PDF - Journal of Clinical and Translational Research
... culmination of this unpredictability was found when vagal bursts were delivered in each heart beat (like the predicted output from the baroreflex) at a critically late timing in the sinus node cycle, where the effect just might or might not reset the ongoing depolarization of the sinus node (Figure ...
... culmination of this unpredictability was found when vagal bursts were delivered in each heart beat (like the predicted output from the baroreflex) at a critically late timing in the sinus node cycle, where the effect just might or might not reset the ongoing depolarization of the sinus node (Figure ...
Sudden death of a premature new-born with hypoplastic left heart
... [4-7]. But the left ventricle exists and has very thick walls, with a nearly embrionar aspect of the myocardium, which stopped its evolution. This issue might be due to the lack of blood flow through the ventricle. ...
... [4-7]. But the left ventricle exists and has very thick walls, with a nearly embrionar aspect of the myocardium, which stopped its evolution. This issue might be due to the lack of blood flow through the ventricle. ...
Change in heart rate after prolong times of exercise. PARTNER ONE
... 3. Now try the strenuous exercise that was instructed to you by your teacher Immediately after the exercisee. Find your pulse on the side of your neck or on the radius side of your wrist. f. Count how many beats your heart makes in 20 seconds (your partner can keep the time). g. Multiply this numbe ...
... 3. Now try the strenuous exercise that was instructed to you by your teacher Immediately after the exercisee. Find your pulse on the side of your neck or on the radius side of your wrist. f. Count how many beats your heart makes in 20 seconds (your partner can keep the time). g. Multiply this numbe ...
Combining Form Meaning
... MAJOR VALVES OF THE HEART tricuspid valve (cusps are flaps of the valves): between right atrium and right ventricle pulmonary valve: between right ventricle and ...
... MAJOR VALVES OF THE HEART tricuspid valve (cusps are flaps of the valves): between right atrium and right ventricle pulmonary valve: between right ventricle and ...
Idiopathic ventricular tachycardia arising from the right ventricular apex
... Figure 3 (A) Intracardiac ventricular electrograms from three different locations within the right ventricle. (B) Surface leads I, AVF, V1, intracardiac electrograms from the ablation catheter at the successful site and virtual unipolar electrograms computed by the ESI system are shown. (C) Isopoten ...
... Figure 3 (A) Intracardiac ventricular electrograms from three different locations within the right ventricle. (B) Surface leads I, AVF, V1, intracardiac electrograms from the ablation catheter at the successful site and virtual unipolar electrograms computed by the ESI system are shown. (C) Isopoten ...
Cardiac Arrhythmia
... •Re-entry: when a cardiac impulse travels in a path such as to return to and reactivate its original site and self perpetuate rapid reactivation independent of normal sinus node conduction ...
... •Re-entry: when a cardiac impulse travels in a path such as to return to and reactivate its original site and self perpetuate rapid reactivation independent of normal sinus node conduction ...
A1981LC32900001
... Pantridge J F & Geddes J S. A mobile intensive-care unit in the management of myocardial infarction. Lancet 2:271-3, 1967. [Cardiac Dept., Royal Victoria Hosp., Belfast, Northern Ireland] ...
... Pantridge J F & Geddes J S. A mobile intensive-care unit in the management of myocardial infarction. Lancet 2:271-3, 1967. [Cardiac Dept., Royal Victoria Hosp., Belfast, Northern Ireland] ...
Diagnostic Electrophysiology Studies
... multiple electrodes to collect data from multiple sites simultaneously, with creation of a three-dimensional display. ...
... multiple electrodes to collect data from multiple sites simultaneously, with creation of a three-dimensional display. ...
Slide 1 - AccessCardiology
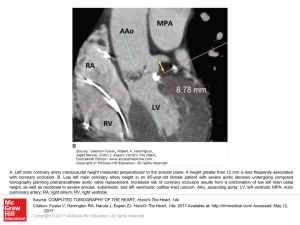
... A. Left main coronary artery craniocaudal height measured perpendicular to the annular plane. A height greater than 12 mm is less frequently associated with coronary occlusion. B. Low left main coronary artery height in an 85-year-old female patient with severe aortic stenosis undergoing computed to ...
... A. Left main coronary artery craniocaudal height measured perpendicular to the annular plane. A height greater than 12 mm is less frequently associated with coronary occlusion. B. Low left main coronary artery height in an 85-year-old female patient with severe aortic stenosis undergoing computed to ...
The Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Introduction
... epithelium and CT surrounding the heart muscle itself b) Parietal Pericardium = outer serous membrane lining inner surface of fibrous pericardium c) Between visceral and parietal pericardia is the pericardial cavity, filled with serous fluid for lubrication 2. Fibrous Pericardium = outermost (3rd me ...
... epithelium and CT surrounding the heart muscle itself b) Parietal Pericardium = outer serous membrane lining inner surface of fibrous pericardium c) Between visceral and parietal pericardia is the pericardial cavity, filled with serous fluid for lubrication 2. Fibrous Pericardium = outermost (3rd me ...
