Particle Physics - UW High Energy Physics
... – Bottom forms mesons but top is so heavy that it decays before QCD can confine it to a meson Are there more generations? – Leptons also form doublets, (e, e), (, ), (, ) – Neutrinos are almost massless – Neutrinos couple to Z boson weakly – Z decay width can predict how many neutrinos are al ...
... – Bottom forms mesons but top is so heavy that it decays before QCD can confine it to a meson Are there more generations? – Leptons also form doublets, (e, e), (, ), (, ) – Neutrinos are almost massless – Neutrinos couple to Z boson weakly – Z decay width can predict how many neutrinos are al ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
... 1. Select the object to which the equations for equilibrium are to be applied. 2. Draw a free-body diagram that shows all of the external forces acting on the object. 3. Choose a convenient set of x, y axes and resolve all forces into components that lie along these axes. 4. Apply the equations t ...
Impulse and Momentum
... object and the time interval over which it acts (measures in Newton-seconds) Momentum: mv, or the product of the object’s mass and the objects velocity Impulse-momentum Theorem: FΔt= pf –pi ; The impulse on an object is equal to the object’s final momentum mines the object’s initial momentum (p= ...
... object and the time interval over which it acts (measures in Newton-seconds) Momentum: mv, or the product of the object’s mass and the objects velocity Impulse-momentum Theorem: FΔt= pf –pi ; The impulse on an object is equal to the object’s final momentum mines the object’s initial momentum (p= ...
Chapter 1 Two-Body Orbital Mechanics 1.1
... Since the time of Aristotle the motion of planets was thought as a combination of smaller circles moving on larger ones. The official birth of modern Astrodynamics is in 1609, when Johann Kepler published his first two laws of planetary motion. The third followed in 1919. First Law – The orbit of ea ...
... Since the time of Aristotle the motion of planets was thought as a combination of smaller circles moving on larger ones. The official birth of modern Astrodynamics is in 1609, when Johann Kepler published his first two laws of planetary motion. The third followed in 1919. First Law – The orbit of ea ...
Gravitation and Other Central Forces - RIT
... are of widespread interest in physics. We have already discussed the isotropic harmonic oscillator in 2 and 3 dimensions. The general law of gravity, the force that holds the universe together, is treated in the non-relativistic sense as a central force, and planetary motion was one of the first app ...
... are of widespread interest in physics. We have already discussed the isotropic harmonic oscillator in 2 and 3 dimensions. The general law of gravity, the force that holds the universe together, is treated in the non-relativistic sense as a central force, and planetary motion was one of the first app ...
Laws of Science- A Compilation - MS Ramaiah University of Applied
... quantum hypothesis realistically and used it to explain the photoelectric effect, in which shining light on certain materials can eject electrons from the material. He won the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics for this work. Einstein further developed this idea to show that an electromagnetic wave such a ...
... quantum hypothesis realistically and used it to explain the photoelectric effect, in which shining light on certain materials can eject electrons from the material. He won the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics for this work. Einstein further developed this idea to show that an electromagnetic wave such a ...
Nominal versus Effective Energy
... The Universality Features are a QCD non–perturbative effect. It will be interesting to study how the Effective Energy is related to the non–Abelian nature of the interaction describing quarks and gluon. References and other details on this topic can be found in the volume edited by Lipatov [5]. Let ...
... The Universality Features are a QCD non–perturbative effect. It will be interesting to study how the Effective Energy is related to the non–Abelian nature of the interaction describing quarks and gluon. References and other details on this topic can be found in the volume edited by Lipatov [5]. Let ...
Ch6 momentum and collision
... In a crash test, a car of mass 1.50 x 103 kg collides with a wall and rebounds. The initial and final velocities of the car are vi = -15.0m/s vf = 2.60m/s, A rocket has a total mass of 1.00 x 105 kg and a respectively. If the collision lasts for 0.150s, find burnout mass of 1.00 x104 kg, including ...
... In a crash test, a car of mass 1.50 x 103 kg collides with a wall and rebounds. The initial and final velocities of the car are vi = -15.0m/s vf = 2.60m/s, A rocket has a total mass of 1.00 x 105 kg and a respectively. If the collision lasts for 0.150s, find burnout mass of 1.00 x104 kg, including ...
4, 7, 9, 13, 15 / 2, 6, 17, 18, 24, 29, 41, 48, 51, 54, 74
... 15. REASONING AND SOLUTION The amount of force F needed to stretch a rod is given by Equation 10.17: F Y( L / L0 )A , where A is the cross-sectional area of the rod, L0 is the original length, L is the change in length, and Y is Young's modulus of the material. Since the cylinders are made of t ...
... 15. REASONING AND SOLUTION The amount of force F needed to stretch a rod is given by Equation 10.17: F Y( L / L0 )A , where A is the cross-sectional area of the rod, L0 is the original length, L is the change in length, and Y is Young's modulus of the material. Since the cylinders are made of t ...
Linear Momentum Test Mr. Kepple
... A 2-kilogram block and an 8-kilogram block are both attached to an ideal spring (for which N/m) and both are initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface, as shown in the diagram above. In an experiment, a 100-gram (0.1 kg) ball of clay is thrown at the 2-kilogram block. The clay is moving ...
... A 2-kilogram block and an 8-kilogram block are both attached to an ideal spring (for which N/m) and both are initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface, as shown in the diagram above. In an experiment, a 100-gram (0.1 kg) ball of clay is thrown at the 2-kilogram block. The clay is moving ...
Angular Momentum
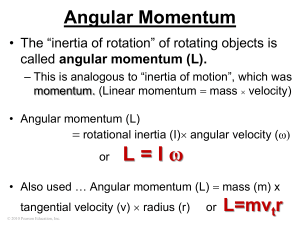
... Angular Momentum • The “inertia of rotation” of rotating objects is called angular momentum (L). – This is analogous to “inertia of motion”, which was momentum. (Linear momentum mass velocity) • Angular momentum (L) rotational inertia (I) angular velocity (ω) or ...
... Angular Momentum • The “inertia of rotation” of rotating objects is called angular momentum (L). – This is analogous to “inertia of motion”, which was momentum. (Linear momentum mass velocity) • Angular momentum (L) rotational inertia (I) angular velocity (ω) or ...
Angular Momentum
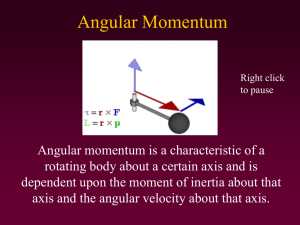
... rotating body about a certain axis and is dependent upon the moment of inertia about that axis and the angular velocity about that axis. ...
... rotating body about a certain axis and is dependent upon the moment of inertia about that axis and the angular velocity about that axis. ...