the displacement and distance traveled in a numerical problem given sufficient information 3.3 Define average speed and average velocity 3.4 Distinguish between average speed and average velocity 3.5 Determine both the average speed and average velocity in a numerical problem give ...