Non-Invasive Transcutaneous Pacing
... of 60. Since the two rates are very close, pacer spikes and intrinsic beats may occur very close to each other for several seconds. In this circumstance, the defibrillator may think the beats are paced based on its simple timing algorithm, but in fact the beats are intrinsic and the timing coinciden ...
... of 60. Since the two rates are very close, pacer spikes and intrinsic beats may occur very close to each other for several seconds. In this circumstance, the defibrillator may think the beats are paced based on its simple timing algorithm, but in fact the beats are intrinsic and the timing coinciden ...
Chapter 7- Cardiovascular System
... Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP) (pg 267-269) TO ASSESS RIGHT SIDED HEART STATUS!!! 1. Reflects status of the right side of the heart 2. Level at which the pulse is visible gives an indication of right atrial pressure a. to assess the patient will be supine with the head elevated. b. turn patients head ...
... Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP) (pg 267-269) TO ASSESS RIGHT SIDED HEART STATUS!!! 1. Reflects status of the right side of the heart 2. Level at which the pulse is visible gives an indication of right atrial pressure a. to assess the patient will be supine with the head elevated. b. turn patients head ...
Heart Lab
... 12. Why are the ventricle walls so much thicker?(Think function) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Find the one-way valves that separate each atria from its ventricle. They look like flaps of ...
... 12. Why are the ventricle walls so much thicker?(Think function) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Find the one-way valves that separate each atria from its ventricle. They look like flaps of ...
Comment on Ferrannini et al. CV Protection in the
... it is tempting to speculate that this mechanism serves as a rescue strategy of the heart to secure its energy demand (3). Together with our previous work and in the light of the elegant thrifty substrate hypothesis by Ferrannini et al. (1), we hypothesize that the heart possesses an endocrine factor ...
... it is tempting to speculate that this mechanism serves as a rescue strategy of the heart to secure its energy demand (3). Together with our previous work and in the light of the elegant thrifty substrate hypothesis by Ferrannini et al. (1), we hypothesize that the heart possesses an endocrine factor ...
AFA Australia Atrial Flutter FACT sheet
... Atrial Flutter is a disturbance of the heart rhythm (arrhythmia) where the upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat very rapidly. The atria are responsible for the control of the heart rate, so this usually results in your pulse becoming fast and often regular. A person may not feel any symptoms whe ...
... Atrial Flutter is a disturbance of the heart rhythm (arrhythmia) where the upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat very rapidly. The atria are responsible for the control of the heart rate, so this usually results in your pulse becoming fast and often regular. A person may not feel any symptoms whe ...
Why QRS Duration Should Be Replaced by Better Measures of
... time, AP antero-posterior, L/RAO left/right anterior oblique, RV right ventricle (adapted from [51]) ...
... time, AP antero-posterior, L/RAO left/right anterior oblique, RV right ventricle (adapted from [51]) ...
- SlideBoom
... Basically, congestive heart failure occurs when the heart begins to fail in its role as a blood pumping muscle. People afflicted with diabetes, high blood pressure, and coronary heart disease signaled by heart attacks or heart rhythm problems run a significantly higher risk of developing Congestive ...
... Basically, congestive heart failure occurs when the heart begins to fail in its role as a blood pumping muscle. People afflicted with diabetes, high blood pressure, and coronary heart disease signaled by heart attacks or heart rhythm problems run a significantly higher risk of developing Congestive ...
Anatomy of the Cardiovascular System
... opening of superior vena cava Atrioventricular node: in rt atrium along lower part of interatrial septum Atrioventricular bundle: originate in AV node & extend by 2 branches thru the 2 sides of the ...
... opening of superior vena cava Atrioventricular node: in rt atrium along lower part of interatrial septum Atrioventricular bundle: originate in AV node & extend by 2 branches thru the 2 sides of the ...
The Heart Myotonic Dystrophy - Myotonic Dystrophy Support Group
... structure of the heart. The structure of the heart in myotonic dystrophy is usually normal but it is important to make sure that other problems are not affecting the heart as well as those caused by myotonic dystrophy. ...
... structure of the heart. The structure of the heart in myotonic dystrophy is usually normal but it is important to make sure that other problems are not affecting the heart as well as those caused by myotonic dystrophy. ...
Mechanical manifestation of human hemodynamics
... Using the force plate and a special bed we measured the force plate output and the ECG signal on 17 healthy adult males. In three cases we measured also the heart sounds. In such a way we obtained a 7 or 8 dimensional time series. The used sampling rate was 1000 Hz. ...
... Using the force plate and a special bed we measured the force plate output and the ECG signal on 17 healthy adult males. In three cases we measured also the heart sounds. In such a way we obtained a 7 or 8 dimensional time series. The used sampling rate was 1000 Hz. ...
fibrous skeleton insulates atria from ventricles
... atria contract, force additional blood into ventricles ventricles now contain end-diastolic volume (EDV) of about 130 ml of blood ...
... atria contract, force additional blood into ventricles ventricles now contain end-diastolic volume (EDV) of about 130 ml of blood ...
