sads support group ireland
... Am I at risk of SADS? A family history of sudden unexplained death, particularly of people under 50 years of age could suggest that there is an inherited heart problem and risk of SADS or SCD in your family. A history of cot death (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome – SIDS) is also very relevant. While a ...
... Am I at risk of SADS? A family history of sudden unexplained death, particularly of people under 50 years of age could suggest that there is an inherited heart problem and risk of SADS or SCD in your family. A history of cot death (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome – SIDS) is also very relevant. While a ...
acoustic cardiography
... time intervals as a non-invasive method of haemodynamic evaluation diminished. This was partly because their acquisition was labour-intensive and partly because of the increasing popularity of echocardiography and radionuclide studies. Acoustic cardiography (Audicor®, Inovise Medical, Inc., Portland ...
... time intervals as a non-invasive method of haemodynamic evaluation diminished. This was partly because their acquisition was labour-intensive and partly because of the increasing popularity of echocardiography and radionuclide studies. Acoustic cardiography (Audicor®, Inovise Medical, Inc., Portland ...
Slide 1
... 4 Excitation spreads down AV bundle. 5 Purkinje fibers distribute excitation through ventricular myocardium. ...
... 4 Excitation spreads down AV bundle. 5 Purkinje fibers distribute excitation through ventricular myocardium. ...
Ischemic Heart Disease MI
... of even the most severe ischemia, myocardial injury is potentially reversible. Thereafter, progressive loss of viability occurs that is complete by 6 to 12 hours. The benefits of reperfusion are greatest when it is achieved early, and are progressively lost when reperfusion is delayed ...
... of even the most severe ischemia, myocardial injury is potentially reversible. Thereafter, progressive loss of viability occurs that is complete by 6 to 12 hours. The benefits of reperfusion are greatest when it is achieved early, and are progressively lost when reperfusion is delayed ...
Obstructive Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
... At 3 days of age, an echocardiography followup showed an thrombi in the aortic arch. Thereupon, emergent surgery to remove the thrombi and to total repair of his VSD and PDA was performed. (Figure 4) Unexpectedly, high oxygenated blood was found in the superior vena cava (SVC) while weaning off the ...
... At 3 days of age, an echocardiography followup showed an thrombi in the aortic arch. Thereupon, emergent surgery to remove the thrombi and to total repair of his VSD and PDA was performed. (Figure 4) Unexpectedly, high oxygenated blood was found in the superior vena cava (SVC) while weaning off the ...
Test Bank Corp
... 10. T or F. The semilunar valves are the aortic and mitral valves. 11. T or F. The job of the heart valves is to prevent backflow of blood. 12. T or F. The vena cava is a large artery that carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. 13. T or F. The three main coronary arteries are the aorta ...
... 10. T or F. The semilunar valves are the aortic and mitral valves. 11. T or F. The job of the heart valves is to prevent backflow of blood. 12. T or F. The vena cava is a large artery that carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. 13. T or F. The three main coronary arteries are the aorta ...
What Is Heart Disease?
... Non-modifiable risk factors- there are four non-modifiable factors increase a person's risk of cardiovascular disease: • age • male gender • family history • race. ...
... Non-modifiable risk factors- there are four non-modifiable factors increase a person's risk of cardiovascular disease: • age • male gender • family history • race. ...
Complex Valvular Heart Disease: A Team Approach Brings
... who identified therapies that could improve the safety of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and reduce the risk of post-procedure bleeding. These two appointments will strengthen our efforts to advance understanding of heart disease in the Center for Cardiovascular Research (CCR) and the Cent ...
... who identified therapies that could improve the safety of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and reduce the risk of post-procedure bleeding. These two appointments will strengthen our efforts to advance understanding of heart disease in the Center for Cardiovascular Research (CCR) and the Cent ...
10 signs of heart disease in cats
... Heart disease in cats presents itself in much the same way as in dogs, with a few exceptions. The biggest difference is that cats tend to mask their signs better than dogs, and therefore go long ...
... Heart disease in cats presents itself in much the same way as in dogs, with a few exceptions. The biggest difference is that cats tend to mask their signs better than dogs, and therefore go long ...
Artificial Heart Valves
... There are two types, tissue, and homograft. Tissue: Made from animal tissue, usually pig, but sometimes horses and cows. Last for an average of 15 years. Are similar to human tissue so they don’t require maintenance through blood thinners and blood tests. Higher chance of rejection. Homograft Blood ...
... There are two types, tissue, and homograft. Tissue: Made from animal tissue, usually pig, but sometimes horses and cows. Last for an average of 15 years. Are similar to human tissue so they don’t require maintenance through blood thinners and blood tests. Higher chance of rejection. Homograft Blood ...
Venous Pressure
... Place one pencil at sternal angle vertical to ground & other pencil at upper limit of venous pulsation horizontal to the ground Measure length of the vertical pencil in cm btw the sternal angle & where it is crossed by the horizontal pencil. Normal JVP up to 3 cm ...
... Place one pencil at sternal angle vertical to ground & other pencil at upper limit of venous pulsation horizontal to the ground Measure length of the vertical pencil in cm btw the sternal angle & where it is crossed by the horizontal pencil. Normal JVP up to 3 cm ...
Quality of Life Analysis for Patients Receiving Heart Implants
... in double quotes, and can contain any combination of letters, numbers, spaces, and punctuation. Text strings were examined as predefined variables. This was done using SAS/Text Miner. Clustering of medications was done using SAS Text Miner with expectation maximization. The expectation-maximization ...
