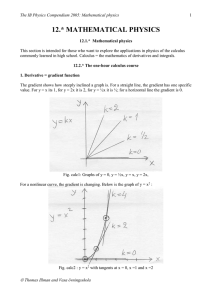
Word document
... 1. Find the work done by a force in moving an object through a displacement. 2. Know that power is the rate at which work is done (or the rate at which energy is delivered or used). Find the power delivered or used in moving an object through some displacement in some time. 3. Find the kinetic energ ...
... 1. Find the work done by a force in moving an object through a displacement. 2. Know that power is the rate at which work is done (or the rate at which energy is delivered or used). Find the power delivered or used in moving an object through some displacement in some time. 3. Find the kinetic energ ...
Work - India Study Channel
... When the Block is released the spring pushes it towards right. The velocity of the block increases till the spring acquires its natural length. There after the block loses contact with the spring and moves with constant velocity. Initially the compression in the spring ...
... When the Block is released the spring pushes it towards right. The velocity of the block increases till the spring acquires its natural length. There after the block loses contact with the spring and moves with constant velocity. Initially the compression in the spring ...
Chapter 3
... designed to limit the extreme front to back and side-to-side movement of the head and neck during a violent crash. Using a collar and yoke system made of carbon fiber and Kevlar, the device is connected to the helmet with a series of quick connect tethers. The HANS® Device is worn around the neck an ...
... designed to limit the extreme front to back and side-to-side movement of the head and neck during a violent crash. Using a collar and yoke system made of carbon fiber and Kevlar, the device is connected to the helmet with a series of quick connect tethers. The HANS® Device is worn around the neck an ...
Motion & Newton`s Laws
... • Ex. In the 100m dash the fastest runner finished in 10s. S= 100m/10s= 10m/s • 3 Types of Speed • Average speed is found by dividing the total distance by the total time taken to reach that distance • Speeds can vary from instant to instant • Ex. Walking in a crowded hallway ...
... • Ex. In the 100m dash the fastest runner finished in 10s. S= 100m/10s= 10m/s • 3 Types of Speed • Average speed is found by dividing the total distance by the total time taken to reach that distance • Speeds can vary from instant to instant • Ex. Walking in a crowded hallway ...
Chapter 10.3-10.5
... • What does Newton’s 1st Law of motion state? – An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • Why is Newton’s 1st law of motion sometimes called the law of intertia? – Inertia is a measure of an object’s tendency to r ...
... • What does Newton’s 1st Law of motion state? – An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • Why is Newton’s 1st law of motion sometimes called the law of intertia? – Inertia is a measure of an object’s tendency to r ...
Rotational Dynamics
... depends on the mass of the rotating object and upon the distribution of its mass with respect to the axis of rotation. • If the mass remains fixed in position, torque and angular acceleration are directly proportional. • If the mass is closer to the axis of rotation, the acceleration produced by the ...
... depends on the mass of the rotating object and upon the distribution of its mass with respect to the axis of rotation. • If the mass remains fixed in position, torque and angular acceleration are directly proportional. • If the mass is closer to the axis of rotation, the acceleration produced by the ...
force and motion study guide
... 21. Describe action force=the initial force on an object reaction force = the force back on the first object…it is always EQUAL AND OPPOSITE the action force 22. Define motion= change in distance over time relative to a reference point 23. Define reference point: (page 118)=the point used for compar ...
... 21. Describe action force=the initial force on an object reaction force = the force back on the first object…it is always EQUAL AND OPPOSITE the action force 22. Define motion= change in distance over time relative to a reference point 23. Define reference point: (page 118)=the point used for compar ...
Powerpoint
... Draw a system schema: • Draw a diagram where you write down the name of each object in the system and then draw a solid circle drawn around it. • Draw two sided arrows like this between the object circles of objects that interact (This illustrates all interactions between the objects in this diagram ...
