Wednesday, Feb. 16, 2011
... Aristotle (384-322BC): The natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs larger forces. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of re ...
... Aristotle (384-322BC): The natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs larger forces. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of re ...
Newton`s Second Law Notes - Mrs. Romito Teaches Science
... Have All of the Necessary Variables 6. Write down the equation(s) you need to solve for the missing variables in your final equation. 7. Convert your units and solve for the missing variables. 8. Plug in those missing variables in your final equation and solve (remember to check your units!!!) ...
... Have All of the Necessary Variables 6. Write down the equation(s) you need to solve for the missing variables in your final equation. 7. Convert your units and solve for the missing variables. 8. Plug in those missing variables in your final equation and solve (remember to check your units!!!) ...
California Physics Standard 1a Send comments to: layton@physics
... After establishing the ratio of the masses of the two objects you plan to drop (27 in the case above) discuss with your students if they think the larger object will fall “27” times faster than the smaller object. They probably will disagree but this was one of the arguments Galileo suggests in his ...
... After establishing the ratio of the masses of the two objects you plan to drop (27 in the case above) discuss with your students if they think the larger object will fall “27” times faster than the smaller object. They probably will disagree but this was one of the arguments Galileo suggests in his ...
Newtons Laws and Its Application
... Broken Atwood’s machine Example4: Two masses connected by a rope and a pulley (Atwood’s machine). The connection part of m2 is broken and m2 is moving with constant acceleration a0 relative to the rope. What are the accelerations of m1 and m2 relative to the ground? (Ignoring the mass of rope and p ...
... Broken Atwood’s machine Example4: Two masses connected by a rope and a pulley (Atwood’s machine). The connection part of m2 is broken and m2 is moving with constant acceleration a0 relative to the rope. What are the accelerations of m1 and m2 relative to the ground? (Ignoring the mass of rope and p ...
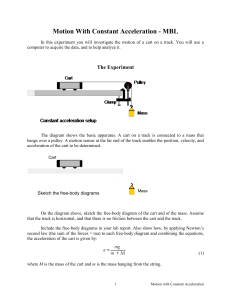
Motion With Constant Acceleration
... QUESTION 3. Compare your experimentally determined values of the acceleration to the theoretical values. Is there good agreement? Do you notice any systematic differences? (e.g., are the experimental values always greater than the theoretical values?) QUESTION 4. You corrected for the effects of fri ...
... QUESTION 3. Compare your experimentally determined values of the acceleration to the theoretical values. Is there good agreement? Do you notice any systematic differences? (e.g., are the experimental values always greater than the theoretical values?) QUESTION 4. You corrected for the effects of fri ...
Lect15
... within this flow field! Rather, when circulation exist it simply means that line integral is finite. For example, if airfoil below is generating lift the circulation taken around a closed curve enclosing the airfoil will be finite, although the fluid elements are by no means executing circles around ...
... within this flow field! Rather, when circulation exist it simply means that line integral is finite. For example, if airfoil below is generating lift the circulation taken around a closed curve enclosing the airfoil will be finite, although the fluid elements are by no means executing circles around ...
AP Rotational Motion 9_05 rev
... Most of our discussion will concerned with rigid bodies— objects with definite shapes that don’t change Purely rotational motion: all points in a body move in circle r O ...
... Most of our discussion will concerned with rigid bodies— objects with definite shapes that don’t change Purely rotational motion: all points in a body move in circle r O ...
CNFM packet NEW
... a. Draw a force vector map for the rocket. b. How long must the engine burn in order to reach this speed? 24. A tennis player returns a 30. m/s serve straight back at 25. m/s, after making contact with the ball for 0.50 s. If the ball has a mass of 0.20 kg, what is the force she exerted on the ball? ...
... a. Draw a force vector map for the rocket. b. How long must the engine burn in order to reach this speed? 24. A tennis player returns a 30. m/s serve straight back at 25. m/s, after making contact with the ball for 0.50 s. If the ball has a mass of 0.20 kg, what is the force she exerted on the ball? ...
Lecture Notes on Classical Mechanics for Physics 106ab – Errata
... The constraint defining rigid-body motion, |~ra − ~rb | = cab for all particles a, b in the body, is similar in form: an allowed virtual displacement keeps the length of the vector separation of the two particles fixed but allows its orientation to change, while the force that maintains the constrai ...
... The constraint defining rigid-body motion, |~ra − ~rb | = cab for all particles a, b in the body, is similar in form: an allowed virtual displacement keeps the length of the vector separation of the two particles fixed but allows its orientation to change, while the force that maintains the constrai ...
conservation of momentum in two dimensions
... In Newton’s time it was known that momentum of objects was conserved in collisions. Momentum is defined as: ...
... In Newton’s time it was known that momentum of objects was conserved in collisions. Momentum is defined as: ...