ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND PERIODICITY
... certain allowed circular orbits for the electron. (2) As the electron becomes more tightly bound, its energy becomes more negative relative to the zero-energy reference state (corresponding to the electron being at an infinite distance from the nucleus). As the electron is brought closer to the nucl ...
... certain allowed circular orbits for the electron. (2) As the electron becomes more tightly bound, its energy becomes more negative relative to the zero-energy reference state (corresponding to the electron being at an infinite distance from the nucleus). As the electron is brought closer to the nucl ...
SUMMARY Phys 2113 (General Physics I) Compiled by Prof
... = rF sin φ; r sin φ = ` = moment or lever arm τ = r × F = lim ∆t → 0 ∆t Torque should not be confused with force. Forces can cause a change in linear motion, as described by Newton’s second law. Forces can also cause a change in rotational motion, but the effectiveness of the forces in causing this ...
... = rF sin φ; r sin φ = ` = moment or lever arm τ = r × F = lim ∆t → 0 ∆t Torque should not be confused with force. Forces can cause a change in linear motion, as described by Newton’s second law. Forces can also cause a change in rotational motion, but the effectiveness of the forces in causing this ...
Oscillations
... A block of mass 1.5 kg is attached to the end of a vertical spring of force constant k=300 N/m. After the block comes to rest, it is pulled down a distance of 2.0 cm and released. (a) What is the frequency of the resulting oscillations? (b) What are the maximum and minimum amounts of stretch of the ...
... A block of mass 1.5 kg is attached to the end of a vertical spring of force constant k=300 N/m. After the block comes to rest, it is pulled down a distance of 2.0 cm and released. (a) What is the frequency of the resulting oscillations? (b) What are the maximum and minimum amounts of stretch of the ...
Atomic Structure and Bonding: A Review
... are filled first). Note that the energy level of a 4s orbital is lower than that of the 3d one, which means that 4s will fill with electrons before 3d. Overall, two main rules are followed for determining the electronic configuration of an atom. These are known as Pauli’s exclusion principle, and th ...
... are filled first). Note that the energy level of a 4s orbital is lower than that of the 3d one, which means that 4s will fill with electrons before 3d. Overall, two main rules are followed for determining the electronic configuration of an atom. These are known as Pauli’s exclusion principle, and th ...
Momentum - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... net force acts on an object, its velocity is constant. Its mass will not change. Therefore, in this situation, momentum is constant. Momentum is conserved. Newton's second law describes how the velocity of a body changes if a net force acts on it. ...
... net force acts on an object, its velocity is constant. Its mass will not change. Therefore, in this situation, momentum is constant. Momentum is conserved. Newton's second law describes how the velocity of a body changes if a net force acts on it. ...
Chap. 14
... • In the current chapter, you will study the motion of systems of particles. • The effective force of a particle is defined as the product of it mass and acceleration. It will be shown that the system of external forces acting on a system of particles is equipollent with the system of effective forc ...
... • In the current chapter, you will study the motion of systems of particles. • The effective force of a particle is defined as the product of it mass and acceleration. It will be shown that the system of external forces acting on a system of particles is equipollent with the system of effective forc ...
On the physical structure of radiant energy: waves and
... In all our considerations on the propagation of radiant energy the concept of ether, like transmissive medium, never appears because whether in the wave theory of electromagnetic field or in the corpuscular theory of light the ether isn’ t necessary to explain phenomena of propagation and diffractio ...
... In all our considerations on the propagation of radiant energy the concept of ether, like transmissive medium, never appears because whether in the wave theory of electromagnetic field or in the corpuscular theory of light the ether isn’ t necessary to explain phenomena of propagation and diffractio ...
Quantum Manipulation Using Light-Atom Interaction
... The obtainable spin squeezing improves with the quality of the resonator and the number of atoms. Fig. 4 shows the calculated spin squeezing for a typical atom number (N=2×104) and varying finesse of the resonator. Note that we obtain excellent agreement between the calculation [23] and the experime ...
... The obtainable spin squeezing improves with the quality of the resonator and the number of atoms. Fig. 4 shows the calculated spin squeezing for a typical atom number (N=2×104) and varying finesse of the resonator. Note that we obtain excellent agreement between the calculation [23] and the experime ...
Nanoscience Student Reading Lesson 4
... spiraling into the nucleus, as classical models predict. This quantization of energy, along with some other atomic properties that are quantized, give quantum mechanics its name. The Wave-Particle Duality of Light and Matter In 1690, Christiaan Huygens theorized that light was composed of waves, whi ...
... spiraling into the nucleus, as classical models predict. This quantization of energy, along with some other atomic properties that are quantized, give quantum mechanics its name. The Wave-Particle Duality of Light and Matter In 1690, Christiaan Huygens theorized that light was composed of waves, whi ...
Aalborg Universitet Quantum Gravity Chromo Dynamics (QGCD) Javadi, Hossein; Forouzbakhsh, Farshid
... electromagnetism. Einstein basically sided with Maxwell! Special relativity makes two postulates: The laws of physics are the same for all non-accelerating observers. The speed of light in vacuum is independent of the motion of all observers and sources, and is observed to have the same value. Consi ...
... electromagnetism. Einstein basically sided with Maxwell! Special relativity makes two postulates: The laws of physics are the same for all non-accelerating observers. The speed of light in vacuum is independent of the motion of all observers and sources, and is observed to have the same value. Consi ...
AP-1 Cutnell 06-10 1st Sem Rev Key Points
... Ex. 9 - A ballistic pendulum consists of a block of wood (mass m2 = 2.50 kg) suspended by a wire. A bullet (mass m1 = 0.0100 kg) is fired with a speed v01. Just after the bullet collides with it, the block (now containing the bullet) has a speed vf and then swings to a maximum height of 0.650 m abo ...
... Ex. 9 - A ballistic pendulum consists of a block of wood (mass m2 = 2.50 kg) suspended by a wire. A bullet (mass m1 = 0.0100 kg) is fired with a speed v01. Just after the bullet collides with it, the block (now containing the bullet) has a speed vf and then swings to a maximum height of 0.650 m abo ...
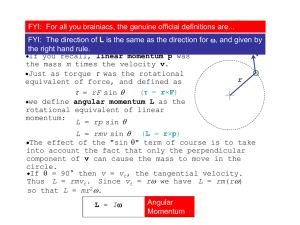
I L - IBPhysicsLund
... FYI: You may recall Topic doing the same when we looked at linear 2.2thing Extended ...
... FYI: You may recall Topic doing the same when we looked at linear 2.2thing Extended ...
sclecture6
... M is the magnetisation - the so-called order parameter of the magnetised ferromagnetic state and M gradM is associated with variations in magnetisation (or applied field) F(T,M) The stable state is found at the minimum of the free energy, ie when T>TCM ...
... M is the magnetisation - the so-called order parameter of the magnetised ferromagnetic state and M gradM is associated with variations in magnetisation (or applied field) F(T,M) The stable state is found at the minimum of the free energy, ie when T>TCM ...
V. Angular momentum
... If the component of the net external torque on a system along a certain axis is zero, the component of the angular momentum of the system along that axis cannot change, no matter what changes take place within the system. This conservation law holds not only within the frame of Newton’s mechanics b ...
... If the component of the net external torque on a system along a certain axis is zero, the component of the angular momentum of the system along that axis cannot change, no matter what changes take place within the system. This conservation law holds not only within the frame of Newton’s mechanics b ...