Newton`s Second Law
... A 50.0 kg wooden box is pushed across a wooden floor (mk=0.20) at a steady speed of 2.0 m/s. a. How much force does she exert? (98 N) b. If she stops pushing, calculate the acceleration. (-1.96 m/s2) c. Calculate how far the box slides until it stops. (1.00 m) ...
... A 50.0 kg wooden box is pushed across a wooden floor (mk=0.20) at a steady speed of 2.0 m/s. a. How much force does she exert? (98 N) b. If she stops pushing, calculate the acceleration. (-1.96 m/s2) c. Calculate how far the box slides until it stops. (1.00 m) ...
Force.
... Notice that when the forces are balanced, the object might still be moving, but the objects are not accelerating, instead they have a constant velocity. Hence, once in motion – it’s always in motion unless acted upon by what? Another Force. ...
... Notice that when the forces are balanced, the object might still be moving, but the objects are not accelerating, instead they have a constant velocity. Hence, once in motion – it’s always in motion unless acted upon by what? Another Force. ...
ppt - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... Use the frictional force equation to determine the magnitude of the frictional force ...
... Use the frictional force equation to determine the magnitude of the frictional force ...
Document
... a) Many Possible Experiments. For example, students could decide to pull with the same force on various air gliders of different masses with spring scales to determine if the acceleration depends on 1/m. b) The best experiment should create the best chance of disproving the relationship a = ΣF/m c) ...
... a) Many Possible Experiments. For example, students could decide to pull with the same force on various air gliders of different masses with spring scales to determine if the acceleration depends on 1/m. b) The best experiment should create the best chance of disproving the relationship a = ΣF/m c) ...
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... opposite to those of the accelerations. They are referred to as “apparent” forces because they ARE NOT applied forces and should not appear on a free body diagram. These apparent forces arise only because we are describing the motion relative to a rotating coordinate frame. In other words, if we cho ...
... opposite to those of the accelerations. They are referred to as “apparent” forces because they ARE NOT applied forces and should not appear on a free body diagram. These apparent forces arise only because we are describing the motion relative to a rotating coordinate frame. In other words, if we cho ...
2.05 AQA F = ma - extra questions
... (a) The toy parachute is thrown with an initial horizontal speed of 9.0 ms–1. Calculate the initial vertical speed. (2 marks) (b) The wall is a horizontal distance of 12 m from the point at which the toy parachute is thrown. You may ignore air resistance in this part of the question. (i) ...
... (a) The toy parachute is thrown with an initial horizontal speed of 9.0 ms–1. Calculate the initial vertical speed. (2 marks) (b) The wall is a horizontal distance of 12 m from the point at which the toy parachute is thrown. You may ignore air resistance in this part of the question. (i) ...
Test hints
... useful hints, strategies, and problem solving tactics for when you go one-on-one with the dreaded (or perhaps welcomed) AP Physics Test. This will be quick and dirty. The guide will provide no solution or problems. It will, however, discuss types of problems and point out the equations that you will ...
... useful hints, strategies, and problem solving tactics for when you go one-on-one with the dreaded (or perhaps welcomed) AP Physics Test. This will be quick and dirty. The guide will provide no solution or problems. It will, however, discuss types of problems and point out the equations that you will ...
Force Practice Problems Name: Per: ______ Answer the following
... a. Which exerts the larger force; the bug on the car or the car on the bug? How come? b. Which experiences a larger acceleration; the bug or the car? How come? 2. A 450.kg mass is accelerated at 2.50m/s2. a. What is the net force causing this acceleration? b. If the mass of the car is doubled, what ...
... a. Which exerts the larger force; the bug on the car or the car on the bug? How come? b. Which experiences a larger acceleration; the bug or the car? How come? 2. A 450.kg mass is accelerated at 2.50m/s2. a. What is the net force causing this acceleration? b. If the mass of the car is doubled, what ...
Paper Reference(s)
... A particle P of mass 2 kg is projected from a point A up a line of greatest slope AB of a fixed plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 to the horizontal and AB = 3 m with B above A, as shown in Fig. 1. The speed of P at A is 10 m s1. Assuming the plane is smooth, (a) find the speed of P at ...
... A particle P of mass 2 kg is projected from a point A up a line of greatest slope AB of a fixed plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 to the horizontal and AB = 3 m with B above A, as shown in Fig. 1. The speed of P at A is 10 m s1. Assuming the plane is smooth, (a) find the speed of P at ...
Sect. 7.4 - TTU Physics
... For a body moving with v we showed: dτ γ-1dt where: γ [1 - β2]-½ , β (v/c) dτ < dt “Time dilation” ...
... For a body moving with v we showed: dτ γ-1dt where: γ [1 - β2]-½ , β (v/c) dτ < dt “Time dilation” ...
Equilibrium is not just translational, is is also rotational. While a set
... Fig 9.19a. The two cables are wrapped around their pulleys, which have radii of 0.600 and 0.200 m. The pulleys form a dual pulley and have a moment of inertia of I = 50.0 kg m2. The tension in the motor cable is maintained at 2150 N. Find the angular acceleration of the dual pulley and the tension i ...
... Fig 9.19a. The two cables are wrapped around their pulleys, which have radii of 0.600 and 0.200 m. The pulleys form a dual pulley and have a moment of inertia of I = 50.0 kg m2. The tension in the motor cable is maintained at 2150 N. Find the angular acceleration of the dual pulley and the tension i ...
TWGHs. Kap Yan Directors` College
... 19. Two blocks X and Y are placed on a horizontal frictionless surface as shown. Two horizontal forces F 1 and F2 are applied on X and Y respectively. Then two blocks move to the right with constant acceleration a since F1 > F2. Given that the mass ratio of the two blocks is 2:3, what is the force ...
... 19. Two blocks X and Y are placed on a horizontal frictionless surface as shown. Two horizontal forces F 1 and F2 are applied on X and Y respectively. Then two blocks move to the right with constant acceleration a since F1 > F2. Given that the mass ratio of the two blocks is 2:3, what is the force ...
document
... Explain how acceleration due to gravity affects the velocity of an object as it falls. ...
... Explain how acceleration due to gravity affects the velocity of an object as it falls. ...
Applying Newton`s Third Law of Motion in the Gravitron Ride
... Bobby: A vector quantity is a quantity that specifies not only a magnitude, which is basically a number, but also a direction, which is usually specified as an angle. Joe: Oh, you mean like five meters northeast? Bobby: Yes. That is an example of displacement where a position is measured with respec ...
... Bobby: A vector quantity is a quantity that specifies not only a magnitude, which is basically a number, but also a direction, which is usually specified as an angle. Joe: Oh, you mean like five meters northeast? Bobby: Yes. That is an example of displacement where a position is measured with respec ...
File
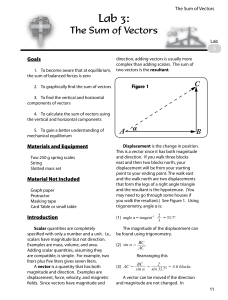
... • Vectors have both magnitude and direction. • Vectors must be added using vector addition. – You will have to treat vertical and horizontal vectors separately. ...
... • Vectors have both magnitude and direction. • Vectors must be added using vector addition. – You will have to treat vertical and horizontal vectors separately. ...