Chemistry English
... The electronic configurations for an atom is written by listing the orbitals occupied by electrons in the atom along with the number of electrons in each orbitals. Three Rules which must be followed in writing electronic configurations are Pauli principle, Aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule. Pauli Pr ...
... The electronic configurations for an atom is written by listing the orbitals occupied by electrons in the atom along with the number of electrons in each orbitals. Three Rules which must be followed in writing electronic configurations are Pauli principle, Aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule. Pauli Pr ...
PDF document
... conditions, and the results are summarized in Table 1. At first, the oxidation was tested with H2O2 as the oxidant in the presence and absence of PEG1000-DAIL catalytic system. In the absence of PEG1000-DAIL, the reaction proceeded very slowly and the yield was only 26% after 24 hours (Table 1, entr ...
... conditions, and the results are summarized in Table 1. At first, the oxidation was tested with H2O2 as the oxidant in the presence and absence of PEG1000-DAIL catalytic system. In the absence of PEG1000-DAIL, the reaction proceeded very slowly and the yield was only 26% after 24 hours (Table 1, entr ...
Boiling Point of Liquids Procedures:
... The boiling point (bp) is an important physical property of a substance and can be used to help identify it or, if known, offer information about its purity. Pure substances have a narrow boiling point range while mixtures may show multiple or broad ranged boiling temperatures. A number of definitio ...
... The boiling point (bp) is an important physical property of a substance and can be used to help identify it or, if known, offer information about its purity. Pure substances have a narrow boiling point range while mixtures may show multiple or broad ranged boiling temperatures. A number of definitio ...
Chemistry Review 3
... 29. State two methods to increase the rate of a chemical reaction and explain, in terms of particle behavior, how each method increases the reaction rate. [2] 30. State two methods to increase the rate of a chemical reaction and explain, in terms of particle behavior, how each method increases the ...
... 29. State two methods to increase the rate of a chemical reaction and explain, in terms of particle behavior, how each method increases the reaction rate. [2] 30. State two methods to increase the rate of a chemical reaction and explain, in terms of particle behavior, how each method increases the ...
___Mg + ___O ___MgO • Mole : Mole ratio
... 1) What is the percentage yield if 5.50 grams of hydrogen gas reacts with nitrogen gas to form 20.4 grams of ammonia (nitrogen trihydride)? 2) What is the percent yield when 2.37 grams of silver nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce water, sodium nitrate and 1.55 grams of silver oxide? ...
... 1) What is the percentage yield if 5.50 grams of hydrogen gas reacts with nitrogen gas to form 20.4 grams of ammonia (nitrogen trihydride)? 2) What is the percent yield when 2.37 grams of silver nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce water, sodium nitrate and 1.55 grams of silver oxide? ...
Soquids Answers M/C 58. C 68. C 27. E 54. A 21. A 49. C 50. B 51
... higher molality of a solution lowers the freezing point more and an equimolar amount of the two solids gives a larger molal solution from the calcium chloride as illustrated by the above equations. (b) Water is more polar than ammonia creating stronger attractions (IMF) between molecules and making ...
... higher molality of a solution lowers the freezing point more and an equimolar amount of the two solids gives a larger molal solution from the calcium chloride as illustrated by the above equations. (b) Water is more polar than ammonia creating stronger attractions (IMF) between molecules and making ...
File
... case of halogenation, various experiments show that this reaction occurs in several steps , and not in one magical step. Indeed, halogenation occurs via a free-radical chain of reactions. • The chain-initiating step is the breaking of the halogen molecule into two halogen atoms. ...
... case of halogenation, various experiments show that this reaction occurs in several steps , and not in one magical step. Indeed, halogenation occurs via a free-radical chain of reactions. • The chain-initiating step is the breaking of the halogen molecule into two halogen atoms. ...
Essential Standard: 8.P.1 Understand the properties of matter and
... that there is a relationship between phase and density and that density is mass per unit volume. ...
... that there is a relationship between phase and density and that density is mass per unit volume. ...
Oxoacids of Phosphorus
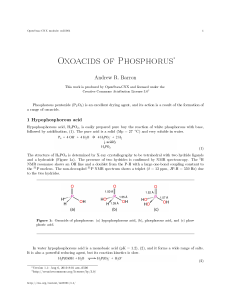
... the phosphorous center being split by a single hydride (δ = 4 ppm, J P-H = 700 Hz). The 1 H NMR spectrum shows a doublet for the hydride and a single resonance of twice the intensity for the hydroxide. As expected, in water phosphorous acid is dibasic, (3). The acid (and the anions) are strong reduc ...