... Draw a system schema: • Draw a diagram where you write down the name of each object in the system and then draw a solid circle drawn around it. • Draw two sided arrows like this between the object circles of objects that interact (This illustrates all interactions between the objects in this diagram ...
Monday, Oct. 6, 2003
... 1. All planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focal point. 2. The radius vector drawn from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal area in equal time intervals. (Angular momentum conservation) 3. The square of the orbital period of any planet is proportional to the cube of the semi-major ...
... 1. All planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focal point. 2. The radius vector drawn from the Sun to a planet sweeps out equal area in equal time intervals. (Angular momentum conservation) 3. The square of the orbital period of any planet is proportional to the cube of the semi-major ...
Document
... Measuring forces - Forces are often measured by determining the elongation of a calibrated spring. - Forces are vectors!! Remember vector addition. - To calculate net force on an object you must use vector addition. ...
... Measuring forces - Forces are often measured by determining the elongation of a calibrated spring. - Forces are vectors!! Remember vector addition. - To calculate net force on an object you must use vector addition. ...
Chapter 1 Matter in Motion
... (distance/time). Interpret a line graph representing an object’s motion in terms of distance over time (speed) using metric units. Explain every object exerts a gravitational force of attraction on every other object. Recognize an object’s weight is a measure of the gravitational force of a planet/m ...
... (distance/time). Interpret a line graph representing an object’s motion in terms of distance over time (speed) using metric units. Explain every object exerts a gravitational force of attraction on every other object. Recognize an object’s weight is a measure of the gravitational force of a planet/m ...
Instructor`s Guide
... Suggestions for Instructors 1. The most fundamental and obvious phenomenon we observe around us is motion. Blowing air, waves in the ocean, flying birds, falling leaves—all of these are examples of motion. Practically all imaginable processes can be traced back to the motion of certain particles or ...
... Suggestions for Instructors 1. The most fundamental and obvious phenomenon we observe around us is motion. Blowing air, waves in the ocean, flying birds, falling leaves—all of these are examples of motion. Practically all imaginable processes can be traced back to the motion of certain particles or ...
____The Force Table
... A vector quantity is one that has direction as well as amount or magnitude. Take force as an example. To be properly described, the direction of a force, as well as its magnitude, must be given. The same is true for velocity also. An object may be acted upon several forces at one time, each varying ...
... A vector quantity is one that has direction as well as amount or magnitude. Take force as an example. To be properly described, the direction of a force, as well as its magnitude, must be given. The same is true for velocity also. An object may be acted upon several forces at one time, each varying ...
Only external forces affect the motion of the center of mass
... A small car weighing m1 is traveling due north when it collides with a pick-up truck weighting m2 which was traveling due east. After the collision the two vehicles move off together at an angle θ north of east. The driver of the car claimed that the truck driver was at fault because he was exceedin ...
... A small car weighing m1 is traveling due north when it collides with a pick-up truck weighting m2 which was traveling due east. After the collision the two vehicles move off together at an angle θ north of east. The driver of the car claimed that the truck driver was at fault because he was exceedin ...
Newton`s Laws & Momentum
... To explain Newton's first law, we can use the example of the X and brakes in a car. For the car to move from rest, a force has to be applied to the X similarly, for the car to stop a force has to be applied to the brakes. In Newton’s second law, we see that multiplying the acceleration and mass of a ...
... To explain Newton's first law, we can use the example of the X and brakes in a car. For the car to move from rest, a force has to be applied to the X similarly, for the car to stop a force has to be applied to the brakes. In Newton’s second law, we see that multiplying the acceleration and mass of a ...
act04
... forces between the same two objects, but which object is exerting the force and which is being acted on are exchanged. (For the purposes of this activity, consider the tension at either end of the string to be the equivalent of a Newton’s Third Law pair although strictly speaking it does not fit the ...
... forces between the same two objects, but which object is exerting the force and which is being acted on are exchanged. (For the purposes of this activity, consider the tension at either end of the string to be the equivalent of a Newton’s Third Law pair although strictly speaking it does not fit the ...