Cardiovascular system
... blood then returns to the left atrium, passes through the left ventricle and is pumped out through the aorta to the systemic circulation−where the oxygen is used and metabolized to carbon dioxide. In addition, the blood carries nutrients from the liver and gastrointestinal tract to various organs of ...
... blood then returns to the left atrium, passes through the left ventricle and is pumped out through the aorta to the systemic circulation−where the oxygen is used and metabolized to carbon dioxide. In addition, the blood carries nutrients from the liver and gastrointestinal tract to various organs of ...
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
... symptoms result from inability of the heart to pump enough blood to the periphery (from left heart), or to the lungs (from the right heart) a) forward failure of left heart:- muscle weakness, fatigue, ...
... symptoms result from inability of the heart to pump enough blood to the periphery (from left heart), or to the lungs (from the right heart) a) forward failure of left heart:- muscle weakness, fatigue, ...
Figure 12-3(a)
... – Right ventricle pumps blood through pulmonary semilunar valve • Enters pulmonary trunk • Flows to lungs through right, left pulmonary arteries where it picks up oxygen ...
... – Right ventricle pumps blood through pulmonary semilunar valve • Enters pulmonary trunk • Flows to lungs through right, left pulmonary arteries where it picks up oxygen ...
Atrial Fibrillation and Sudden Cardiac Death
... (13–15). Furthermore, digoxin is also associated with increased risks of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks, even after adjustment for AF (16). This finding represents yet another association that requires further investigation, particularly given the known safety concerns surrounding digox ...
... (13–15). Furthermore, digoxin is also associated with increased risks of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks, even after adjustment for AF (16). This finding represents yet another association that requires further investigation, particularly given the known safety concerns surrounding digox ...
Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Atrial systole begins: Atrial
... Side Note: Decreased Compliance leads to decreased stretch of the heart. As per Frank Starlings Law this means less force of contraction. With less force of contraction there will be a greater end systolic volume which will cause a decrease stroke volume. Since CO = Stroke Volume X HR a decreased St ...
... Side Note: Decreased Compliance leads to decreased stretch of the heart. As per Frank Starlings Law this means less force of contraction. With less force of contraction there will be a greater end systolic volume which will cause a decrease stroke volume. Since CO = Stroke Volume X HR a decreased St ...
MADIT II - Primary Prevention of SCD - 2004
... Are Doctors and Patients Paying Attention To This Issue In the typical CHF clinic (Cardiology Run) 25-35% of eligible patients have no ICD. Many patients will never use their ICD ...
... Are Doctors and Patients Paying Attention To This Issue In the typical CHF clinic (Cardiology Run) 25-35% of eligible patients have no ICD. Many patients will never use their ICD ...
A Case of Left Atrial Sarcoma Presenting with Mitral Valve
... Introduction: Primary cardiac tumors are extremely rare with an incidence ranging from 0.0017 to 0.019% [1]. Myxoma, a benign tumor, represent by far almost three quarters of them while the remaining are malignant, predominantly sarcomas [2], [3]. On the other hand, metastatic tumors in the heart ar ...
... Introduction: Primary cardiac tumors are extremely rare with an incidence ranging from 0.0017 to 0.019% [1]. Myxoma, a benign tumor, represent by far almost three quarters of them while the remaining are malignant, predominantly sarcomas [2], [3]. On the other hand, metastatic tumors in the heart ar ...
Real-time and patient-specific simulation of the heart. Application to
... electrophysiological and mechanical behaviour of the heart at scales ranging from cell to tissue and organ levels. Principles of continuum mechanics are key in creating a realistic multi-scale model of the heart. They allow to describe the directly observable behaviour of the heart by incorporating ...
... electrophysiological and mechanical behaviour of the heart at scales ranging from cell to tissue and organ levels. Principles of continuum mechanics are key in creating a realistic multi-scale model of the heart. They allow to describe the directly observable behaviour of the heart by incorporating ...
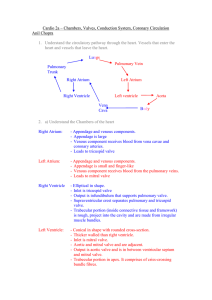
Chambers Valves, Conduction System, Coronary Circulation
... has 3 cusps (leaflets), antero-superior, mural, septal. between right atria and ventricles. Mitral (bicuspid) Valves: has 2 cusps between left atria and ventricles, anterior and posterior. Arterial Valves (semilunar) prevent reflux from arteries into ventricles oven when ventricles contrac ...
... has 3 cusps (leaflets), antero-superior, mural, septal. between right atria and ventricles. Mitral (bicuspid) Valves: has 2 cusps between left atria and ventricles, anterior and posterior. Arterial Valves (semilunar) prevent reflux from arteries into ventricles oven when ventricles contrac ...
File - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... a. Atria must contract before the ventricles. b. AV valves must have time to close. c. Contraction of papillary muscle must begin before ventricular contraction. d. Tachycardia results if the delay is absent. BACK TO GAME ...
... a. Atria must contract before the ventricles. b. AV valves must have time to close. c. Contraction of papillary muscle must begin before ventricular contraction. d. Tachycardia results if the delay is absent. BACK TO GAME ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.