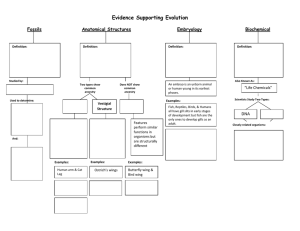
Evolution
... Mollusca, Cnidaria, Arthropoda, Porifera, Chordata, Echinodermata o Annelida – segmented worms o Nematoda – round worms o Platyhelminthes flat worms o Mollusca – soft-bodied; squid, octopus o Cnidaria – stinging cells; radial symmetry, jelly fish o Arthropoda – jointed-legs, exoskeleton; bee, spider ...
... Mollusca, Cnidaria, Arthropoda, Porifera, Chordata, Echinodermata o Annelida – segmented worms o Nematoda – round worms o Platyhelminthes flat worms o Mollusca – soft-bodied; squid, octopus o Cnidaria – stinging cells; radial symmetry, jelly fish o Arthropoda – jointed-legs, exoskeleton; bee, spider ...
Ecology is the study of the interactions between
... and temperature that affect organisms living in a particular area. Organization in the environment: The environment is arranged into different levels. Level 1- Organism – contains the individual organism. Level 2 – Population – contains similar organisms, which form a population. A population is a g ...
... and temperature that affect organisms living in a particular area. Organization in the environment: The environment is arranged into different levels. Level 1- Organism – contains the individual organism. Level 2 – Population – contains similar organisms, which form a population. A population is a g ...
1) the study of how organisms interact with their environment. It
... Whereas nonliving factors such as air, sunlight, and land are known as 20)___________________. The total number of organisms that an ecosystem is capable of supporting is its 21)____________________. When organisms live together in ecosystems, they interact. 22)____________________ occurs when organ ...
... Whereas nonliving factors such as air, sunlight, and land are known as 20)___________________. The total number of organisms that an ecosystem is capable of supporting is its 21)____________________. When organisms live together in ecosystems, they interact. 22)____________________ occurs when organ ...
Organism
... ◦ One organism (parasite) derives nourishment by living in or on another organism (host) ...
... ◦ One organism (parasite) derives nourishment by living in or on another organism (host) ...
Community Relationships
... It can go to the bathroom and fertilize the ground. It can die and its body will go back to the earth. ...
... It can go to the bathroom and fertilize the ground. It can die and its body will go back to the earth. ...
Review Presentation
... organisms as you move up the food chain? If there is less energy passed on to each level, then there is not enough energy to support a lot of organisms at the higher levels. ...
... organisms as you move up the food chain? If there is less energy passed on to each level, then there is not enough energy to support a lot of organisms at the higher levels. ...
Interactions Chapter 4
... • No two species can occupy the same niche. If they do, competition between the two will be intense and one species will outcompete the other • This can lead to: ...
... • No two species can occupy the same niche. If they do, competition between the two will be intense and one species will outcompete the other • This can lead to: ...
Visual Study Guide: Ch 13
... when the body must rely on homeostasis. • What are signals the body gives you when you have not maintained homeostasis? ...
... when the body must rely on homeostasis. • What are signals the body gives you when you have not maintained homeostasis? ...
Animal Science - Van Buren Public Schools
... Groups of cells form tissues. A tissue is a cluster of cells that are alike in structure and activity. An organ is a group of tissues with a similar function. An organ system is a group of organs working together to carry out a specific activity. ...
... Groups of cells form tissues. A tissue is a cluster of cells that are alike in structure and activity. An organ is a group of tissues with a similar function. An organ system is a group of organs working together to carry out a specific activity. ...
Intro Notes
... a. Early students of A&P were concerned with treating illnesses and injuries or preparing for death. b. 460 BC Hippocrates – Father of Medicine - 1st school of medicine c. 131 AD Galen – Started physiology study d. Catholic Church became powerful and discouraged further work. e. 1514 AD Andreas Vesa ...
... a. Early students of A&P were concerned with treating illnesses and injuries or preparing for death. b. 460 BC Hippocrates – Father of Medicine - 1st school of medicine c. 131 AD Galen – Started physiology study d. Catholic Church became powerful and discouraged further work. e. 1514 AD Andreas Vesa ...
Communities and Ecosystems
... Symbiosis - Close, physical relationship between two different species. At least one species derives benefit from the interaction. – Parasitism - One organism (parasite) lives in or on another organism (host), from which it derives nourishment. Ectoparasites - Live on host’s surface. ¾ Fleas End ...
