Electrocardiography
... • Passes to bundle of His, down Purkinje fibres • Action potential restarts ...
... • Passes to bundle of His, down Purkinje fibres • Action potential restarts ...
Control of the cardiac cycle
... • The sinoatrial node (SAN) (pacemaker) generates electrical activity at regular intervals. This causes the atrial cardiac muscles to contract (atrial systole) • The atrioventricular node (AVN) delays the electrical activity to allow blood to flow into the ventricles. • The Purkyne tissue is a speci ...
... • The sinoatrial node (SAN) (pacemaker) generates electrical activity at regular intervals. This causes the atrial cardiac muscles to contract (atrial systole) • The atrioventricular node (AVN) delays the electrical activity to allow blood to flow into the ventricles. • The Purkyne tissue is a speci ...
Heart Physiology
... • Sinoatrial (SA) node – pacemaker "sinus rhythm". • Atrioventricular (AV) node • AV Bundle • Bundle branches • Purkinje fibers ...
... • Sinoatrial (SA) node – pacemaker "sinus rhythm". • Atrioventricular (AV) node • AV Bundle • Bundle branches • Purkinje fibers ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Weber State University
... Normal P wave has amplitude of ≤ 0.25 mV Q wave is first downward deflection after P wave; signals start of ventricular depolarization R wave is positive deflection after Q wave S wave is negative deflection preceded by Q or R waves T wave follows QRS ...
... Normal P wave has amplitude of ≤ 0.25 mV Q wave is first downward deflection after P wave; signals start of ventricular depolarization R wave is positive deflection after Q wave S wave is negative deflection preceded by Q or R waves T wave follows QRS ...
History of the Development of the ECG Machine
... engineer by the name of Jan Rasmussen recognized the need to obtain reliable traces from bio signals. This led to the design and development of high quality single-use electrodes for accurate monitoring to be used with newer more streamlined ECG machines. Additional ECG Historical Trivia Einthoven i ...
... engineer by the name of Jan Rasmussen recognized the need to obtain reliable traces from bio signals. This led to the design and development of high quality single-use electrodes for accurate monitoring to be used with newer more streamlined ECG machines. Additional ECG Historical Trivia Einthoven i ...
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
... connected to separate wires or leads that connect to the ECG machine. Once the leads are placed, the test is recorded in seconds. The test itself doesn’t hurt — but after the test is done, the technician will remove the stickers, which is similar to pulling off a Band-Aid . The right and left atria ...
... connected to separate wires or leads that connect to the ECG machine. Once the leads are placed, the test is recorded in seconds. The test itself doesn’t hurt — but after the test is done, the technician will remove the stickers, which is similar to pulling off a Band-Aid . The right and left atria ...
LBBB - EDExam
... rheumatic fever, syphilis, cardiac tumours, post-cardiac surgery and in congenital heart disease. Indicates total failure of conduction in the left bundle branch system. Complete reversal of the direction of depolarisation of the interventricular septum. Delay in the initiation and velocity of depol ...
... rheumatic fever, syphilis, cardiac tumours, post-cardiac surgery and in congenital heart disease. Indicates total failure of conduction in the left bundle branch system. Complete reversal of the direction of depolarisation of the interventricular septum. Delay in the initiation and velocity of depol ...
The ECG in clinical practice: making the diagnosis at a glance
... • Impulse depolarizes successively the atria then the ventricles follow by repolarization for each . • Depolarization and repolarization are then recorder graphically as an ECG in form of a curve by means of electrodes attached to the patient’s body surface at conventional spots. • Depolarization an ...
... • Impulse depolarizes successively the atria then the ventricles follow by repolarization for each . • Depolarization and repolarization are then recorder graphically as an ECG in form of a curve by means of electrodes attached to the patient’s body surface at conventional spots. • Depolarization an ...
Electrophysiologic backround for ECG evaluation
... preliminary diagnosis, other informations on patient 2) To control technical quality of ECG record, speed of ECG record, sensuitivity of recording device (inappropriate contact of electrodes with the skin, interference of electricity, other 3) Evaluation frequency of QRS complexes, P waves 4) Evalua ...
... preliminary diagnosis, other informations on patient 2) To control technical quality of ECG record, speed of ECG record, sensuitivity of recording device (inappropriate contact of electrodes with the skin, interference of electricity, other 3) Evaluation frequency of QRS complexes, P waves 4) Evalua ...
The 12 lead ECG Some General Facts General lead placement
... pedestal around which a person can move while taking photographs (different views) from all angles. See skeleton with heart inside. ...
