II BCA SYLLABUS
... Stacks: Definition, ADT, Array and Linked representations, Implementations and Applications Queues: Definition, ADT, Array and Linked representations, Circular Queues, Dequeues, Implementations and Applications. OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING JAVA UNIT I: Introduction to java: Features of Java, T ...
... Stacks: Definition, ADT, Array and Linked representations, Implementations and Applications Queues: Definition, ADT, Array and Linked representations, Circular Queues, Dequeues, Implementations and Applications. OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING USING JAVA UNIT I: Introduction to java: Features of Java, T ...
Honors Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review
... 11) Explain the Big Bang Theory. ______________________________________________________________________ ...
... 11) Explain the Big Bang Theory. ______________________________________________________________________ ...
Topics on Chapter 10 Test: The Mole
... to counteract the effects of histamine. A sample of histamine having a mass of 385 mg is composed of 208 mg of carbon, 31 mg hydrogen, and 146 mg nitrogen. The molar mass of histamine is 111g/mol. What is the molecular formula for histamine? ...
... to counteract the effects of histamine. A sample of histamine having a mass of 385 mg is composed of 208 mg of carbon, 31 mg hydrogen, and 146 mg nitrogen. The molar mass of histamine is 111g/mol. What is the molecular formula for histamine? ...
CHY - 101 - NIT Arunachal Pradesh
... Introduction to Resonance and Hyperconjugation with examples. Solutions of problems related Electro negativity and Electron affinity. Introduction to carbocation, carbanion and free radicals with examples. Properties of Carbocation, carbanion and free radicals. Discussion of carbocation/carbanion/fr ...
... Introduction to Resonance and Hyperconjugation with examples. Solutions of problems related Electro negativity and Electron affinity. Introduction to carbocation, carbanion and free radicals with examples. Properties of Carbocation, carbanion and free radicals. Discussion of carbocation/carbanion/fr ...
Chemistry (CP) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 10. a substance formed in a chemical reaction ____ 11. starting substance in a chemical reaction Match each item with the correct statement below. a. atomic emission spectrum d. photon b. frequency e. quantum c. wavelength f. spectrum ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ...
... ____ 10. a substance formed in a chemical reaction ____ 11. starting substance in a chemical reaction Match each item with the correct statement below. a. atomic emission spectrum d. photon b. frequency e. quantum c. wavelength f. spectrum ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ...
Unit Two Objectives
... a. Aristotle: Matter is made of Air, Fire, Earth, & Water. b. Democritus: The first to say that matter is composed of atom, or “atomos.” c. Dalton: Had five basic principles in his model of the atom d. Thomson: discovered the charge of the electron by deflecting the flow of electrons through his Cat ...
... a. Aristotle: Matter is made of Air, Fire, Earth, & Water. b. Democritus: The first to say that matter is composed of atom, or “atomos.” c. Dalton: Had five basic principles in his model of the atom d. Thomson: discovered the charge of the electron by deflecting the flow of electrons through his Cat ...
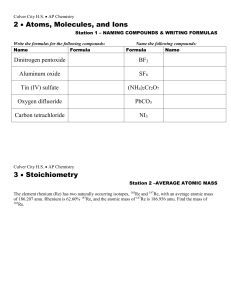
Average Atomic Mass
... Average Atomic Mass - the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of the element. Average Atomic Mass = [(isotope mass)(percent abundance)]/100% To solve for percent abundance assign the first isotope percentage x and the second isotope percentage equal to 100% - x 49. There are two natura ...
... Average Atomic Mass - the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of the element. Average Atomic Mass = [(isotope mass)(percent abundance)]/100% To solve for percent abundance assign the first isotope percentage x and the second isotope percentage equal to 100% - x 49. There are two natura ...
Review Station Ideas
... 3 Stoichiometry Station 10 – HYDRATES A student is assigned the task of determining the number of moles of water in one mole of MgCl2 · n H2O. The student collects the data shown in the following table. Mass of empty container Initial mass of sample and container Mass of sample and container after ...
... 3 Stoichiometry Station 10 – HYDRATES A student is assigned the task of determining the number of moles of water in one mole of MgCl2 · n H2O. The student collects the data shown in the following table. Mass of empty container Initial mass of sample and container Mass of sample and container after ...
Chemistry – V – BSC – 503
... Argentometric Titration (I) Mohar’s method (II) Fazan’s method (III) olhard’s method with use of proper indicator, graph and it’s practical application Examples of calculation based on pH, Normality, Molarity,Ksp etc. ...
... Argentometric Titration (I) Mohar’s method (II) Fazan’s method (III) olhard’s method with use of proper indicator, graph and it’s practical application Examples of calculation based on pH, Normality, Molarity,Ksp etc. ...
What Can I Do With a Major In Chemistry
... agricultural and forest products, plastics, coal, petroleum, dyes and rubber. Physical chemistry uses mathematics and the concepts of physics to study the chemical behaviour of reactions among substances. Chemistry majors can be employed in a number of settings including: research & development, gov ...
... agricultural and forest products, plastics, coal, petroleum, dyes and rubber. Physical chemistry uses mathematics and the concepts of physics to study the chemical behaviour of reactions among substances. Chemistry majors can be employed in a number of settings including: research & development, gov ...
Chemistry
... taking into account the percent and mass of each different isotope. C4.10e C4.10c Calculate the average atomic mass of an element given the percent abundance and mass of the individual isotopes. C4.10d Predict which isotope will have the greatest abundance given the possible isotopes for an element ...
... taking into account the percent and mass of each different isotope. C4.10e C4.10c Calculate the average atomic mass of an element given the percent abundance and mass of the individual isotopes. C4.10d Predict which isotope will have the greatest abundance given the possible isotopes for an element ...
Test Booklet
... 10 According to this balanced chemical equation, what volume of C2 H2 is required to form 40.0 L of CO2 ? 2C2 H2 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 2H2 O (g) + 4CO2 (g) ...
... 10 According to this balanced chemical equation, what volume of C2 H2 is required to form 40.0 L of CO2 ? 2C2 H2 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 2H2 O (g) + 4CO2 (g) ...
Homology Modelling and Methods for Fold Recognition
... •Although fold prediction methods are not 100% accurate, the methods are still very useful. •Run many different methods on many sequences from your homologous protein family. After all these runs, one can build up a consensus picture of the likely fold. •Remember that a correct fold may not be at th ...
... •Although fold prediction methods are not 100% accurate, the methods are still very useful. •Run many different methods on many sequences from your homologous protein family. After all these runs, one can build up a consensus picture of the likely fold. •Remember that a correct fold may not be at th ...
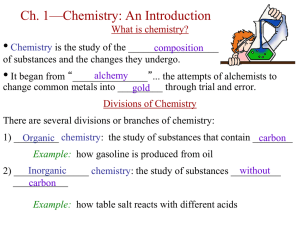
All That Matters - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... A binary compound is a simple sort of compound usually made up of ions. The compound made when a positive and negative ion combine has a collective charge of zero and is not an ion as a whole. Table salt made up of sodium and chlorine is an example of this. The sodium ion has a +1 charge, and the ch ...
... A binary compound is a simple sort of compound usually made up of ions. The compound made when a positive and negative ion combine has a collective charge of zero and is not an ion as a whole. Table salt made up of sodium and chlorine is an example of this. The sodium ion has a +1 charge, and the ch ...