File
... Tells the types and amounts of elements in the compound Ex: H2O is the chemical formula for water ...
... Tells the types and amounts of elements in the compound Ex: H2O is the chemical formula for water ...
review sheet
... Which carboxylic acid is most acidic? (Which one forms the most stable anion?) Why? Which of the carboxylic acid derivatives (acid chloride, acid anhydride, ester, amide) is the most stable? Which is the most reactive? Why are acid chlorides highly reactive? What is the mechanism for nucleophilic ac ...
... Which carboxylic acid is most acidic? (Which one forms the most stable anion?) Why? Which of the carboxylic acid derivatives (acid chloride, acid anhydride, ester, amide) is the most stable? Which is the most reactive? Why are acid chlorides highly reactive? What is the mechanism for nucleophilic ac ...
Structure and Bonding in Organic Compounds
... While organic chemistry is a vast subject, we will concern ourselves with one fundamental concepts that will form a solid foundation for those students who will be continuing with Chem 104 or Chem 150: an understanding of the structure and bonding in organic compounds. This experiment is designed to ...
... While organic chemistry is a vast subject, we will concern ourselves with one fundamental concepts that will form a solid foundation for those students who will be continuing with Chem 104 or Chem 150: an understanding of the structure and bonding in organic compounds. This experiment is designed to ...
ESTERIFICATION
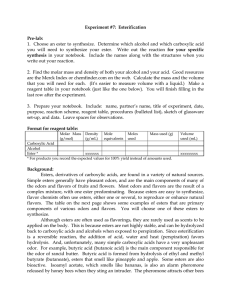
... the odors and flavors of fruits and flowers. Most odors and flavors are the result of a complex mixture, with one ester predominating. Because esters are easy to synthesize, flavor chemists often use esters, either one or several, to reproduce or enhance natural flavors. The table on the next page s ...
... the odors and flavors of fruits and flowers. Most odors and flavors are the result of a complex mixture, with one ester predominating. Because esters are easy to synthesize, flavor chemists often use esters, either one or several, to reproduce or enhance natural flavors. The table on the next page s ...
Chem expo 12
... balanced chemical equations is also essential. An understanding of bonding theory as it relates to ionic, metallic and molecular compounds is also necessary. The following shows how the coursework studied at Year 11 is related to that covered in Year 12. Year 11 topic ...
... balanced chemical equations is also essential. An understanding of bonding theory as it relates to ionic, metallic and molecular compounds is also necessary. The following shows how the coursework studied at Year 11 is related to that covered in Year 12. Year 11 topic ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... structure of graphite is organized in layers. The bonds between carbon atoms within each layer of graphite are strong. The bonds between carbon atoms that connect different layers of graphite are weak because the shared electrons in these bonds are loosely held by the carbon atoms. The crystal struc ...
... structure of graphite is organized in layers. The bonds between carbon atoms within each layer of graphite are strong. The bonds between carbon atoms that connect different layers of graphite are weak because the shared electrons in these bonds are loosely held by the carbon atoms. The crystal struc ...
unit 5b hw packet File - District 196 e
... 1. Add the number of valence electrons in each atom to determine the total number of valence electrons. (For polyatomic anions, add one electron for each unit of negative charge. For polyatomic cations, subtract one electron for each unit of positive charge.) 2. Put electrons around each atom. Start ...
... 1. Add the number of valence electrons in each atom to determine the total number of valence electrons. (For polyatomic anions, add one electron for each unit of negative charge. For polyatomic cations, subtract one electron for each unit of positive charge.) 2. Put electrons around each atom. Start ...
thermochermistry ap - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... 5.7 Enthalpies of Formation There are many types of enthalpy for each substance: o Enthalpy of vaporization is the energy it takes to change a liquid to a gas o Enthalpy of fusion is the amount of energy it takes to melt a solid substance o Enthalpy of combustion is the amount of energy it takes t ...
... 5.7 Enthalpies of Formation There are many types of enthalpy for each substance: o Enthalpy of vaporization is the energy it takes to change a liquid to a gas o Enthalpy of fusion is the amount of energy it takes to melt a solid substance o Enthalpy of combustion is the amount of energy it takes t ...
Zumdahl`s Chap. 4 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... If at least one is “strong,” neutralization will be complete because H2O is very “weak!” Choose indicator for strong visual signal at completion. For titrant, CV dispensed gives moles. Stoichiometry determines moles sample Sample moles / sample vol = original M ...
... If at least one is “strong,” neutralization will be complete because H2O is very “weak!” Choose indicator for strong visual signal at completion. For titrant, CV dispensed gives moles. Stoichiometry determines moles sample Sample moles / sample vol = original M ...
Elias lecture chemistry of chlorine 2016 nov
... In fact the structure-activity relationships that have been established for derivatives of phenol are: •the −OH group is required for activity; •activity increases with a halogen in the 4- position (ie opposite the −OH group in the ring); •activity increases with alkyl substituents of increased cha ...
... In fact the structure-activity relationships that have been established for derivatives of phenol are: •the −OH group is required for activity; •activity increases with a halogen in the 4- position (ie opposite the −OH group in the ring); •activity increases with alkyl substituents of increased cha ...
Final Exam Review Day 1
... Many electrons are shared. They are ______________. Classify the following chemical bonds as ionic, covalent or metallic: _____ CuO _____AlBr3 _____ H2O _____ PCl5 _____ MgSO4 ...
