Kreutter/Costello: Linear Dynamics 6 Newton`s Second Law
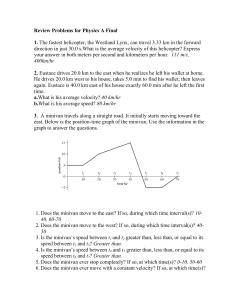
... Imagine that after student A has moved for a while, as shown on the graph above, student B starts pulling student A in the directions opposite to A’s motion. Eventually, student A comes to a stop. ...
... Imagine that after student A has moved for a while, as shown on the graph above, student B starts pulling student A in the directions opposite to A’s motion. Eventually, student A comes to a stop. ...
Force due to gravity: A field force (a vector quantity) that always is
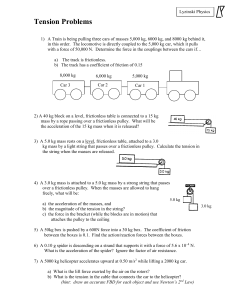
... between the boxes is 0.1. Find the action/reaction forces between the boxes. 6) A 0.10 g spider is descending on a strand that supports it with a force of 5.6 x 10–4 N. What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignore the factor of air resistance. 7) A 5000 kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.50 m/s ...
... between the boxes is 0.1. Find the action/reaction forces between the boxes. 6) A 0.10 g spider is descending on a strand that supports it with a force of 5.6 x 10–4 N. What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignore the factor of air resistance. 7) A 5000 kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.50 m/s ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... 1. Misconception - A force is needed to continue the objects motion An object can fly through space with a constant velocity as long as no external forces act on it (unbalanced force). 2. Misconception – There are no forces in spaces A spaceship can be accelerated if acted upon an external force (ex ...
... 1. Misconception - A force is needed to continue the objects motion An object can fly through space with a constant velocity as long as no external forces act on it (unbalanced force). 2. Misconception – There are no forces in spaces A spaceship can be accelerated if acted upon an external force (ex ...
Newton`s Laws
... being prosecuted. On the day of his death, the first copy was delivered to him. ...
... being prosecuted. On the day of his death, the first copy was delivered to him. ...
Physics Pre-AP/AP Power Standards
... Define electric current as the rate of flow of charge. Define resistance and resistivity Draw schematic diagrams of circuits, including measuring devices such as ammeters and voltmeters and also resistors and switches. State and apply Ohm’s law in problem solutions. Derive the equations for electric ...
... Define electric current as the rate of flow of charge. Define resistance and resistivity Draw schematic diagrams of circuits, including measuring devices such as ammeters and voltmeters and also resistors and switches. State and apply Ohm’s law in problem solutions. Derive the equations for electric ...
Physics Pre-AP/AP Power Standards
... Define electric current as the rate of flow of charge. Define resistance and resistivity Draw schematic diagrams of circuits, including measuring devices such as ammeters and voltmeters and also resistors and switches. State and apply Ohm’s law in problem solutions. Derive the equations for electric ...
... Define electric current as the rate of flow of charge. Define resistance and resistivity Draw schematic diagrams of circuits, including measuring devices such as ammeters and voltmeters and also resistors and switches. State and apply Ohm’s law in problem solutions. Derive the equations for electric ...
Chapter 8 Summary
... • The moment of inertia, I, plays the same role that mass did in translational motion • For a ball and massless hinged rod, I = m r2 ...
... • The moment of inertia, I, plays the same role that mass did in translational motion • For a ball and massless hinged rod, I = m r2 ...