"Immortal" flatworms: a weapon against bacteria
... (2) In 1814, JG Dalyell discovered that a planarian cut into 279 fragments could regenerate itself in 15 days to produce 279 new worms. ...
... (2) In 1814, JG Dalyell discovered that a planarian cut into 279 fragments could regenerate itself in 15 days to produce 279 new worms. ...
Bacteria and Viruses (SE).
... every 5 minutes. If one bacterium invades the human body, how many bacteria will be present in the body after 3 hours? ...
... every 5 minutes. If one bacterium invades the human body, how many bacteria will be present in the body after 3 hours? ...
The Biosphere
... of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationship among the various organisms in an ecosystem. ...
... of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationship among the various organisms in an ecosystem. ...
summary - All Party Parliamentary Food and Health Forum
... and non-GM equivalent and again this is too short. However, some of these studies showed significant changes which might indicate disease: MON863 GM maize causes haematological disturbances and organ weight loss in rats. A study in the International Journal of Biological Sciences (2009) (see slide 1 ...
... and non-GM equivalent and again this is too short. However, some of these studies showed significant changes which might indicate disease: MON863 GM maize causes haematological disturbances and organ weight loss in rats. A study in the International Journal of Biological Sciences (2009) (see slide 1 ...
... Kirby Bauer method. Results Out of the total specimens (1,384) analysed over the four-year study period, 455 of the urine samples (32.9 %) were culture positive, most (81.4 %) having come from females. The bacterium isolated most frequently was Escherichia coli (60.1 %) followed by Klebsiella pneumo ...
Slide 1
... make microbes more versatile than multicellular organisms. Discuss the roles of bacteria in nitrogen, carbon and sulfur cycling. What are the basic steps in these processes? Who fixes nitrogen, and why are there so few types of organisms that do? Discuss the role of the chemoautotroph in extreme env ...
... make microbes more versatile than multicellular organisms. Discuss the roles of bacteria in nitrogen, carbon and sulfur cycling. What are the basic steps in these processes? Who fixes nitrogen, and why are there so few types of organisms that do? Discuss the role of the chemoautotroph in extreme env ...
File
... with their physical environment (soil, water, climate, and so on). An ecosystem, or ecological system, consists of a community and all the physical aspects of its habitat, such as the soil, water, and weather. ...
... with their physical environment (soil, water, climate, and so on). An ecosystem, or ecological system, consists of a community and all the physical aspects of its habitat, such as the soil, water, and weather. ...
A Systems Biology and Ecology Framework for POPs
... analysis of the ODE model. Using Flux Balance Analysis (FBA) we have reconstructed the metabolic pathways of PCB bioremedation, by extending a FBA model of P. Putida [1]. In this way, we investigate the multiscale effects of the optimization of bacterial functions and perturbations (e.g. gene knocko ...
... analysis of the ODE model. Using Flux Balance Analysis (FBA) we have reconstructed the metabolic pathways of PCB bioremedation, by extending a FBA model of P. Putida [1]. In this way, we investigate the multiscale effects of the optimization of bacterial functions and perturbations (e.g. gene knocko ...
Flyswatter Review Community - all the populations of organisms
... Trophic Level - The different levels of organisms on a food chain, based on what they consume. Rule of 10 - Each time an eating event occurs, only 10% of that energy is available for use by the consuming organism. Bioaccumulation - The increase of a toxin in an organism over time Biomagnification - ...
... Trophic Level - The different levels of organisms on a food chain, based on what they consume. Rule of 10 - Each time an eating event occurs, only 10% of that energy is available for use by the consuming organism. Bioaccumulation - The increase of a toxin in an organism over time Biomagnification - ...
ecology definitions
... value can be given quantitatively e.g. as a population or qualitatively e.g. using terms such as rare or frequent giving a relative indication of number. ...
... value can be given quantitatively e.g. as a population or qualitatively e.g. using terms such as rare or frequent giving a relative indication of number. ...
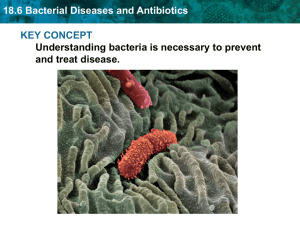
18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotics
... Some bacteria cause disease. • Bacteria cause disease by invading tissues or making toxins. • A toxin is a poison released by an organism. ...
... Some bacteria cause disease. • Bacteria cause disease by invading tissues or making toxins. • A toxin is a poison released by an organism. ...
Anti-biotic Resistance
... passenger in the human body, but it can cause pneumonia, toxic shock syndrome, the most common cause of food poisoning. The first penicillin-resistant strains of “Staph” were isolated in 1947! 1967, penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae and gonorrhea ...
