................................................................. Wave–particle duality of C molecules
... couplings to the environment. Such couplings are essential for the appearance of decoherence7,8, suggesting that interference experiments with large molecules should facilitate detailed studies of this process. When considering de Broglie wave phenomena of larger and more complex objects than atoms, ...
... couplings to the environment. Such couplings are essential for the appearance of decoherence7,8, suggesting that interference experiments with large molecules should facilitate detailed studies of this process. When considering de Broglie wave phenomena of larger and more complex objects than atoms, ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... The atomic weights listed on the periodic chart are the weights of a mole of atoms. For example a mole of hydrogen atoms weighs 1.00797 g and a mole of carbon atoms weighs 12.01 g. ...
... The atomic weights listed on the periodic chart are the weights of a mole of atoms. For example a mole of hydrogen atoms weighs 1.00797 g and a mole of carbon atoms weighs 12.01 g. ...
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH)
... the equilibrium. One consequence of this is that removing a product from a reaction mixture as it is formed drives the equilibrium to the right, forming more product. Thus, the alkene, which usually has a lower boiling point than the starting alcohol, can be removed by distillation as it is formed, ...
... the equilibrium. One consequence of this is that removing a product from a reaction mixture as it is formed drives the equilibrium to the right, forming more product. Thus, the alkene, which usually has a lower boiling point than the starting alcohol, can be removed by distillation as it is formed, ...
Slides
... EC 3 : hydrolases (enzymes that use water to break up some other molecules ) EC 3.4 : hydrolases that act on peptide bonds EC 3.4.11 : hydrolases that cleave off the aminoterminal amino acid from polypeptide EC 3.4.11.4 : hydrolases that cleave off the aminoReference: terminal end from a tripeptide ...
... EC 3 : hydrolases (enzymes that use water to break up some other molecules ) EC 3.4 : hydrolases that act on peptide bonds EC 3.4.11 : hydrolases that cleave off the aminoterminal amino acid from polypeptide EC 3.4.11.4 : hydrolases that cleave off the aminoReference: terminal end from a tripeptide ...
HYDROCARBONS
... only carbon and hydrogen. Two other terms which describe alkanes are saturated and paraffins. • Alkanes are SATURATED which means that each carbon is bonded to four other atoms through single covalent bonds. Hydrogen atoms usually occupy all available bonding positions after the carbons have bonded ...
... only carbon and hydrogen. Two other terms which describe alkanes are saturated and paraffins. • Alkanes are SATURATED which means that each carbon is bonded to four other atoms through single covalent bonds. Hydrogen atoms usually occupy all available bonding positions after the carbons have bonded ...
Combining transition metal catalysis and organocatalysis
... Y amamoto, H. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 10412 ...
... Y amamoto, H. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 10412 ...
Balancing a Chemical Equation
... read quickly. It shows all of the relevant information, including quantities of reactants and products, the direction of the reaction, and any catalysts in a set form that can be quickly read. ...
... read quickly. It shows all of the relevant information, including quantities of reactants and products, the direction of the reaction, and any catalysts in a set form that can be quickly read. ...
CChemical Reactions and Radioactivity
... with a basis for understanding mechanism behind many aspects (that are usually more complicated) from our day-to-day lives. For example, student acquisition of knowledge regarding the nature of chemical reactions and how they are based on the law of conservation of mass and the various types of chem ...
... with a basis for understanding mechanism behind many aspects (that are usually more complicated) from our day-to-day lives. For example, student acquisition of knowledge regarding the nature of chemical reactions and how they are based on the law of conservation of mass and the various types of chem ...
Physical Chemistry 20130410 week 2 Wednesday April 10 2013
... since dividing the formula for [C] by the formula for [D] for rate of reaction simplifies to k1/k2. If k1/k2 >>1 then [C]>>[D] so C is favored kinetically. If K1/K2<<1 then [D]>>[D] so D is favored thermodynamically. See handout for 1,3 butadiene. HBr is a very strong acid. The intermediate of a rea ...
... since dividing the formula for [C] by the formula for [D] for rate of reaction simplifies to k1/k2. If k1/k2 >>1 then [C]>>[D] so C is favored kinetically. If K1/K2<<1 then [D]>>[D] so D is favored thermodynamically. See handout for 1,3 butadiene. HBr is a very strong acid. The intermediate of a rea ...
