Quanta and Waves - Calderglen High School
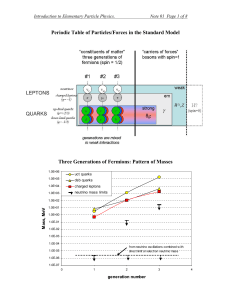
... Matter was thought to be ‘atomistic’ with particles making basic interactions and the properties of these particles continually changing smoothly from place to place. Waves moved continuously from place to place. Classical mechanics could not explain the various quantisation rules, those which attem ...
... Matter was thought to be ‘atomistic’ with particles making basic interactions and the properties of these particles continually changing smoothly from place to place. Waves moved continuously from place to place. Classical mechanics could not explain the various quantisation rules, those which attem ...
Momentum
... Sample Questions • Which has more momentum, a 1-ton car moving at 100 km/hr or a 2-ton truck moving at 50 km/hr? ...
... Sample Questions • Which has more momentum, a 1-ton car moving at 100 km/hr or a 2-ton truck moving at 50 km/hr? ...
Study Material 1
... a. An electron in the hydrogen atom can move around the nucleus in a circular path of fixed radius and energy. These paths are called orbits orenergy levels. These orbits are arranged concentrically around thenucleus. b. As long as an electron remains in a particular orbit, it does not lose or gain ...
... a. An electron in the hydrogen atom can move around the nucleus in a circular path of fixed radius and energy. These paths are called orbits orenergy levels. These orbits are arranged concentrically around thenucleus. b. As long as an electron remains in a particular orbit, it does not lose or gain ...
Appl. Comput. Math. 7 (2008)
... space developed by D. Hestenes [18]. In STA, each relative frame of an observer is defined by a unique, future pointing, Minkowski timelike unit vector tangent to the timelike curve called the history of that observer. The exact relationship between STA and the 3-dimensional Euclidean space of the W ...
... space developed by D. Hestenes [18]. In STA, each relative frame of an observer is defined by a unique, future pointing, Minkowski timelike unit vector tangent to the timelike curve called the history of that observer. The exact relationship between STA and the 3-dimensional Euclidean space of the W ...
Aage Bohr - Pontifical Academy of Sciences
... His father was Niels Bohr, one of the giants of physics in the early 20th century, who was able to untangle the confusing mysteries of quantum mechanics. Aage Bohr’s childhood was one in which a pantheon of great physicists were friends visiting the family home. The remarkable generation of scientis ...
... His father was Niels Bohr, one of the giants of physics in the early 20th century, who was able to untangle the confusing mysteries of quantum mechanics. Aage Bohr’s childhood was one in which a pantheon of great physicists were friends visiting the family home. The remarkable generation of scientis ...
Powerpoint - University of Pittsburgh
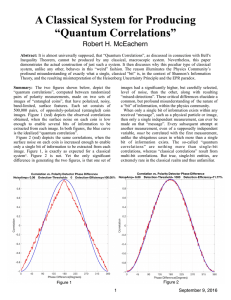
... Well, not always. "Monochromatic radiation of low density behaves--as long as Wien's radiation formula is valid [i.e. at high values of frequency/temperature]--in a thermodynamic sense, as if it consisted of mutually independent energy quanta of magnitude [h]." ...
... Well, not always. "Monochromatic radiation of low density behaves--as long as Wien's radiation formula is valid [i.e. at high values of frequency/temperature]--in a thermodynamic sense, as if it consisted of mutually independent energy quanta of magnitude [h]." ...
A Gravity Model for Superconductors & (Non
... • Goal #2: Fermionic spectral function of HTSC---measurable experimentally ...
... • Goal #2: Fermionic spectral function of HTSC---measurable experimentally ...
Wednesday, June 25, 2008
... If you grab onto a pole while running, your body will rotate about the pole, gaining angular momentum. We’ve used the linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, the angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass ...
... If you grab onto a pole while running, your body will rotate about the pole, gaining angular momentum. We’ve used the linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, the angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass ...
File
... Elastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. Inelastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the c ...
... Elastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. Inelastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the c ...
ENERGY - Chapter 3
... gravitation to the structure of space and time The force of gravity arises from a warping of spacetime around a body of matter so that a nearby mass tends to move toward the body General Relativity does not interpret gravity as a ...
... gravitation to the structure of space and time The force of gravity arises from a warping of spacetime around a body of matter so that a nearby mass tends to move toward the body General Relativity does not interpret gravity as a ...
PH2011 - Physics 2A - University of St Andrews
... - Identify invariant quantities in special relativity, distinguish invariants from conserved quantities, and use both concepts to determine the outcome of relativistic collisions. - State the zeroth, first and second laws of thermodynamics, explain their physical meaning and relate them to the therm ...
... - Identify invariant quantities in special relativity, distinguish invariants from conserved quantities, and use both concepts to determine the outcome of relativistic collisions. - State the zeroth, first and second laws of thermodynamics, explain their physical meaning and relate them to the therm ...