... Many electrons are shared. They are ______________. Classify the following chemical bonds as ionic, covalent or metallic: _____ CuO _____AlBr3 _____ H2O _____ PCl5 _____ MgSO4 ...
Esters, fats and oils
... Emulsifiers for use in food are commonly made by reacting edible oils with glycerol to form molecules in which either one or two fatty acid groups are linked to a glycerol backbone rather than the three normally found in edible oils. ...
... Emulsifiers for use in food are commonly made by reacting edible oils with glycerol to form molecules in which either one or two fatty acid groups are linked to a glycerol backbone rather than the three normally found in edible oils. ...
Chapter 6 - CHEM 10 HOME
... – Lactic acid is associated with the ―burn‖ associated with heavy exercise – If too much lactic acid builds up, your muscles give out ...
... – Lactic acid is associated with the ―burn‖ associated with heavy exercise – If too much lactic acid builds up, your muscles give out ...
Practice problem chap3 1. The atomic mass of 35Cl (75.53%) and
... Practice problem chap3 1. The atomic mass of Cl (75.53%) and 37Cl (24.47%) are 34.968amu and 36.956amu.Calculate the average atomic mass in amu. 2. What is the mass percent (%) for O in SO2? (a) 38.09 (b) 45.41 (c) 50.00 (d) 53.86 (e) 56.43 3. How many molecules of ethane (C2H6) are present in 0.334 ...
... Practice problem chap3 1. The atomic mass of Cl (75.53%) and 37Cl (24.47%) are 34.968amu and 36.956amu.Calculate the average atomic mass in amu. 2. What is the mass percent (%) for O in SO2? (a) 38.09 (b) 45.41 (c) 50.00 (d) 53.86 (e) 56.43 3. How many molecules of ethane (C2H6) are present in 0.334 ...
Formal Charge
... with four covalent bonds in any combination (four single, one double and two single, etc.) would possess 4 electrons (half of each covalent bond) and would have nv = 4, thus q = 0. An oxygen atom with three lone pairs of a electrons and one covalent bond would have n = 7 (three wholly owned pairs an ...
... with four covalent bonds in any combination (four single, one double and two single, etc.) would possess 4 electrons (half of each covalent bond) and would have nv = 4, thus q = 0. An oxygen atom with three lone pairs of a electrons and one covalent bond would have n = 7 (three wholly owned pairs an ...
Final Exam Study Guide Chapters 1-12
... ____ 84. The reaction represented by the equation Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) H2(g) + MgCl2(aq) is a a. composition reaction. c. single-displacement reaction. b. decomposition reaction. d. double-displacement reaction. ____ 85. In one type of synthesis reaction, an element combines with oxygen to yield a(n) ...
... ____ 84. The reaction represented by the equation Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) H2(g) + MgCl2(aq) is a a. composition reaction. c. single-displacement reaction. b. decomposition reaction. d. double-displacement reaction. ____ 85. In one type of synthesis reaction, an element combines with oxygen to yield a(n) ...
Chemistry
... structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been introduced to the fundamental idea that matter is made up of particles and the simple atomic model (electrons in discrete shells around a positively charged nucleus). This allows students to apply the key ideas ...
... structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been introduced to the fundamental idea that matter is made up of particles and the simple atomic model (electrons in discrete shells around a positively charged nucleus). This allows students to apply the key ideas ...
Lab 7_Esterification
... the odors and flavors of fruits and flowers. Most odors and flavors are the result of a complex mixture, with one ester predominating. Because esters are easy to synthesize, flavor chemists often use esters, either one or several, to reproduce or enhance natural flavors. The table on the next page s ...
... the odors and flavors of fruits and flowers. Most odors and flavors are the result of a complex mixture, with one ester predominating. Because esters are easy to synthesize, flavor chemists often use esters, either one or several, to reproduce or enhance natural flavors. The table on the next page s ...
Final Review
... c. chemical equilibrium e. Le Chatelier’s principle b. catalyst d. collision theory f. reaction mechanism Draw energy diagrams and label the reactants, products, activated complex, activation energy, and energy change for: a. an exothermic reaction b. and endothermic reaction c. a reaction with and ...
... c. chemical equilibrium e. Le Chatelier’s principle b. catalyst d. collision theory f. reaction mechanism Draw energy diagrams and label the reactants, products, activated complex, activation energy, and energy change for: a. an exothermic reaction b. and endothermic reaction c. a reaction with and ...
ppt
... In a phosphate group, a phosphorus atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms; one oxygen is bonded to the carbon skeleton; two oxygens carry negative charges; abbreviated P . The phosphate group (—OPO32–) is an ionized form of a phosphoric acid group (—OPO3H2; note the ...
... In a phosphate group, a phosphorus atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms; one oxygen is bonded to the carbon skeleton; two oxygens carry negative charges; abbreviated P . The phosphate group (—OPO32–) is an ionized form of a phosphoric acid group (—OPO3H2; note the ...
CHEMISTRY PHYSICAL SETTING Thursday, PS/CHEMISTRY
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
CH. 3 - STOICHIOMETRY: CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I. Molecular
... A. molecular mass - sum of masses of atoms represented in a molecular formula B. formula mass - sum of masses of atoms or ions present in a formula unit II. The Mole and Avogadro’s Number A. mole (mol) - amount of substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in exactly 12g ...
... A. molecular mass - sum of masses of atoms represented in a molecular formula B. formula mass - sum of masses of atoms or ions present in a formula unit II. The Mole and Avogadro’s Number A. mole (mol) - amount of substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in exactly 12g ...