Michaelis-Menten kinetic theory of enzyme action 1. Effect of
... MULTIPLE FACTORS AFFECT THE RATES OF ENZYME-CATALYSED REACTIONS pH. A change in pH can alter the rates of enzymecatalyzed reactions, with many enzymes exhibiting a bellshaped curve when enzyme activity is plotted against pH. Changes in pH can alter the following: 1. The ionization state of the subs ...
... MULTIPLE FACTORS AFFECT THE RATES OF ENZYME-CATALYSED REACTIONS pH. A change in pH can alter the rates of enzymecatalyzed reactions, with many enzymes exhibiting a bellshaped curve when enzyme activity is plotted against pH. Changes in pH can alter the following: 1. The ionization state of the subs ...
3672 been studied in detail by Kebarle, et al., who
... Although little mechanistic work has been carried out on the nucleophilic cleavage of sulfenate esters,6 closely analogous reactions of trivalent phosphorus with both disulfides’ and peroxidess have been demonstrated to follow a mechanistically similar pathway. In direct analogy with these systems, ...
... Although little mechanistic work has been carried out on the nucleophilic cleavage of sulfenate esters,6 closely analogous reactions of trivalent phosphorus with both disulfides’ and peroxidess have been demonstrated to follow a mechanistically similar pathway. In direct analogy with these systems, ...
Chapter 20 – The Representative Elements
... Elements of Group 5A overwhelmingly form covalent compounds. Whereas nitrogen can form a maximum of four covalent bonds, other elements in the group can form more than four covalent bonds by utilizing one or more of the nd orbitals. Nitrogen and phosphorus form simple anion with “-3” charge when rea ...
... Elements of Group 5A overwhelmingly form covalent compounds. Whereas nitrogen can form a maximum of four covalent bonds, other elements in the group can form more than four covalent bonds by utilizing one or more of the nd orbitals. Nitrogen and phosphorus form simple anion with “-3” charge when rea ...
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER SIR.S.M.TAHIR CHEMISTRY Mob: 9557076999
... Miss Rita was asked to synthesized alcohol by acidic hydration of 1-butene. She was unaware of the fact that the vessel she used had some coating of a metal and in addition to alcohol (b.p. 373 K), compound X (b.p. 353 K) was also isolated. X form bisulphate compound as well as 2, 4-dinitrophenyl hy ...
... Miss Rita was asked to synthesized alcohol by acidic hydration of 1-butene. She was unaware of the fact that the vessel she used had some coating of a metal and in addition to alcohol (b.p. 373 K), compound X (b.p. 353 K) was also isolated. X form bisulphate compound as well as 2, 4-dinitrophenyl hy ...
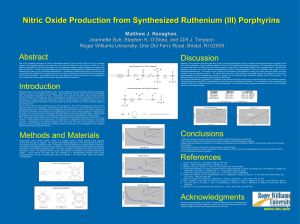
Nitric Oxide Production from Synthesized Ruthenium (III) Porphyrins
... and between cells.2 iron ion is found at the center of heme structures of living organisms. Ru (II) heme analogs are found to be more stable than their Fe (II) counterparts, while behaving with similar chemistry to the Fe derivatives since Ru is a chemically similar metal.3 The importance of investi ...
... and between cells.2 iron ion is found at the center of heme structures of living organisms. Ru (II) heme analogs are found to be more stable than their Fe (II) counterparts, while behaving with similar chemistry to the Fe derivatives since Ru is a chemically similar metal.3 The importance of investi ...
Review Chapters 4-6 problems Chem 105 Final Sp07
... and multiplying this ratio by 100%. 33. A French scientist named __________ introduced the law of conservation of matter. 34. In the reaction below, how many grams of PF5 can be produced from the reaction of 1.00 g P4 with 1.00 g F2? P4(s) + 10 F2(g) 4 PF5(g) 35. The pH of 1.0 10-5 M HNO3 is ___ ...
... and multiplying this ratio by 100%. 33. A French scientist named __________ introduced the law of conservation of matter. 34. In the reaction below, how many grams of PF5 can be produced from the reaction of 1.00 g P4 with 1.00 g F2? P4(s) + 10 F2(g) 4 PF5(g) 35. The pH of 1.0 10-5 M HNO3 is ___ ...
SUPPLEMENTAL PROBLEMS FOR CHEM 110
... 10. Which series of quantum numbers describes the orbital in which the highest energy electron in potassium resides in the ground state? ...
... 10. Which series of quantum numbers describes the orbital in which the highest energy electron in potassium resides in the ground state? ...