... Symbiosis - Close, physical relationship between two different species. At least one species derives benefit from the interaction. – Parasitism - One organism (parasite) lives in or on another organism (host), from which it derives nourishment. Ectoparasites - Live on host’s surface. ¾ Fleas End ...
Movement of Chemicals in Plants and Animals
... bigger in size and so their total surface area to volume ratio is smaller. Cells near the centre of these organisms would be way to far away from the surface for substances from the outside environment to reach them efficiently by diffusion and osmosis. thesun.co.uk ...
... bigger in size and so their total surface area to volume ratio is smaller. Cells near the centre of these organisms would be way to far away from the surface for substances from the outside environment to reach them efficiently by diffusion and osmosis. thesun.co.uk ...
2.4 Movement of Chemicals in Plants and Animals
... bigger in size and so their total surface area to volume ratio is smaller. Cells near the centre of these organisms would be way to far away from the surface for substances from the outside environment to reach them efficiently by diffusion and osmosis. thesun.co.uk ...
... bigger in size and so their total surface area to volume ratio is smaller. Cells near the centre of these organisms would be way to far away from the surface for substances from the outside environment to reach them efficiently by diffusion and osmosis. thesun.co.uk ...
Adaptation Review - burns
... shelter to reproduce and grow. There is a limited amount of these resources (limiting factors?), and the most/best quality resources go to the organism that can edge out the competition. However, Mother Nature attempts to break up the fight: Niches reduce competition. By specializing how you obtain ...
... shelter to reproduce and grow. There is a limited amount of these resources (limiting factors?), and the most/best quality resources go to the organism that can edge out the competition. However, Mother Nature attempts to break up the fight: Niches reduce competition. By specializing how you obtain ...
Ecology Terms
... Community: a group of interacting populations of different species living in the same area. Competition: the struggle between organisms to obtain a sufficient supply of a resource of limited quantity. Conservation: is the protection and wise management of the environment Benefits include: existing e ...
... Community: a group of interacting populations of different species living in the same area. Competition: the struggle between organisms to obtain a sufficient supply of a resource of limited quantity. Conservation: is the protection and wise management of the environment Benefits include: existing e ...
Ecology Dictionary
... Community: a group of interacting populations of different species living in the same area. Competition: the struggle between organisms to obtain a sufficient supply of a resource of limited quantity. Conservation: is the protection and wise management of the environment Benefits include: existing e ...
... Community: a group of interacting populations of different species living in the same area. Competition: the struggle between organisms to obtain a sufficient supply of a resource of limited quantity. Conservation: is the protection and wise management of the environment Benefits include: existing e ...
Unit 8: Biodiversity Content Outline: Animal Characteristics (8.7
... Endoderm (Makes the digestive organs/tract, liver, and lungs.) 2. Dorsal (Back/top), ventral (front/bottom), anterior (toward the head), posterior (toward the tail) 3. Cephalization (the accumulation of senses in the head region of an animal.) C. Acoelomates - These are “without a cavity” animals. ( ...
... Endoderm (Makes the digestive organs/tract, liver, and lungs.) 2. Dorsal (Back/top), ventral (front/bottom), anterior (toward the head), posterior (toward the tail) 3. Cephalization (the accumulation of senses in the head region of an animal.) C. Acoelomates - These are “without a cavity” animals. ( ...
Nervous System
... Be able to distinguish between unicellular and multi cellular organism Unicellular Organisms ...
... Be able to distinguish between unicellular and multi cellular organism Unicellular Organisms ...
Environmental Systems Test Review Texas Ecoregions Fill in the
... 12. Compare & contrast biotic & abiotic factors within an ecosystem. Biotic – living or once living – dead tree, scat, animals, plants Abiotic – nonliving – soil type, rocks, temp, precip Population Dynamics 1. What is a population? What do all members of a population have in common? A group of the ...
... 12. Compare & contrast biotic & abiotic factors within an ecosystem. Biotic – living or once living – dead tree, scat, animals, plants Abiotic – nonliving – soil type, rocks, temp, precip Population Dynamics 1. What is a population? What do all members of a population have in common? A group of the ...
Organisms and Their Environment
... Levels of Organization • A biome is a large group of ecosystems that share the same climate and have similar types of communities. • All of the biomes on Earth combine to form the highest level of organization – the ...
... Levels of Organization • A biome is a large group of ecosystems that share the same climate and have similar types of communities. • All of the biomes on Earth combine to form the highest level of organization – the ...