... pedestal around which a person can move while taking photographs (different views) from all angles. See skeleton with heart inside. ...
ECG - WordPress.com
... • 1938 -AHA and Cardiac society of great Britan defined and position of chest leads • 1942- Goldberger increased Wilson’s Unipolar lead voltage by 50% and made Augmented leads • 2005- successful reduction in time of onset of chest pain and PTCA by wireless ...
... • 1938 -AHA and Cardiac society of great Britan defined and position of chest leads • 1942- Goldberger increased Wilson’s Unipolar lead voltage by 50% and made Augmented leads • 2005- successful reduction in time of onset of chest pain and PTCA by wireless ...
File
... • 1938 -AHA and Cardiac society of great Britan defined and position of chest leads • 1942- Goldberger increased Wilson’s Unipolar lead voltage by 50% and made Augmented leads • 2005- successful reduction in time of onset of chest pain and PTCA by wireless transmission of ECG on his PDA. ...
... • 1938 -AHA and Cardiac society of great Britan defined and position of chest leads • 1942- Goldberger increased Wilson’s Unipolar lead voltage by 50% and made Augmented leads • 2005- successful reduction in time of onset of chest pain and PTCA by wireless transmission of ECG on his PDA. ...
Principles of Vectorial Analysis of EKG`s (cont`d)
... vector, with the arrowhead pointing in the positive ...
... vector, with the arrowhead pointing in the positive ...
Physiologic signals - O6U E
... • Instruct the patient to place their arms down by their side and to relax their shoulders. • Make sure the patient’s legs are uncrossed. • Move any electrical devices, such as cell phones, away from the patient as they may interfere with the ...
... • Instruct the patient to place their arms down by their side and to relax their shoulders. • Make sure the patient’s legs are uncrossed. • Move any electrical devices, such as cell phones, away from the patient as they may interfere with the ...
EKG
... ELECTROCARDIOGRAM An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a graphic representation of the heart’s electrical activity. ...
... ELECTROCARDIOGRAM An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a graphic representation of the heart’s electrical activity. ...
Slide ()
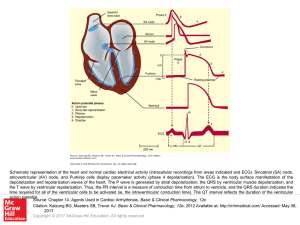
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
1893
... the electrical activity of the heart. The breakthrough came when Willem Einthoven, working in Leiden, The Netherlands, used the string galvanometer invented by him in 1901, which was much more sensitive than the capillary electrometer that Waller had used. He connected electrodes to a patient and sh ...
... the electrical activity of the heart. The breakthrough came when Willem Einthoven, working in Leiden, The Netherlands, used the string galvanometer invented by him in 1901, which was much more sensitive than the capillary electrometer that Waller had used. He connected electrodes to a patient and sh ...
Chapter02_Detailed_Answers
... Bipolar leads require two electrodes of opposite polarity. Bipolar leads have a third (and often a fourth) electrode called a ground. The ground is used to help prevent electrical interference from appearing on the ECG and has zero electrical potential when compared with the positive and negative el ...
... Bipolar leads require two electrodes of opposite polarity. Bipolar leads have a third (and often a fourth) electrode called a ground. The ground is used to help prevent electrical interference from appearing on the ECG and has zero electrical potential when compared with the positive and negative el ...
ECG ONE OF THE MOST USEFUL METHODS OF THE 20TH
... The triangle is composed of the leads I, II, and III forming the shape. Leads aVL, aVR and aVF perpendicularly intersect each side to the triangle. Together, these six leads can paint a large picture of the patient’s overall cardiac health. Using these leads to assess axis and aid in rhythm determin ...
... The triangle is composed of the leads I, II, and III forming the shape. Leads aVL, aVR and aVF perpendicularly intersect each side to the triangle. Together, these six leads can paint a large picture of the patient’s overall cardiac health. Using these leads to assess axis and aid in rhythm determin ...
Electrocardiography - PharmStressTech.com
... The ECG is a record of the voltage variations of the heart plotted against time. From the surface of the body, an ECG measures the electrical currents that the heart generates. The waveforms recorded by the ECG are labeled alphabetically from P to U. Each waveform represents a particular event in th ...
... The ECG is a record of the voltage variations of the heart plotted against time. From the surface of the body, an ECG measures the electrical currents that the heart generates. The waveforms recorded by the ECG are labeled alphabetically from P to U. Each waveform represents a particular event in th ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.