... in double quotes, and can contain any combination of letters, numbers, spaces, and punctuation. Text strings were examined as predefined variables. This was done using SAS/Text Miner. Clustering of medications was done using SAS Text Miner with expectation maximization. The expectation-maximization ...
08_Main symptoms and syndromes in ischemic heart disease
... • 6. Effect of different drugs on pain. ...
... • 6. Effect of different drugs on pain. ...
CENTRAL LINES
... Patient is moved to the side of the bed so physician would not lean over The bed is high enough so physician would not have to stoop over Patient should be flat without a pillow, Trendelenburg position if patient is ...
... Patient is moved to the side of the bed so physician would not lean over The bed is high enough so physician would not have to stoop over Patient should be flat without a pillow, Trendelenburg position if patient is ...
46. Anatomy of the heart
... • Defined by branch that gives rise to posterior interventricular a. – Right (80%) • From right coronary a. ...
... • Defined by branch that gives rise to posterior interventricular a. – Right (80%) • From right coronary a. ...
In the Footsteps of Virchow - JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging
... cryoimaging and histopathology was successfully introduced. Early data yielded sensitivities of OCT within range reported in previous research. Errors in screening are typically related to misidentification of lipid versus fibrous and calcified plaques (5). Cryoimaging is a promising adjuvant for plaqu ...
... cryoimaging and histopathology was successfully introduced. Early data yielded sensitivities of OCT within range reported in previous research. Errors in screening are typically related to misidentification of lipid versus fibrous and calcified plaques (5). Cryoimaging is a promising adjuvant for plaqu ...
Clinical Implications of cTnI Elevation Curve following Primary
... primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) for ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), yet its possible prognostic implications and relation to infarct‐related parameters have not been explored. Methods: We prospectively collected cardiac troponin I levels from blood samples of 175 c ...
... primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) for ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), yet its possible prognostic implications and relation to infarct‐related parameters have not been explored. Methods: We prospectively collected cardiac troponin I levels from blood samples of 175 c ...
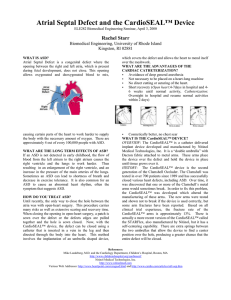
Atrial Septal Defect and the CardioSEAL™ Device
... implant device developed and manufactured by Nitinol Medical Technologies, Inc. It is a “double umbrella” with Dacron fabric attached to metal arms. These arms place the device over the defect and hold the device in place until tissue grows over it. HISTORY: The CardioSEAL™ device is the second gene ...
... implant device developed and manufactured by Nitinol Medical Technologies, Inc. It is a “double umbrella” with Dacron fabric attached to metal arms. These arms place the device over the defect and hold the device in place until tissue grows over it. HISTORY: The CardioSEAL™ device is the second gene ...
20-1 Anatomy of the Heart
... Plaques can be removed surgically via catheter (laser or “roto-rooter”) or via balloon angioplasty; stents (wire mesh) used to keep artery open Coronary bypass surgery - use healthy veins (from legs) to create anastomoses around blockages; most people have 4 major coronary arteries, hence “quadruple ...
... Plaques can be removed surgically via catheter (laser or “roto-rooter”) or via balloon angioplasty; stents (wire mesh) used to keep artery open Coronary bypass surgery - use healthy veins (from legs) to create anastomoses around blockages; most people have 4 major coronary arteries, hence “quadruple ...
Case Study - Zephyr™ Performance Systems
... the miners’ response to physical activity in that particular extreme environment. Then, I would contrast it with the predictive physiological behavioral pattern I had developed based in the cardiac and respiratory response to psychological stress and my previous experiences on human response to ext ...
... the miners’ response to physical activity in that particular extreme environment. Then, I would contrast it with the predictive physiological behavioral pattern I had developed based in the cardiac and respiratory response to psychological stress and my previous experiences on human response to ext ...
Physics of the Heart: Dynamics & Control of Ventricular
... reentrant rhythms -a dual pathway with differing electrophysiologic properties; suggested that the twin conditions of unidirectional block and slow conduction may occur in abnormal myocardial tissue - allowing a circulating wavefront to be sustained as conductive tissue is always available for excit ...
... reentrant rhythms -a dual pathway with differing electrophysiologic properties; suggested that the twin conditions of unidirectional block and slow conduction may occur in abnormal myocardial tissue - allowing a circulating wavefront to be sustained as conductive tissue is always available for excit ...
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG*) is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time using electrodes placed on a patient's body. These electrodes detect the tiny electrical changes on the skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each heartbeat.In a conventional 12 lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient's limbs and on the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart's electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles (""leads"") and is recorded over a period of time (usually 10 seconds). In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart's electrical depolarization is captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle. The graph of voltage versus time produced by this noninvasive medical procedure is referred to as an electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG).During each heartbeat, a healthy heart will have an orderly progression of depolarization that starts with pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node, spreads out through the atrium, passes through the atrioventricular node down into the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers spreading down and to the left throughout the ventricles. This orderly pattern of depolarization gives rise to the characteristic ECG tracing. To the trained clinician, an ECG conveys a large amount of information about the structure of the heart and the function of its electrical conduction system. Among other things, an ECG can be used to measure the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart chambers, the presence of any damage to the heart's muscle cells or conduction system, the effects of cardiac drugs, and the function of implanted pacemakers.