Contents and Concepts
... 1. When is a large negative number (more negative than about – 10 kJ), the reaction is spontaneous as written, and reactants transform almost entirely into products when equilibrium is reached. 2. When ∆Go is a large positive number (more positive than about + 10 kJ), the reaction is not spontaneous ...
... 1. When is a large negative number (more negative than about – 10 kJ), the reaction is spontaneous as written, and reactants transform almost entirely into products when equilibrium is reached. 2. When ∆Go is a large positive number (more positive than about + 10 kJ), the reaction is not spontaneous ...
OCR A Level Chemistry B (Salters) Multiple Choice Questions Quiz
... with either molecule (both could react with bromine in the presence of an acid catalyst). The learner is trying to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated compounds but in both molecules the double bond is a C=O not C=C. ...
... with either molecule (both could react with bromine in the presence of an acid catalyst). The learner is trying to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated compounds but in both molecules the double bond is a C=O not C=C. ...
i principi di base - Structural Biology
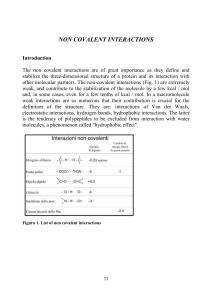
... The hydrogen bond occurs between a donor and an acceptor of hydrogen atoms. When the interaction takes place between charged groups it is often referred to as salt bridge and it has properties typical either of an electrostatic interaction either of an hydrogen bond. The weak bonds between atoms wit ...
... The hydrogen bond occurs between a donor and an acceptor of hydrogen atoms. When the interaction takes place between charged groups it is often referred to as salt bridge and it has properties typical either of an electrostatic interaction either of an hydrogen bond. The weak bonds between atoms wit ...
Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... 1.0 mol of CO2 0.70 mol of H2O 0.20 mol of NO2 Assume that all the atoms in nicotine are present as products. a. Determine the number of moles of carbon present in the products of this combustion. ...
... 1.0 mol of CO2 0.70 mol of H2O 0.20 mol of NO2 Assume that all the atoms in nicotine are present as products. a. Determine the number of moles of carbon present in the products of this combustion. ...
Chemical Reaction
... reaction is called a single-displacement reaction. (synonyms: move, shift, rearrange) • Double Displacement: A double-displacement reaction is a reaction in which ions from two compounds exchange places. (synonyms: move, shift, rearrange) • Chemical Reaction: when two or more molecules interact and ...
... reaction is called a single-displacement reaction. (synonyms: move, shift, rearrange) • Double Displacement: A double-displacement reaction is a reaction in which ions from two compounds exchange places. (synonyms: move, shift, rearrange) • Chemical Reaction: when two or more molecules interact and ...
sOLUBILITY
... Functional groups Solubility in water indicates the presence of OH group Solubility in a basic solvent (NaHCO3) indicates the presence of an acidic ...
... Functional groups Solubility in water indicates the presence of OH group Solubility in a basic solvent (NaHCO3) indicates the presence of an acidic ...
PPT
... –e and adding –al. • All other branches and groups are named and located using standard IUPAC system. ...
... –e and adding –al. • All other branches and groups are named and located using standard IUPAC system. ...
17 ADSORPTION AND CATALYSIS S MODULE - 5
... (i) Nature and Surface Area of the Adsorbent Different solids would adsorb different amounts of the same gas even under similar conditions. Substances like charcoal and silica gel are excellent adsorbents. The substances that are porous in nature and have rough surfaces are better adsorbents. The ex ...
... (i) Nature and Surface Area of the Adsorbent Different solids would adsorb different amounts of the same gas even under similar conditions. Substances like charcoal and silica gel are excellent adsorbents. The substances that are porous in nature and have rough surfaces are better adsorbents. The ex ...
PVS103 - unit 6 notes
... We have already seen how electronegativity increases on moving across the periodic table. Can you remember why? As a result electronegativity is a periodic property, so for example, the halogens (Group 7a elements) are all highly electronegative. ...
... We have already seen how electronegativity increases on moving across the periodic table. Can you remember why? As a result electronegativity is a periodic property, so for example, the halogens (Group 7a elements) are all highly electronegative. ...
Chapter 2 polymers
... 2.1 Introducting Polymers Monomer: the smallest repeating unit of a polymer (propene in polypropylene). Polymer: a long chain molecule made up of many small identical units (monomers). Polymerization: process of linking monomer units into a polymer. Can be accomplished by addition or condensation r ...
