Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation
... Anti-inflammatory and growth suppression effects Influences awareness and sleep habits ...
... Anti-inflammatory and growth suppression effects Influences awareness and sleep habits ...
doc Lectures 1
... The Endocrine Control Centre The hypothalamus (not a ductless gland! It's a CNS structure) and pituitary. Located in the diencephalon, just inferior to the thalamus. Controls a number of endocrine glands and a range of physiological activities. Major point of interaction of NS and ES. Hypothalamus i ...
... The Endocrine Control Centre The hypothalamus (not a ductless gland! It's a CNS structure) and pituitary. Located in the diencephalon, just inferior to the thalamus. Controls a number of endocrine glands and a range of physiological activities. Major point of interaction of NS and ES. Hypothalamus i ...
Human Physiology Unit 3A: Endocrine System
... (Up-regulation, Down-regulation) is where target cells form more receptors in response to a hormone, while (Up-regulation, Down-regulation) is where target cells lose receptors in response to a hormone Hormone Interactions 1. ______________ Effect: 2 hormones required to activate cell, one hormone ...
... (Up-regulation, Down-regulation) is where target cells form more receptors in response to a hormone, while (Up-regulation, Down-regulation) is where target cells lose receptors in response to a hormone Hormone Interactions 1. ______________ Effect: 2 hormones required to activate cell, one hormone ...
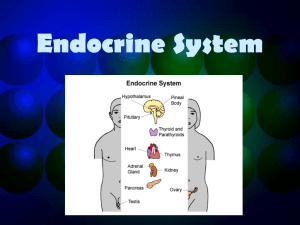
Organs of the Endocrine System and Their Products
... – carries regulatory hormones from hypothalamus to pituitary • releasing hormones stimulate secretion of pituitary hormones • inhibitory hormones inhibit secretion ...
... – carries regulatory hormones from hypothalamus to pituitary • releasing hormones stimulate secretion of pituitary hormones • inhibitory hormones inhibit secretion ...
Chapter 13 The Endocrine System • Endocrine System Produces
... Causes uterine contractions during labor and milk ejection through neuroendocrine reflex ...
... Causes uterine contractions during labor and milk ejection through neuroendocrine reflex ...
Endocrine System
... Each gland has two parts: Adrenal cortex, the outer part, produces hormones called corticosteroids that influence or regulate salt and water balance in the body, the body's response to stress, metabolism, the immune system, and sexual development and function. Adrenal medulla, the inner part p ...
... Each gland has two parts: Adrenal cortex, the outer part, produces hormones called corticosteroids that influence or regulate salt and water balance in the body, the body's response to stress, metabolism, the immune system, and sexual development and function. Adrenal medulla, the inner part p ...
Thyroid Problems - Improving Care In ED
... T3: 20%; mostly derived from T4; >99% protein bound; more biologically active than T4 as more free RT3, calcitonin TSH: reflects thyroid function better than thyroxine; normal = 0.3-5 Effects: metabolism of cholesterol/carbohydrate/protein/lipids; GI motility; glucose absorption; protein cata ...
... T3: 20%; mostly derived from T4; >99% protein bound; more biologically active than T4 as more free RT3, calcitonin TSH: reflects thyroid function better than thyroxine; normal = 0.3-5 Effects: metabolism of cholesterol/carbohydrate/protein/lipids; GI motility; glucose absorption; protein cata ...
Endocrine Physiology
... growth and development of sex organs in female Progesterone – maintains lining of the uterus ...
... growth and development of sex organs in female Progesterone – maintains lining of the uterus ...
Bio 3201 Ch. 13 Notes 2010
... • Cycles of secretion maintain physiological and homeostatic control. • These cycles can range from hours to months in duration. (one positive loop – oxytocin) ...
... • Cycles of secretion maintain physiological and homeostatic control. • These cycles can range from hours to months in duration. (one positive loop – oxytocin) ...
SAP 1 – Students will analyze anatomical structures in
... respond to it because there is something wrong with their insulin receptors • this type of diabetes is often called adult onset diabetes because it usually does not develop until later in life • it is not known what causes type 2 diabetes; however, we do know that heredity, obesity, and smoking are ...
... respond to it because there is something wrong with their insulin receptors • this type of diabetes is often called adult onset diabetes because it usually does not develop until later in life • it is not known what causes type 2 diabetes; however, we do know that heredity, obesity, and smoking are ...
Endocrine System
... • Endocrine glands: secrete hormones in small amounts directly into the bloodstream. • Specific hormones effect specific body parts. • They travel through the bloodstream until they reach their target cells (they cell that the hormone acts on) • Hormones do NOT affect other cells other than the targ ...
... • Endocrine glands: secrete hormones in small amounts directly into the bloodstream. • Specific hormones effect specific body parts. • They travel through the bloodstream until they reach their target cells (they cell that the hormone acts on) • Hormones do NOT affect other cells other than the targ ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... The hormone- receptor complex triggers activation or inactivation of specific genes Synthesis of new protein alters cellular activity causing a physiological response ...
