Catalysis Web Pages for Pre-University
... The catalyst speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the overall reaction; in other words there is as much catalyst at the end of reaction as at the start. In a homogenous reaction the catalyst takes part in the reaction and gets regenerated. Catalysts can be transition metals or their compou ...
... The catalyst speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the overall reaction; in other words there is as much catalyst at the end of reaction as at the start. In a homogenous reaction the catalyst takes part in the reaction and gets regenerated. Catalysts can be transition metals or their compou ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
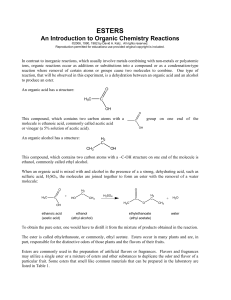
... Natural Products vs. Synthetic Organic compounds 1) Natural Products are compounds we find in the environment a) May need to be refined or isolated from the source b) Are starting materials for synthetic compounds 2) Synthetic Organic compounds do not occur naturally and must be O synthesized from s ...
... Natural Products vs. Synthetic Organic compounds 1) Natural Products are compounds we find in the environment a) May need to be refined or isolated from the source b) Are starting materials for synthetic compounds 2) Synthetic Organic compounds do not occur naturally and must be O synthesized from s ...
GO C3 B Changing Concentration Of Harmful Chemicals
... Biodegradation Biodegradation occurs in the environment because living things (earthworms, bacteria and fungi) are actively breaking down organic substances, including many pollutants. Micro-organisms are especially important in the biodegradation of pollutants. The existing organic molecules provi ...
... Biodegradation Biodegradation occurs in the environment because living things (earthworms, bacteria and fungi) are actively breaking down organic substances, including many pollutants. Micro-organisms are especially important in the biodegradation of pollutants. The existing organic molecules provi ...
Miami-Dade College
... a. Using tabulated values of absolute entropies and standard molar free energy of formation to calculate entropy changes (ΔS) and free energy changes (ΔG), respectively. f. Working out problems that involve the relationship between: free energy changes, enthalpy changes, entropy changes, and tempera ...
... a. Using tabulated values of absolute entropies and standard molar free energy of formation to calculate entropy changes (ΔS) and free energy changes (ΔG), respectively. f. Working out problems that involve the relationship between: free energy changes, enthalpy changes, entropy changes, and tempera ...
A = 27
... #32) Al+3 has lost 3 electrons (each + charge represents a lost electron). The neutral atom has 13 protons, thus there are 13 electrons in the neutral atom. If three e- were lost 10, are remaining. ANS-4 #33 The excited state must have the same # of electrons as the neutral atom, however one or more ...
... #32) Al+3 has lost 3 electrons (each + charge represents a lost electron). The neutral atom has 13 protons, thus there are 13 electrons in the neutral atom. If three e- were lost 10, are remaining. ANS-4 #33 The excited state must have the same # of electrons as the neutral atom, however one or more ...
Discussion 8
... Next to that scale, we use horizontal lines and arrows to show either a particular value of energy, or a change in energy. The size of the horizontal lines do not matter, only their vertal location along the scale. The size of the vertial arrows, however, show a specific range on the energy scale an ...
... Next to that scale, we use horizontal lines and arrows to show either a particular value of energy, or a change in energy. The size of the horizontal lines do not matter, only their vertal location along the scale. The size of the vertial arrows, however, show a specific range on the energy scale an ...
Chem BIG REVIEW - Jones-wiki
... Metals are elements that have luster, conduct heat and electricity, usually bend without breaking (malleable) and are ductile. Most have extremely high melting points. Reactivity increases as you go down within a group for metals. With metals the greater the tendency to lose electrons, the more reac ...
... Metals are elements that have luster, conduct heat and electricity, usually bend without breaking (malleable) and are ductile. Most have extremely high melting points. Reactivity increases as you go down within a group for metals. With metals the greater the tendency to lose electrons, the more reac ...
Παρουσίαση του PowerPoint
... Before and during these syntheses, groups of chemists sitting around blackboards or piles of paper plan the work they are about to undertake. Possible routes are drawn out, criticized, modified again when the behavior of the compounds in the flask turns out to be different from what was expected, un ...
... Before and during these syntheses, groups of chemists sitting around blackboards or piles of paper plan the work they are about to undertake. Possible routes are drawn out, criticized, modified again when the behavior of the compounds in the flask turns out to be different from what was expected, un ...
Halogens - Cronodon
... In elemental form, the halogens exist as simple molecular compounds, containing diatomic molecules (i.e. molecules of two atoms): F2, Cl2, Br2, I2. Fluorine is a paleyellow gas of F2 molecules, chlorine is a greenish-yellow gas of Cl2 molecules. Bromine is a reddish-orange liquid of Br2 molecules wi ...
... In elemental form, the halogens exist as simple molecular compounds, containing diatomic molecules (i.e. molecules of two atoms): F2, Cl2, Br2, I2. Fluorine is a paleyellow gas of F2 molecules, chlorine is a greenish-yellow gas of Cl2 molecules. Bromine is a reddish-orange liquid of Br2 molecules wi ...
