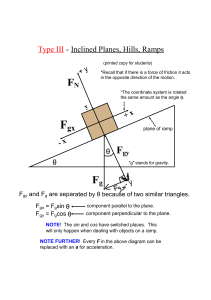
Type III Inclined Planes, Hills, Ramps
... constant velocity by exerting a force of 211 N parallel to the inclined plane. a) What is the sum of your applied force, friction and the parallel component of the trunk's weight? Justify your ...
... constant velocity by exerting a force of 211 N parallel to the inclined plane. a) What is the sum of your applied force, friction and the parallel component of the trunk's weight? Justify your ...
04_Lecture_Outline
... body acted on by zero net force moves with constant velocity and zero acceleration.” ...
... body acted on by zero net force moves with constant velocity and zero acceleration.” ...
Lecture Outline
... body acted on by zero net force moves with constant velocity and zero acceleration.” ...
... body acted on by zero net force moves with constant velocity and zero acceleration.” ...
The Laws of Motion - St. Joseph Hill Academy
... will not change if balanced forces act on it. The tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion is called inertia (ihn UR shuh). Inertia explains the motion of a crash-test dummy. Before a crash, the car and the dummy move with constant velocity. If no other force acts on them, the car and ...
... will not change if balanced forces act on it. The tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion is called inertia (ihn UR shuh). Inertia explains the motion of a crash-test dummy. Before a crash, the car and the dummy move with constant velocity. If no other force acts on them, the car and ...
MiSP Force and Gravity Teacher`s Guide
... This unit uses BASE jumping and skydiving to illustrate Newton’s three laws of motion and to explore the concept of gravity. The activities are either taken directly from or are modified from ideas in “Gravity Rules” AIMS Educational Foundation, 1998. Gravity is used as an example of a force. The st ...
... This unit uses BASE jumping and skydiving to illustrate Newton’s three laws of motion and to explore the concept of gravity. The activities are either taken directly from or are modified from ideas in “Gravity Rules” AIMS Educational Foundation, 1998. Gravity is used as an example of a force. The st ...
L9.ppt - University of Iowa Physics
... • When the block is moving it experiences a smaller friction force called the kinetic friction force • It is a common experience that it takes more force to get something moving than to keep it moving. ...
... • When the block is moving it experiences a smaller friction force called the kinetic friction force • It is a common experience that it takes more force to get something moving than to keep it moving. ...
horizontal motion with resistance
... Model (1) for linear resistance is often applicable when the object is moving with low speeds. In the motion through a fluid, the resistive force FR v is often called the viscous drag and it arises from the cohesive forces between the layers of the fluid. The S.I. units for the constant are ...
... Model (1) for linear resistance is often applicable when the object is moving with low speeds. In the motion through a fluid, the resistive force FR v is often called the viscous drag and it arises from the cohesive forces between the layers of the fluid. The S.I. units for the constant are ...
Physics 2A Chapter 5 HW Solutions
... P5.3. Prepare: We assume the speaker is a particle in static equilibrium under the influence of three forces: gravity and the tensions in the two cables. So, all the forces acting on it must cancel to give a zero net force. The forces acting on the speaker are shown on a free-body diagram below. Bec ...
... P5.3. Prepare: We assume the speaker is a particle in static equilibrium under the influence of three forces: gravity and the tensions in the two cables. So, all the forces acting on it must cancel to give a zero net force. The forces acting on the speaker are shown on a free-body diagram below. Bec ...
First Law of Motion - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... that composes the person). A reduction in mass leads to a reduction in weight. It is possible to change weight (only) if the person moves further from the Earth’s surface or to another place (such as the moon). ...
... that composes the person). A reduction in mass leads to a reduction in weight. It is possible to change weight (only) if the person moves further from the Earth’s surface or to another place (such as the moon). ...
2004_11_03ImpulseMomentum
... Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
... Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
Review - bYTEBoss
... 1. Forces of 4 N and 6 N act on the object. What is the minimum value for the sum of these two forces? 2. Two ropes are being used to pull a car out of a ditch. Each rope exerts a force of 700 N on the car. Is it possible for the sum of these two forces to have a magnitude of 1000N? Explain your rea ...
... 1. Forces of 4 N and 6 N act on the object. What is the minimum value for the sum of these two forces? 2. Two ropes are being used to pull a car out of a ditch. Each rope exerts a force of 700 N on the car. Is it possible for the sum of these two forces to have a magnitude of 1000N? Explain your rea ...
The meaning of inertia Inertia is the property of an object which
... Inertia is the reluctance of an object to move once it is at rest or the reluctance of an object to stop once it is in uniform velocity. ...
... Inertia is the reluctance of an object to move once it is at rest or the reluctance of an object to stop once it is in uniform velocity. ...
Homework Answers pg 98-101
... For Matt and the truck to move forward from rest, both of them must experience a positive horizontal acceleration. The horizontal forces acting on Matt are the friction force of the ground pushing him forward and the truck pulling him backward. The ground must push Matt forward with a stronger force ...
... For Matt and the truck to move forward from rest, both of them must experience a positive horizontal acceleration. The horizontal forces acting on Matt are the friction force of the ground pushing him forward and the truck pulling him backward. The ground must push Matt forward with a stronger force ...
Buoyancy
In science, buoyancy (pronunciation: /ˈbɔɪ.ənᵗsi/ or /ˈbuːjənᵗsi/; also known as upthrust) is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. This pressure difference results in a net upwards force on the object. The magnitude of that force exerted is proportional to that pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid.For this reason, an object whose density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is either less dense than the liquid or is shaped appropriately (as in a boat), the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a reference frame which either has a gravitational field or is accelerating due to a force other than gravity defining a ""downward"" direction (that is, a non-inertial reference frame). In a situation of fluid statics, the net upward buoyancy force is equal to the magnitude of the weight of fluid displaced by the body.The center of buoyancy of an object is the centroid of the displaced volume of fluid.