... the phosphorous center being split by a single hydride (δ = 4 ppm, J P-H = 700 Hz). The 1 H NMR spectrum shows a doublet for the hydride and a single resonance of twice the intensity for the hydroxide. As expected, in water phosphorous acid is dibasic, (3). The acid (and the anions) are strong reduc ...
Chapter 22
... continuous carbon chain and use this name as the base (a). If two chains of equal length are present, choose the one with the more branch points as the parent. ...
... continuous carbon chain and use this name as the base (a). If two chains of equal length are present, choose the one with the more branch points as the parent. ...
Final Review Answers
... How many g of NH3 will be produced if 37.3 g of H2 are reacted? 2.10x102 g NH3 What volume of N2 is required to react with 271 g of H2 at STP? 1.00x103 L N2 If 2.3 mol of N2 react with 5.7 mol H2, how many mol NH3 will be produced? 3.8 mol NH3 What is the limiting reagent? H2 5) If 3.6 mol of NH3 ar ...
... How many g of NH3 will be produced if 37.3 g of H2 are reacted? 2.10x102 g NH3 What volume of N2 is required to react with 271 g of H2 at STP? 1.00x103 L N2 If 2.3 mol of N2 react with 5.7 mol H2, how many mol NH3 will be produced? 3.8 mol NH3 What is the limiting reagent? H2 5) If 3.6 mol of NH3 ar ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 2 Elements of Chemical Change
... reactions, and double replacement reactions. (1) Combination reactions. A combination reaction can be represented by the chemical equation A + B --> AB (one atom of A plus one atom of B yield one molecule of AB). A specific example of this type of reaction is the combination of a metal with oxygen t ...
... reactions, and double replacement reactions. (1) Combination reactions. A combination reaction can be represented by the chemical equation A + B --> AB (one atom of A plus one atom of B yield one molecule of AB). A specific example of this type of reaction is the combination of a metal with oxygen t ...
Slide 1
... •If A originally had an octet count of only 6 then we have simply completed the octet. •If the octet of A was originally complete at 8 then we must withdraw some other pi electrons from A to make room for the newly formed bond. A becomes more negative ...
... •If A originally had an octet count of only 6 then we have simply completed the octet. •If the octet of A was originally complete at 8 then we must withdraw some other pi electrons from A to make room for the newly formed bond. A becomes more negative ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... contain atoms of two or more elements arranged in a specific ratio that is always the same. Unlike mixtures, compounds cannot be separated by physical means; separation can only be done chemically. [When a compound is formed, its properties are usually nothing like the properties of the atoms that m ...
... contain atoms of two or more elements arranged in a specific ratio that is always the same. Unlike mixtures, compounds cannot be separated by physical means; separation can only be done chemically. [When a compound is formed, its properties are usually nothing like the properties of the atoms that m ...
Experiment #3: Asymmetric Synthesis – Use of a Chiral Manganese
... glacial acetic acid is added in one portion. Product begins to precipitate from solution shortly after the addition, and it continues to precipitate resulting in a thick suspension. The reaction mixture is cooled in an ice/water bath. After sitting for at least 30 min in the ice bath, the product is ...
... glacial acetic acid is added in one portion. Product begins to precipitate from solution shortly after the addition, and it continues to precipitate resulting in a thick suspension. The reaction mixture is cooled in an ice/water bath. After sitting for at least 30 min in the ice bath, the product is ...
UNIT-1 - Andhra University
... electron affinity, electronic structure and color, electronic structure and magnetism. 2. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: The Covalent Bond: The simplest molecule H+ ion its exact description, dative Bond and its influence on Covalence-the concept of resonance and Hybridization. Multiple b ...
... electron affinity, electronic structure and color, electronic structure and magnetism. 2. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: The Covalent Bond: The simplest molecule H+ ion its exact description, dative Bond and its influence on Covalence-the concept of resonance and Hybridization. Multiple b ...
Chemical with Petro
... electron affinity, electronic structure and color, electronic structure and magnetism. 2. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: The Covalent Bond: The simplest molecule H+ ion its exact description, dative Bond and its influence on Covalence-the concept of resonance and Hybridization. Multiple b ...
... electron affinity, electronic structure and color, electronic structure and magnetism. 2. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: The Covalent Bond: The simplest molecule H+ ion its exact description, dative Bond and its influence on Covalence-the concept of resonance and Hybridization. Multiple b ...
Chapter 1
... •If A originally had an octet count of only 6 then we have simply completed the octet. •If the octet of A was originally complete at 8 then we must withdraw some other pi electrons from A to make room for the newly formed bond. A becomes more negative ...
... •If A originally had an octet count of only 6 then we have simply completed the octet. •If the octet of A was originally complete at 8 then we must withdraw some other pi electrons from A to make room for the newly formed bond. A becomes more negative ...