Part II
... Free radicals – have unpaired electron(s). Atmospheric lifetimes seconds, minutes. e.g., •O-H radical, missing one bond (H), wants to steal one from somewhere. Similar story for •CH3 radical, missing one bond. Or the HO2 radical, H-O-O• These free radicals are usually generated by sunlight (photoche ...
... Free radicals – have unpaired electron(s). Atmospheric lifetimes seconds, minutes. e.g., •O-H radical, missing one bond (H), wants to steal one from somewhere. Similar story for •CH3 radical, missing one bond. Or the HO2 radical, H-O-O• These free radicals are usually generated by sunlight (photoche ...
Lab
... Special fees apply. Prerequisites: CHEM F331; MATH F253X; or permission of instructor. (3+3) Course Goal: Chemistry 332 is the second semester of a two-semester series in physical chemistry. Our goal is to understand how physical and mathematical theories can be used to explain chemical behavior. Le ...
... Special fees apply. Prerequisites: CHEM F331; MATH F253X; or permission of instructor. (3+3) Course Goal: Chemistry 332 is the second semester of a two-semester series in physical chemistry. Our goal is to understand how physical and mathematical theories can be used to explain chemical behavior. Le ...
Summer Work
... Third Exercise: Writing the balanced ionic Equation, predict the products for the following solutions are combined. Circle the precipitate (if any), place a box around the spectator ions. a. potassium chloride(aq) + silver(I) nitrate(aq) → b. lead (II) nitrate(aq) + hydrogen chloride(aq) → c. sodium ...
... Third Exercise: Writing the balanced ionic Equation, predict the products for the following solutions are combined. Circle the precipitate (if any), place a box around the spectator ions. a. potassium chloride(aq) + silver(I) nitrate(aq) → b. lead (II) nitrate(aq) + hydrogen chloride(aq) → c. sodium ...
Los Angeles Mission College 13356 Eldgridge Avenue Sylmar, CA 91342
... structure of organic molecule. Course Goals and Objective: Offered for students in physical and biological sciences, medical and dental professions and other majors concerned with the nature of organic substances. Chem. 212 is the second course sequence in organic chemistry. This first course provid ...
... structure of organic molecule. Course Goals and Objective: Offered for students in physical and biological sciences, medical and dental professions and other majors concerned with the nature of organic substances. Chem. 212 is the second course sequence in organic chemistry. This first course provid ...
Honors Chemistry
... : a species that appears in some steps but not in the overall reaction. It is relatively short lived. So, in the above example, H2I is the reaction intermediate. ...
... : a species that appears in some steps but not in the overall reaction. It is relatively short lived. So, in the above example, H2I is the reaction intermediate. ...
No Slide Title
... • Cu is called the reducing agent because it caused Ag+ to be reduced; and Ag+ is called the oxidizing agent because it caused Cu to be oxidized. ...
... • Cu is called the reducing agent because it caused Ag+ to be reduced; and Ag+ is called the oxidizing agent because it caused Cu to be oxidized. ...
Semester 2 Review WS
... b.) When hydrochloric acid is added to sodium bicarbonate, it produces water, sodium chloride and carbon dioxide. If 20.0 grams of sodium bicarbonate reacts and 6.75 g of CO2 is produced, what is the percent yield of the carbon dioxide? ...
... b.) When hydrochloric acid is added to sodium bicarbonate, it produces water, sodium chloride and carbon dioxide. If 20.0 grams of sodium bicarbonate reacts and 6.75 g of CO2 is produced, what is the percent yield of the carbon dioxide? ...
Lecture 3: Reaction Tables and Limiting Reactants start with PRS
... H2(g) left over, there will be 50 O2(g) left over and 100 H2O(g) will be formed. This is an easy problem and this detailed treatment is not necessary in this case, but the general method we just used to solve the limiting reactant problem using a reaction table is a very powerful method that will h ...
... H2(g) left over, there will be 50 O2(g) left over and 100 H2O(g) will be formed. This is an easy problem and this detailed treatment is not necessary in this case, but the general method we just used to solve the limiting reactant problem using a reaction table is a very powerful method that will h ...
A Closure Study of the Reaction between Sulfur
... the structures and energetics of various systems, especially when used with the dispersion correction.15−17 Initial structures for the systems were taken from our previous work8 and reoptimized in CP2K with the abovementioned density functional and basis set. We found earlier that the SO3SO3− ion is ...
... the structures and energetics of various systems, especially when used with the dispersion correction.15−17 Initial structures for the systems were taken from our previous work8 and reoptimized in CP2K with the abovementioned density functional and basis set. We found earlier that the SO3SO3− ion is ...
the ap chemistry summer assignment
... [email protected] Welcome to AP Chemistry! You already have a background in chemistry from your general chemistry class, but AP Chemistry is very different. Rather than memorizing how to do particular types of problems, you must really understand the chemistry and be able to apply it to different ...
... [email protected] Welcome to AP Chemistry! You already have a background in chemistry from your general chemistry class, but AP Chemistry is very different. Rather than memorizing how to do particular types of problems, you must really understand the chemistry and be able to apply it to different ...