Chapter_049
... Unipolar leads with a single positive electrode that uses the right leg for grounding aVr – records the electrical activity of the atria from the right shoulder; P waves and QRS complexes are deflected below the baseline aVl – records the electrical activity of the lateral wall of the left ventricle ...
... Unipolar leads with a single positive electrode that uses the right leg for grounding aVr – records the electrical activity of the atria from the right shoulder; P waves and QRS complexes are deflected below the baseline aVl – records the electrical activity of the lateral wall of the left ventricle ...
Biology 118
... 26. Post-menopausal women were often recommended to take calcium & Vit. D to reduce their risk of _______. In Fig. 5, women taking the supplements had a ______ risk of having a heart attack or a stroke, than women not taking these supplements. a. osteoporosis – slightly lower b. lung cancer – slight ...
... 26. Post-menopausal women were often recommended to take calcium & Vit. D to reduce their risk of _______. In Fig. 5, women taking the supplements had a ______ risk of having a heart attack or a stroke, than women not taking these supplements. a. osteoporosis – slightly lower b. lung cancer – slight ...
DOC - Gericareonline.net
... chambers of the heart. The heart is made up of four chambers. The upper two chambers of the heart are called the atria, and the lower two are called the ventricles. This irregular heart rhythm often causes the upper chambers to beat too fast. This leaves too little time for blood to pump into the tw ...
... chambers of the heart. The heart is made up of four chambers. The upper two chambers of the heart are called the atria, and the lower two are called the ventricles. This irregular heart rhythm often causes the upper chambers to beat too fast. This leaves too little time for blood to pump into the tw ...
information
... of the heart and blood vessels electrical conduction system of the heart cardiac cycle (electric system) EKG strip analysis (P,Q,R,S,T wave form interpretation) normal sinus rhythm, sinus bradycardis, sinus tachycardia basic EKG interpretation, sinus rhythm, and ventricular rhythms, asysto ...
... of the heart and blood vessels electrical conduction system of the heart cardiac cycle (electric system) EKG strip analysis (P,Q,R,S,T wave form interpretation) normal sinus rhythm, sinus bradycardis, sinus tachycardia basic EKG interpretation, sinus rhythm, and ventricular rhythms, asysto ...
Document
... When during the cardiac cycle do ventricles contain their maximal amount of blood? What is this quantity called? a. at the end of ventricular systole; ESV b. at the end of atrial systole; EDV c. at the end of ventricular diastole; EDV ...
... When during the cardiac cycle do ventricles contain their maximal amount of blood? What is this quantity called? a. at the end of ventricular systole; ESV b. at the end of atrial systole; EDV c. at the end of ventricular diastole; EDV ...
Lab 4 Toad Heart Lab Protocol.pages
... allow calcium and sodium ions to slowly leak into the cells. This leaking causes a slow depolarization to threshold, thus causing the firing of an action potential, and initiating muscle contraction. The cells that are most "leaky" to ions and that depolarize fastest control the rate of contraction ...
... allow calcium and sodium ions to slowly leak into the cells. This leaking causes a slow depolarization to threshold, thus causing the firing of an action potential, and initiating muscle contraction. The cells that are most "leaky" to ions and that depolarize fastest control the rate of contraction ...
Cardiovascular System: Physiology
... ischemia (inadequate blood supply) of the myocardium can lead to fibrillation ...
... ischemia (inadequate blood supply) of the myocardium can lead to fibrillation ...
5 Bioelectric Measurements Experiment 5.1
... When the heart is at rest, the inside of the heart muscle cells are negatively charged and the exterior of the cells are positively charged. The cells are said to be polarized. Depolarization and repolarization of the heart muscle cells causes the heart to contract and blood to be pumped throughout ...
... When the heart is at rest, the inside of the heart muscle cells are negatively charged and the exterior of the cells are positively charged. The cells are said to be polarized. Depolarization and repolarization of the heart muscle cells causes the heart to contract and blood to be pumped throughout ...
Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy
... atherosclerotic disease, and the metabolic syndrome. Stage B HF includes patients with structural heart disease (i.e., previous myocardial infarction [MI], asymptomatic valvular disease, and LV hypertrophy) but without symptoms of HF. Stage C HF is structural heart disease with prior or current symp ...
... atherosclerotic disease, and the metabolic syndrome. Stage B HF includes patients with structural heart disease (i.e., previous myocardial infarction [MI], asymptomatic valvular disease, and LV hypertrophy) but without symptoms of HF. Stage C HF is structural heart disease with prior or current symp ...
Normal MCG - Click on this File
... vector’s dynamics (changes over time) helps understanding the underlying electrical process. ...
... vector’s dynamics (changes over time) helps understanding the underlying electrical process. ...
AQT90 FLEX parameters
... These clots may grow very large and block the blood flow in the legs ...
... These clots may grow very large and block the blood flow in the legs ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.