Lecture 8, PPT version
... The bystander says that 1 second after the lamp was switched on, the light (photons) have traveled 300,000 km up and down the track and the lamp has moved 100,000 km from its location when it was turned on. The bystander says the back door opens before the front door, because the light catches up to ...
... The bystander says that 1 second after the lamp was switched on, the light (photons) have traveled 300,000 km up and down the track and the lamp has moved 100,000 km from its location when it was turned on. The bystander says the back door opens before the front door, because the light catches up to ...
Final Exam Practice questions
... 32) A 4.0 kg hollow cylinder of radius 5.0 cm starts from rest and rolls without slipping down a 30 degree incline. If the length of the incline is 50 cm, then the velocity of the center of mass of the cylinder at the bottom of the incline is, a) 1.35 m/s b) 1.82 m/s c) 2.21 m/s d) 2.55 m/s e) 3.02 ...
... 32) A 4.0 kg hollow cylinder of radius 5.0 cm starts from rest and rolls without slipping down a 30 degree incline. If the length of the incline is 50 cm, then the velocity of the center of mass of the cylinder at the bottom of the incline is, a) 1.35 m/s b) 1.82 m/s c) 2.21 m/s d) 2.55 m/s e) 3.02 ...
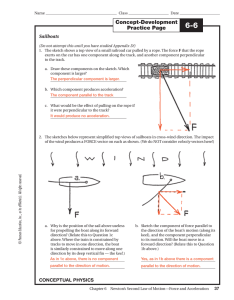
Matt Katz Newton`s Laws Newton`s First Law • AKA law of ineria • A
... • A body will have zero acceleration if no forces act on it • An object in motion stays in a straight path of motion unless acted upon by an external force • An object at rest stays at rest unless acted upon by an external force • Formulated by Gallileo • Rolled objects along horizontal surfaces and ...
... • A body will have zero acceleration if no forces act on it • An object in motion stays in a straight path of motion unless acted upon by an external force • An object at rest stays at rest unless acted upon by an external force • Formulated by Gallileo • Rolled objects along horizontal surfaces and ...
Concept Questions
... string detaches from the rotor, the rotor coasts to a stop with an angular acceleration of magnitude 2. Let g denote the gravitational constant. What is the moment of inertia of the rotor assembly (including the washer) about the rotation axis? ...
... string detaches from the rotor, the rotor coasts to a stop with an angular acceleration of magnitude 2. Let g denote the gravitational constant. What is the moment of inertia of the rotor assembly (including the washer) about the rotation axis? ...
linacs_CAS_al_2 - Indico
... the synchronous particles enters/exits a cavity. • For a given cavity length there is an optimum velocity (or beta) such that a particle traveling at this velocity goes through the cavity in half an RF period. • The difference in time of arrival between the synchronous particles and the particle tra ...
... the synchronous particles enters/exits a cavity. • For a given cavity length there is an optimum velocity (or beta) such that a particle traveling at this velocity goes through the cavity in half an RF period. • The difference in time of arrival between the synchronous particles and the particle tra ...
KEY Chapter 8 – Rotational Motion Chapter 6 – Work, Energy
... A. force & energy B. force & distance C. distance & energy D. energy & momentum 2. Work is done only if the applied force does which of the following? A. equals zero B. acts in the same direction as gravity C. is greater than the weight D. produces motion 3. The transfer of energy by mechanical mean ...
... A. force & energy B. force & distance C. distance & energy D. energy & momentum 2. Work is done only if the applied force does which of the following? A. equals zero B. acts in the same direction as gravity C. is greater than the weight D. produces motion 3. The transfer of energy by mechanical mean ...
Dynamics Review Sheet Solutions
... 13. A satellite is observed to move in a circle about the earth at a constant speed. This means that the force acting upon it is: A. zero B. opposite of the satellite’s velocity C. perpendicular to the satellite’s velocity D. parallel to the satellite’s velocity ...
... 13. A satellite is observed to move in a circle about the earth at a constant speed. This means that the force acting upon it is: A. zero B. opposite of the satellite’s velocity C. perpendicular to the satellite’s velocity D. parallel to the satellite’s velocity ...
Motion, Forces, and Simple Machines
... Types of Simple Machines A. Pulley * object with a groove, like a wheel, with a rope or chain running through the groove. * Changes the direction of the input force. ...
... Types of Simple Machines A. Pulley * object with a groove, like a wheel, with a rope or chain running through the groove. * Changes the direction of the input force. ...