9-1 Simple Rotations of a Rigid Body
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
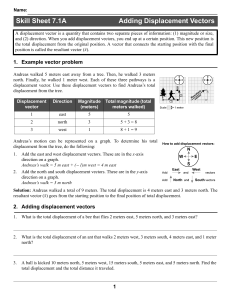
Skill Sheet 7.1A Adding Displacement Vectors
... theorem. This useful theorem states that a2 + b2 = c2, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of any right triangle. For example, suppose you need to know the distance represented by the displacement vector (4,3)m. If you walked east 4 meters then north 3 meters, you would walk a total of 7 ...
... theorem. This useful theorem states that a2 + b2 = c2, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of any right triangle. For example, suppose you need to know the distance represented by the displacement vector (4,3)m. If you walked east 4 meters then north 3 meters, you would walk a total of 7 ...
Rotational Motion
... Solution The pivot point is at the hinges of the door, opposite to where you were pushing the door. The force you used was 50N, at a distance 1.0m from the pivot point. You hit the door perpendicular to its plane, so the angle between the door and the direction of force was 90 degrees. Since = r x ...
... Solution The pivot point is at the hinges of the door, opposite to where you were pushing the door. The force you used was 50N, at a distance 1.0m from the pivot point. You hit the door perpendicular to its plane, so the angle between the door and the direction of force was 90 degrees. Since = r x ...
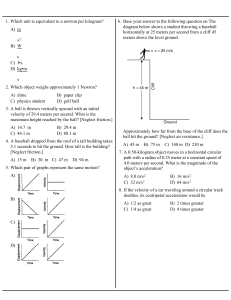
Version PREVIEW – Practice 8 – carroll – (11108) 1 This print
... L = constant since the perpendicular distance from the line of flight to Earth’s surface doesn’t change. Asteroid Collision 010 (part 1 of 3) 10.0 points Consider an Earth-like planet hit by an asteroid. The planet has mass Mp = 6.72 × 1023 kg and radius Rp = 6.55 × 106 m, and you may approximate it ...
... L = constant since the perpendicular distance from the line of flight to Earth’s surface doesn’t change. Asteroid Collision 010 (part 1 of 3) 10.0 points Consider an Earth-like planet hit by an asteroid. The planet has mass Mp = 6.72 × 1023 kg and radius Rp = 6.55 × 106 m, and you may approximate it ...
File
... System: A collection of any number of particles interacting with one another are said to form a system. ...
... System: A collection of any number of particles interacting with one another are said to form a system. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion (power point file)
... For every force that is exerted by one body on a second body there is an equal (magnitude) and opposite (direction) simultaneous force exerted by the second body on the first • Therefore every force which is applied by a body is accompanied by a reaction force on that body • Difficult to visualise b ...
... For every force that is exerted by one body on a second body there is an equal (magnitude) and opposite (direction) simultaneous force exerted by the second body on the first • Therefore every force which is applied by a body is accompanied by a reaction force on that body • Difficult to visualise b ...
Lecture 8, PPT version
... The bystander says that 1 second after the lamp was switched on, the light (photons) have traveled 300,000 km up and down the track and the lamp has moved 100,000 km from its location when it was turned on. The bystander says the back door opens before the front door, because the light catches up to ...
... The bystander says that 1 second after the lamp was switched on, the light (photons) have traveled 300,000 km up and down the track and the lamp has moved 100,000 km from its location when it was turned on. The bystander says the back door opens before the front door, because the light catches up to ...
Chapter 10 Dynamics of Rotational Motion
... When force acts on an object it can change its translational as well as rotational motion. The effect on the rotational motion depends not only on the magnitude of the applied force, but also to which point the force is applied. For example, when a wrench is used to loosen a bolt, the force applied n ...
... When force acts on an object it can change its translational as well as rotational motion. The effect on the rotational motion depends not only on the magnitude of the applied force, but also to which point the force is applied. For example, when a wrench is used to loosen a bolt, the force applied n ...