... The hormone- receptor complex triggers activation or inactivation of specific genes Synthesis of new protein alters cellular activity causing a physiological response ...
(12) Endocrine System
... • additive (epinephrine, norepinephrine on heart) • complementary (FSH/LH on spermatogenesis) ...
... • additive (epinephrine, norepinephrine on heart) • complementary (FSH/LH on spermatogenesis) ...
Module 25 / Stimuli Regulating Hormone Production
... (auto- means self) affects local cells other than the secreting cells. While traditionally a hormone is thought to have its effect at a distances from where it is secreted, the definition of hormones now include paracrine and autocrine mechanisms as well. The all-inclusive term, Endocrine signaling, ...
... (auto- means self) affects local cells other than the secreting cells. While traditionally a hormone is thought to have its effect at a distances from where it is secreted, the definition of hormones now include paracrine and autocrine mechanisms as well. The all-inclusive term, Endocrine signaling, ...
Endocrine System
... Gonads Hormones • Estrogen-development of female reproductive organs, secondary sex characteristics. ...
... Gonads Hormones • Estrogen-development of female reproductive organs, secondary sex characteristics. ...
Normal pituitary Magnetic resonance scan
... ACTH (ATHAR, COSYNTROPIN) - Not used clinically to treat adrenal insufficiency due to expense - Used for stimulation testing. ACTH (IV ACTH should result in in peak plasma levels of glucocorticoids in 3-60 min - Tx myasthenia gravis Adverse Effects (Prolonged use): Suppression of hypothalamic pitu ...
... ACTH (ATHAR, COSYNTROPIN) - Not used clinically to treat adrenal insufficiency due to expense - Used for stimulation testing. ACTH (IV ACTH should result in in peak plasma levels of glucocorticoids in 3-60 min - Tx myasthenia gravis Adverse Effects (Prolonged use): Suppression of hypothalamic pitu ...
Hormones
... • The endocrine system comprises a group of ductless glands that secrete chemical messenger substances, called hormones, into the bloodstream. • Hormones are responsible for the longterm regulation of many bodily functions. • The endocrine system includes the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus ...
... • The endocrine system comprises a group of ductless glands that secrete chemical messenger substances, called hormones, into the bloodstream. • Hormones are responsible for the longterm regulation of many bodily functions. • The endocrine system includes the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus ...
The Endocrine Syetem
... pancreas secretes insulin to move blood-sugar into cells, thus decreasing levels ...
... pancreas secretes insulin to move blood-sugar into cells, thus decreasing levels ...
Chapter 18 - Illini West High School
... Breast Self-exam • Breast cancer is the most common cancer and the second leading cause of death, after lung cancer for women in the United States • The American Cancer Society recommends that females examine their breasts once a month, right after the menstrual period ...
... Breast Self-exam • Breast cancer is the most common cancer and the second leading cause of death, after lung cancer for women in the United States • The American Cancer Society recommends that females examine their breasts once a month, right after the menstrual period ...
Endocrine System - walker2016
... Endocrine glands – ductless organs that secrete their molecules directly into the ...
... Endocrine glands – ductless organs that secrete their molecules directly into the ...
Endocrine System 2
... • Human Growth Hormone can be prescribed to treat growth disorders in children • Also currently used in U.S. livestock milk production, deemed controvercial • Athletes have been abusing this drug since 1982 as it is an “anabolic” agent, was impossible to detect difference in blood test b/t natural a ...
... • Human Growth Hormone can be prescribed to treat growth disorders in children • Also currently used in U.S. livestock milk production, deemed controvercial • Athletes have been abusing this drug since 1982 as it is an “anabolic” agent, was impossible to detect difference in blood test b/t natural a ...
Anatomy chapter 11 (Endocrine system)
... • Releasing hormones from the hypothalamus control the secretions of the anterior pituitary. •A small gland located in the brain that is important for puberty and sexual cycles. •Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates ...
... • Releasing hormones from the hypothalamus control the secretions of the anterior pituitary. •A small gland located in the brain that is important for puberty and sexual cycles. •Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates ...
Hormones
... Lack insulin receptors at target cells ~90% of all diabetics Strong links within family Treated with drugs to stimulate insulin secretion Also with diet & exercise ...
... Lack insulin receptors at target cells ~90% of all diabetics Strong links within family Treated with drugs to stimulate insulin secretion Also with diet & exercise ...
Bio 160 – Endocrine System
... Bio 160 Study Guide – Endocrine System – Chapter 10 Compare the Endocrine system as a control system to the Nervous system, including response time, duration of effects, type of signaling (electrical? Chemical?), type of effects on body, etc Where are endocrine tissues found in the body (provide spe ...
... Bio 160 Study Guide – Endocrine System – Chapter 10 Compare the Endocrine system as a control system to the Nervous system, including response time, duration of effects, type of signaling (electrical? Chemical?), type of effects on body, etc Where are endocrine tissues found in the body (provide spe ...