4. chemical kinetics
... In case of solids, rate increases with decrease in the size of particle. Rate is faster in powdered state than that of undivided state because surface area increases and the possibility of contact between reactant molecules increases. ...
... In case of solids, rate increases with decrease in the size of particle. Rate is faster in powdered state than that of undivided state because surface area increases and the possibility of contact between reactant molecules increases. ...
Blue and Red Gradient
... Ketones – used in perfumes and paints as a stabilizer Formaldehyde – Used in tanning, preserving, and embalming and as a germicide, fungicide, and insecticide for plants and vegetables Methyl Ethyl Ketone (MEK) – solvent, poison, used in rubber based cement and ink ...
... Ketones – used in perfumes and paints as a stabilizer Formaldehyde – Used in tanning, preserving, and embalming and as a germicide, fungicide, and insecticide for plants and vegetables Methyl Ethyl Ketone (MEK) – solvent, poison, used in rubber based cement and ink ...
Alcohols and Phenols
... group, and derive the parent name by replacing the -e ending of the corresponding alkane with -ol Number the chain from the end nearer the hydroxyl group Number substituents according to position on chain, listing the substituents in alphabetical order ...
... group, and derive the parent name by replacing the -e ending of the corresponding alkane with -ol Number the chain from the end nearer the hydroxyl group Number substituents according to position on chain, listing the substituents in alphabetical order ...
! !! ! n nn N P =
... Which of the following is the Zeroth law of thermodynamics? A. Energy can never be created or destroyed but it can be changed from one form to another. B. Two bodies in thermal contact are at thermal equilibrium with each other if the two bodies are at the same absolute temperature. C. Any process c ...
... Which of the following is the Zeroth law of thermodynamics? A. Energy can never be created or destroyed but it can be changed from one form to another. B. Two bodies in thermal contact are at thermal equilibrium with each other if the two bodies are at the same absolute temperature. C. Any process c ...
NAME: CHEMISTRY I CHAPTER 6 TYPES OF CHEMICAL
... partners, as in the precipitation of silver chloride when solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed: AgNO3(aq) + ...
... partners, as in the precipitation of silver chloride when solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed: AgNO3(aq) + ...
ppt file
... leaving group Includes: Y = halide (acid halides), acyloxy (anhydrides), alkoxy (esters), amine (amides), thiolate (thioesters), phosphate (acyl phosphates) ...
... leaving group Includes: Y = halide (acid halides), acyloxy (anhydrides), alkoxy (esters), amine (amides), thiolate (thioesters), phosphate (acyl phosphates) ...
Summer_Assignment_AP_Chemistry_TW 2015
... year of high school chemistry, since that provides them with a solid foundation. In order to ensure the best start for you next fall, I prepared a Summer Assignment that reviews many basic chemistry concepts. You will find much of the material in the summer assignment to be very familiar. This is a ...
... year of high school chemistry, since that provides them with a solid foundation. In order to ensure the best start for you next fall, I prepared a Summer Assignment that reviews many basic chemistry concepts. You will find much of the material in the summer assignment to be very familiar. This is a ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
... leaving group Includes: Y = halide (acid halides), acyloxy (anhydrides), alkoxy (esters), amine (amides), thiolate (thioesters), phosphate (acyl phosphates) ...
... leaving group Includes: Y = halide (acid halides), acyloxy (anhydrides), alkoxy (esters), amine (amides), thiolate (thioesters), phosphate (acyl phosphates) ...
50 Chapter 4: Nonionic Compounds and Their Nomenclature A
... Many elements are found in their natural state in the form of molecules. Examples are hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and so on. The chemical formulas for these molecules are H2, O2, N2, S8, ...
... Many elements are found in their natural state in the form of molecules. Examples are hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and so on. The chemical formulas for these molecules are H2, O2, N2, S8, ...
ASFG High School Summer Assignment Summer 2016
... 31.An extensive property is one that depends on the amount of the sample. Which of the following properties are extensive? a. volume b. density c. temperature d. energy e. melting point. F. pressure ...
... 31.An extensive property is one that depends on the amount of the sample. Which of the following properties are extensive? a. volume b. density c. temperature d. energy e. melting point. F. pressure ...
4 - Chemistry Biochemistry and Bio
... All the elements other than hydrogen have more than one electron shell surrounding their nuclei. For instance, an atom of Li has two electron shells, but as well as an atom of H has just one electron in its outer shell. The difference is, that Li has this electron on its 2s orbital and if this only ...
... All the elements other than hydrogen have more than one electron shell surrounding their nuclei. For instance, an atom of Li has two electron shells, but as well as an atom of H has just one electron in its outer shell. The difference is, that Li has this electron on its 2s orbital and if this only ...
Document
... KMTG Supposes that the constituent particles (atoms) of the gas obey the laws of classical physics. Accounts for the random behavior of the particles with statistics, thereby establishing a new branch of physics statistical mechanics. Offers an explanation of the macroscopic behavior of gases. Predi ...
... KMTG Supposes that the constituent particles (atoms) of the gas obey the laws of classical physics. Accounts for the random behavior of the particles with statistics, thereby establishing a new branch of physics statistical mechanics. Offers an explanation of the macroscopic behavior of gases. Predi ...
Refined structure of c-phycocyanin from the cyanobacterium
... the Fremyella diplosiphon (Fd-PC) structure shows solvent molecules in similar positions, indicating that this is not characteristic of PC from thermophiles only. The positions of the propionic acids have not been indicated as important for energy transfer per se; however, by obtaining their proper ...
... the Fremyella diplosiphon (Fd-PC) structure shows solvent molecules in similar positions, indicating that this is not characteristic of PC from thermophiles only. The positions of the propionic acids have not been indicated as important for energy transfer per se; however, by obtaining their proper ...
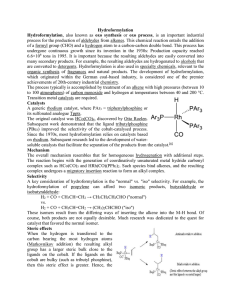
Hydroformylation Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or
... into an acetyl ligand (this is when the alkyl carbon forms a bond with the carbon of a carbonyl ligand). The vacant site on the metal is filled by two hydrogens (from the oxidative insertion of a hydrogen molecule. One of these hydrides then takes part in a reductive elimination to form the molecule ...
... into an acetyl ligand (this is when the alkyl carbon forms a bond with the carbon of a carbonyl ligand). The vacant site on the metal is filled by two hydrogens (from the oxidative insertion of a hydrogen molecule. One of these hydrides then takes part in a reductive elimination to form the molecule ...
Unit 1 – Chapters 4, 5
... vegetable wax) and paraffin (a mineral wax) are commonly encountered waxes which occur naturally. Ear wax is a sticky substance found in the human ear. Some artificial materials that exhibit similar properties are also described as wax or waxy. Chemically, a wax may be an ester of ethylene glycol (e ...
... vegetable wax) and paraffin (a mineral wax) are commonly encountered waxes which occur naturally. Ear wax is a sticky substance found in the human ear. Some artificial materials that exhibit similar properties are also described as wax or waxy. Chemically, a wax may be an ester of ethylene glycol (e ...