... passenger in the human body, but it can cause pneumonia, toxic shock syndrome, the most common cause of food poisoning. The first penicillin-resistant strains of “Staph” were isolated in 1947! 1967, penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae and gonorrhea ...
Name: Period: _____ Symbiotic Interactions Classify the interaction
... 1. _______________________ Fungus and lichens live together. The fungus gets food from the algae while the algae have a place to live. 2. _______________________ The parasitic roundworm anchors itself to the wall of the intestine and causes diseases to the organisms. 3. _______________________ Spide ...
... 1. _______________________ Fungus and lichens live together. The fungus gets food from the algae while the algae have a place to live. 2. _______________________ The parasitic roundworm anchors itself to the wall of the intestine and causes diseases to the organisms. 3. _______________________ Spide ...
Background Factsheet: Microbes
... The Proteobacteria are a major group (phylum) of bacteria. They include a wide variety of pathogens, such as Escherichia, Salmonella, Vibrio, Helicobacter, and many other notable genera. Others are free-living, and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation.Rhodoferax ferrireduce ...
... The Proteobacteria are a major group (phylum) of bacteria. They include a wide variety of pathogens, such as Escherichia, Salmonella, Vibrio, Helicobacter, and many other notable genera. Others are free-living, and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation.Rhodoferax ferrireduce ...
microbe mission test
... bacteria. Samples can then be taken from the resulting colonies and a microbiological culture can be grown on a new plate so that the organism can be identified, studied, or tested. ...
... bacteria. Samples can then be taken from the resulting colonies and a microbiological culture can be grown on a new plate so that the organism can be identified, studied, or tested. ...
ANTIMICROBIALS 1
... Ampicillin and amoxicillin: effective against gram negative bacteria as they can bind to the bacteria’s cell wall ◦ Amoxicillin is often combined with clavulanic acid to add protection against beta lactamases ...
... Ampicillin and amoxicillin: effective against gram negative bacteria as they can bind to the bacteria’s cell wall ◦ Amoxicillin is often combined with clavulanic acid to add protection against beta lactamases ...
Introduction to Microbiology
... Careers in Microbiology Medical Microbiology involves the study of pathogens and the diseases they cause, as well as how the body fights those diseases Clinical Microbiology deals mainly with the diagnosis of infectious diseases ...
... Careers in Microbiology Medical Microbiology involves the study of pathogens and the diseases they cause, as well as how the body fights those diseases Clinical Microbiology deals mainly with the diagnosis of infectious diseases ...
Ecology Study Guide Unit 2 Test on Friday 9-25
... 1. Which of the following descriptions about the organization of an ecosystem is correct? 2. The simplest grouping of more than one kind of organism in the biosphere is a(an) 3. The algae at the beginning of the food chain are 4. Which of the following organisms does NOT require sunlight to live? 5. ...
... 1. Which of the following descriptions about the organization of an ecosystem is correct? 2. The simplest grouping of more than one kind of organism in the biosphere is a(an) 3. The algae at the beginning of the food chain are 4. Which of the following organisms does NOT require sunlight to live? 5. ...
Note Sheet
... Herbivore: eats only plants Carnivore: eats only animals (meat) Omnivore: eats plants and animals Scavenger: animals that feed on bodies of dead animals ...
... Herbivore: eats only plants Carnivore: eats only animals (meat) Omnivore: eats plants and animals Scavenger: animals that feed on bodies of dead animals ...
power point notes
... species that live in one area at one time. • Examples – all the red squirrels in Red Wing, all the oak trees in a forest, all the leeches in a lake ...
... species that live in one area at one time. • Examples – all the red squirrels in Red Wing, all the oak trees in a forest, all the leeches in a lake ...
Ch 18-1 and 18
... A. The science of classifying organisms and assigning them a scientific name. B. Why are scientific names necessary? 1. Many common names for the same organism depending on regions. 2. Many different languages, which have different names for the same organism. ...
... A. The science of classifying organisms and assigning them a scientific name. B. Why are scientific names necessary? 1. Many common names for the same organism depending on regions. 2. Many different languages, which have different names for the same organism. ...
Triclocarban

Triclocarban is an antibacterial agent common in personal care products like soaps and lotions as well as in the medical field, for which it was originally developed. Studies on its antibacterial qualities and mechanisms are growing. Research suggests that it is similar in its mechanism to triclosan and is effective in fighting infections by targeting the growth of bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. Additional research seeks to understand its potential for causing antibacterial resistance and its effects on organismal and environmental health.