... 2.1 Introducting Polymers Monomer: the smallest repeating unit of a polymer (propene in polypropylene). Polymer: a long chain molecule made up of many small identical units (monomers). Polymerization: process of linking monomer units into a polymer. Can be accomplished by addition or condensation r ...
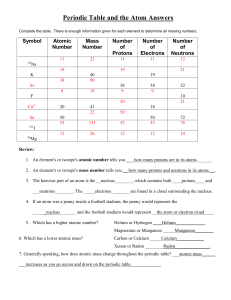
Periodic Table and the Atom Answers
... stoichiometry problems, I would highly suggest consulting this section of the site before answering these questions. When doing stoichiometry problems, people are frequently worried by statements such as “if you have an excess of (compound X)”. This statement shouldn’t worry you… what it really mean ...
... stoichiometry problems, I would highly suggest consulting this section of the site before answering these questions. When doing stoichiometry problems, people are frequently worried by statements such as “if you have an excess of (compound X)”. This statement shouldn’t worry you… what it really mean ...
106KB - NZQA
... molecular mass, particularly the number of carbon atoms. The lower / higher its molecular mass is, the lower / higher the temperature (boiling point) at which it will condense. This determines whereabouts on the tower the particular fraction is collected. Products formed during Process 1 may include ...
... molecular mass, particularly the number of carbon atoms. The lower / higher its molecular mass is, the lower / higher the temperature (boiling point) at which it will condense. This determines whereabouts on the tower the particular fraction is collected. Products formed during Process 1 may include ...
17.2.3 Interhalogen compounds(65-67)
... IF3 but ClF3 and BrF3 are well-characterized volatile molecular liquids. Both have an unusual T-shaped structure of CzV symmetry, consistent with the presence of 10 electrons in the valency shell of the central atom (Fig. 17.7a,b). A notable feature of both structures is the slight deviation from co ...
... IF3 but ClF3 and BrF3 are well-characterized volatile molecular liquids. Both have an unusual T-shaped structure of CzV symmetry, consistent with the presence of 10 electrons in the valency shell of the central atom (Fig. 17.7a,b). A notable feature of both structures is the slight deviation from co ...
CHEM 121: chapter 16
... Chapter 16:Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Other Acid Derivatives 16.1 Structure of Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives 16.2 IUPAC Nomenclature for Carboxylic Acids 16.3 Common Names for Carboxylic Acids 16.4 Polyfunctional Carboxylic Acids 16.5 "Metabolic" Acids 16.6 Physical Properties of Carbox ...
... Chapter 16:Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Other Acid Derivatives 16.1 Structure of Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives 16.2 IUPAC Nomenclature for Carboxylic Acids 16.3 Common Names for Carboxylic Acids 16.4 Polyfunctional Carboxylic Acids 16.5 "Metabolic" Acids 16.6 Physical Properties of Carbox ...
Chemistry
... in a liquid – Henry’s law, graph of partial pressure of a gas vs its mole fraction in solution, effect of pressure, temperature, applications of Henry’s law. Solution of liquid in liquid – Raoult’s law- statement, mathematical expression, numerical problems, ideal solution – characteristics, graph, ...
... in a liquid – Henry’s law, graph of partial pressure of a gas vs its mole fraction in solution, effect of pressure, temperature, applications of Henry’s law. Solution of liquid in liquid – Raoult’s law- statement, mathematical expression, numerical problems, ideal solution – characteristics, graph, ...
NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION & ELIMINATION ON Csp 3
... It was said that a nucleophile is a Lewis base (el-rich, capable of donating an electron pair) As a rule, nucleophiles are Brønsted bases (Brønsted base – capable of accepting H+) but the relation is not simple: Within the same group elements become weaker Brønsted bases but better nucleophiles: ...
... It was said that a nucleophile is a Lewis base (el-rich, capable of donating an electron pair) As a rule, nucleophiles are Brønsted bases (Brønsted base – capable of accepting H+) but the relation is not simple: Within the same group elements become weaker Brønsted bases but better nucleophiles: ...
International Indian School Dammam
... (ii) What are multimolecular and macromolecular colloids? Write one example each. (i) Discuss briefly the role of coordination compounds in: (a) Biological systems (b) Medicinal chemistry (ii) Draw labelled diagram to show splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field. Account for the follo ...
... (ii) What are multimolecular and macromolecular colloids? Write one example each. (i) Discuss briefly the role of coordination compounds in: (a) Biological systems (b) Medicinal chemistry (ii) Draw labelled diagram to show splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field. Account for the follo ...