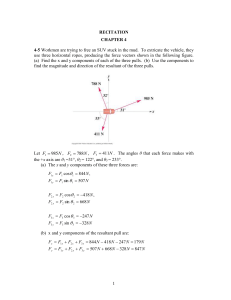
Recitation Ch 4-1
... fA and f A' are the friction forces between the crates and nA and n A' are the normal forces the crates exert on each other. ...
... fA and f A' are the friction forces between the crates and nA and n A' are the normal forces the crates exert on each other. ...
Motion
... the same position as its center of gravity. The center of gravity of an object is the point through which the Earth’s gravitational force acts on the object. ...
... the same position as its center of gravity. The center of gravity of an object is the point through which the Earth’s gravitational force acts on the object. ...
Which of the following lists of elements contains an alkaline earth
... 2. Water at the top of Niagara Falls can be said to have energy that can be used to do work as it “falls”. This is an example of a. b. c. d. ...
... 2. Water at the top of Niagara Falls can be said to have energy that can be used to do work as it “falls”. This is an example of a. b. c. d. ...
Forces and Newton`s Laws
... Summarize the relationship between a moving object’s mass, its inertia, and the forces acting on it. Accept all reasonable responses. The greater the object’s mass, the more inertia it has, and the larger the net force needed to change the object’s velocity. A moving object will tend to keep moving ...
... Summarize the relationship between a moving object’s mass, its inertia, and the forces acting on it. Accept all reasonable responses. The greater the object’s mass, the more inertia it has, and the larger the net force needed to change the object’s velocity. A moving object will tend to keep moving ...
Chapter 4 – Newton`s Laws of Motion
... the greatest scientists of all time and his work provides the foundation of classical mechanics. In addition to the laws of motion, Newton also discovered the law of universal gravitation, which applies to planetary and satellite. He also invented calculus. Newton’s laws of motion are 1. A body at r ...
... the greatest scientists of all time and his work provides the foundation of classical mechanics. In addition to the laws of motion, Newton also discovered the law of universal gravitation, which applies to planetary and satellite. He also invented calculus. Newton’s laws of motion are 1. A body at r ...
Document
... d. The sofa moves up at constant velocity, FNET = 0 FNET = Fapp – Ff – mgsin , Fapp = Ff + mgsin = 0.9 (60 kg x 9.8 m/s2 cos 250) + 60 kg x 9.8 m/s2 sin 250) = 479.6 + 248.5 = 728 N 6. Newton’s 3rd Law is for every force there is an equal in magnitude and opposite in direction reaction force. Th ...
... d. The sofa moves up at constant velocity, FNET = 0 FNET = Fapp – Ff – mgsin , Fapp = Ff + mgsin = 0.9 (60 kg x 9.8 m/s2 cos 250) + 60 kg x 9.8 m/s2 sin 250) = 479.6 + 248.5 = 728 N 6. Newton’s 3rd Law is for every force there is an equal in magnitude and opposite in direction reaction force. Th ...
Ch. 4 Motion and Forces
... 5. Complete the flowchart below, which describes how a squid moves through water. ...
... 5. Complete the flowchart below, which describes how a squid moves through water. ...
Forces and motion are one of the most important things in our lives
... Another important thing to us, is motion. Motion is to do with the changing of location and position with an object. The two main things about motion is velocity and acceleration. Acceleration is how quickly things speed up. Velocity is the speed of an object in one direction. If the direction of a ...
... Another important thing to us, is motion. Motion is to do with the changing of location and position with an object. The two main things about motion is velocity and acceleration. Acceleration is how quickly things speed up. Velocity is the speed of an object in one direction. If the direction of a ...
CTNewtonLaws
... During the impact, the truck exerts a force Ftruck on the car and the car exerts a force Fcar on the truck. Which of the following statements about these forces is true) A) The force exerted by the truck on the car is the same size as the force exerted by the car on the truck) Ftruck = Fcar B) Ftruc ...
... During the impact, the truck exerts a force Ftruck on the car and the car exerts a force Fcar on the truck. Which of the following statements about these forces is true) A) The force exerted by the truck on the car is the same size as the force exerted by the car on the truck) Ftruck = Fcar B) Ftruc ...
Lecture 4
... Law 1: An object subject to no external forces is at rest or moves with a constant velocity if viewed from an inertial reference frame. Law 2: For any object, FNET = F = ma Law 3: Forces occur in pairs: FA-B = - FB-A (For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.) ...
... Law 1: An object subject to no external forces is at rest or moves with a constant velocity if viewed from an inertial reference frame. Law 2: For any object, FNET = F = ma Law 3: Forces occur in pairs: FA-B = - FB-A (For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.) ...
Chapter-05
... certain instant of time has a downward acceleration. Which force is larger in magnitude? 1. The force on the gymnast by the rings (together). 2. The gravitational force on the gymnast by Earth (i.e. the weight of the gymnast). 3. Neither, these forces are equal. ...
... certain instant of time has a downward acceleration. Which force is larger in magnitude? 1. The force on the gymnast by the rings (together). 2. The gravitational force on the gymnast by Earth (i.e. the weight of the gymnast). 3. Neither, these forces are equal. ...
Newtons Laws
... one of the following statements concerning the net force acting on the rock at the top of its path is true? 1) It is equal to the weight of the rock. 2) It is instantaneously equal to zero newtons. 3) Its direction changes from up to down. 4) It is greater than the weight of the rock. 5) It is less ...
... one of the following statements concerning the net force acting on the rock at the top of its path is true? 1) It is equal to the weight of the rock. 2) It is instantaneously equal to zero newtons. 3) Its direction changes from up to down. 4) It is greater than the weight of the rock. 5) It is less ...
force-problems-with-acceleration-2-step
... second ball rolled with the same force accelerates 4 m/sec2. What are the masses of the two balls? ...
... second ball rolled with the same force accelerates 4 m/sec2. What are the masses of the two balls? ...
Chapter 1 - Lemon Bay High School
... ____________________________ is the fluid friction acting on an object moving through the air. ...
... ____________________________ is the fluid friction acting on an object moving through the air. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - Madison County Schools
... water reacts by pushing the fish forward, moving the fish through the water. The size of the force on the water equals the size of the force on the fish; the direction of the force on the water (backwards) is opposite the direction of the force on the fish (forwards). ...
... water reacts by pushing the fish forward, moving the fish through the water. The size of the force on the water equals the size of the force on the fish; the direction of the force on the water (backwards) is opposite the direction of the force on the fish (forwards). ...
Describing Motion - Science
... What about the ladder on top of the truck? The ladder is in motion because the truck is in motion. When the truck stops, the ladder stays in motion. The truck is stopped by the force of the car, but the ladder is not. What force stops the ladder? ...
... What about the ladder on top of the truck? The ladder is in motion because the truck is in motion. When the truck stops, the ladder stays in motion. The truck is stopped by the force of the car, but the ladder is not. What force stops the ladder? ...
Buoyancy
In science, buoyancy (pronunciation: /ˈbɔɪ.ənᵗsi/ or /ˈbuːjənᵗsi/; also known as upthrust) is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. This pressure difference results in a net upwards force on the object. The magnitude of that force exerted is proportional to that pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid.For this reason, an object whose density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is either less dense than the liquid or is shaped appropriately (as in a boat), the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a reference frame which either has a gravitational field or is accelerating due to a force other than gravity defining a ""downward"" direction (that is, a non-inertial reference frame). In a situation of fluid statics, the net upward buoyancy force is equal to the magnitude of the weight of fluid displaced by the body.The center of buoyancy of an object is the centroid of the displaced volume of fluid.