chapter 1 - Allied Schools
... Diabetes insipidus is the result of a hyposecretion of ADH. This results in large volumes of dilute urine being formed, causing dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Prolactin stimulates breast development during pregnancy and milk secretion (milk let-down) after pregnancy. Oxytocin stimulates uter ...
... Diabetes insipidus is the result of a hyposecretion of ADH. This results in large volumes of dilute urine being formed, causing dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Prolactin stimulates breast development during pregnancy and milk secretion (milk let-down) after pregnancy. Oxytocin stimulates uter ...
Endocrine System Webquest - Biology with Mrs. Jennings
... answers. a. Be sure to play the animation showing the menstrual cycle when you get to it and pay particular attention to the hormones involved. This is an excellent example of how multiple hormones can influence each other and control a major biological process like menstruation. It is often used as ...
... answers. a. Be sure to play the animation showing the menstrual cycle when you get to it and pay particular attention to the hormones involved. This is an excellent example of how multiple hormones can influence each other and control a major biological process like menstruation. It is often used as ...
Bio Endocrine System Art
... Growth hormone problems. Too much growth hormone in kids and teens who are still growing will make their bones and other body parts grow excessively. This rare condition (sometimes called gigantism) is usually caused by a pituitary tumor and can be treated by ...
... Growth hormone problems. Too much growth hormone in kids and teens who are still growing will make their bones and other body parts grow excessively. This rare condition (sometimes called gigantism) is usually caused by a pituitary tumor and can be treated by ...
Chapter 17 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Other endocrine glands Hormones and their actions Stress and adaptation Eicosanoids and paracrine signaling Endocrine disorders ...
... Other endocrine glands Hormones and their actions Stress and adaptation Eicosanoids and paracrine signaling Endocrine disorders ...
Endocrine System
... Other endocrine glands Hormones and their actions Stress and adaptation Eicosanoids and paracrine signaling Endocrine disorders ...
... Other endocrine glands Hormones and their actions Stress and adaptation Eicosanoids and paracrine signaling Endocrine disorders ...
Ch 17
... Other endocrine glands Hormones and their actions Stress and adaptation Eicosanoids and paracrine signaling Endocrine disorders ...
... Other endocrine glands Hormones and their actions Stress and adaptation Eicosanoids and paracrine signaling Endocrine disorders ...
1 Chapter 11: The Endocrine System • Exocrine glands will produce
... Endocrine glands will produce a substance (hormone) that will be secreted into bodily fluids to travel to a specific or target cell or gland Characteristics of the Endocrine System o Coordinates and integrates with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis o Utilizes hormones secreted from endocrin ...
... Endocrine glands will produce a substance (hormone) that will be secreted into bodily fluids to travel to a specific or target cell or gland Characteristics of the Endocrine System o Coordinates and integrates with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis o Utilizes hormones secreted from endocrin ...
Growth Hormone Treatment
... HORSE LIVER. When it enters the human liver it causes chaos. The liver recognizes it as estrogen but it is already marked as waste. The already conjugated estrogen interferes with IGF/1 (growth hormone) and other hormones. The horse conjugated estrogen then travels to the cells where it causes even ...
... HORSE LIVER. When it enters the human liver it causes chaos. The liver recognizes it as estrogen but it is already marked as waste. The already conjugated estrogen interferes with IGF/1 (growth hormone) and other hormones. The horse conjugated estrogen then travels to the cells where it causes even ...
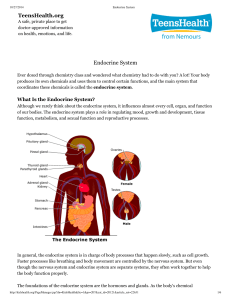
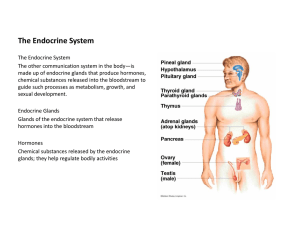
The Endocrine System
... The Endocrine System The Endocrine System The other communication system in the body—is made up of endocrine glands that produce hormones, chemical substances released into the bloodstream to guide such processes as metabolism, growth, and sexual development. Endocrine Glands Glands of the endocrine ...
... The Endocrine System The Endocrine System The other communication system in the body—is made up of endocrine glands that produce hormones, chemical substances released into the bloodstream to guide such processes as metabolism, growth, and sexual development. Endocrine Glands Glands of the endocrine ...
The Endocrine System
... Characteristics of Hormone Function 1. most if not all organs produce hormones “officially” the endocrine system consists of several major glands and many minor glands 2. Structurally, the major hormones are of two basic types: a. amino acid derived hormones i. amines (acetylcholine, thyroid hormon ...
... Characteristics of Hormone Function 1. most if not all organs produce hormones “officially” the endocrine system consists of several major glands and many minor glands 2. Structurally, the major hormones are of two basic types: a. amino acid derived hormones i. amines (acetylcholine, thyroid hormon ...
The Endocrine System
... hours) has been used to stimulate GH release in patients with GH deficiency that is not of pituitary origin. IV, SC, intranasal ...
... hours) has been used to stimulate GH release in patients with GH deficiency that is not of pituitary origin. IV, SC, intranasal ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Protein kinases activate (or deactivate) all kinds of enzymes by phosphorylating them, that is they add phosphates to them. This whole business is referred to as a "cascade" effect: One hormone molecule can set a G protein on its way to hooking up with many Adenylate Cyclases. These make many cyclic ...
... Protein kinases activate (or deactivate) all kinds of enzymes by phosphorylating them, that is they add phosphates to them. This whole business is referred to as a "cascade" effect: One hormone molecule can set a G protein on its way to hooking up with many Adenylate Cyclases. These make many cyclic ...
Chapters 15, and 16
... In males, the testes produce sperm that mature in the epididymides and may be stored in the vasa deferentia before entering the urethra, along with secretions produced by seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands. Orgasm in Males The penis is the male organ of sexual intercourse ...
... In males, the testes produce sperm that mature in the epididymides and may be stored in the vasa deferentia before entering the urethra, along with secretions produced by seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands. Orgasm in Males The penis is the male organ of sexual intercourse ...
Endocrine System
... pituitary gland senses the normal levels of thyroid hormone in the bloodstream and adjusts its release of thyrotropin, the pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. Another example is parathyroid hormone, which increases the level of calcium in the blood. When ...
... pituitary gland senses the normal levels of thyroid hormone in the bloodstream and adjusts its release of thyrotropin, the pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. Another example is parathyroid hormone, which increases the level of calcium in the blood. When ...
Pituitary and Hypothalamus Disorders MBBS III Seminar
... – Prolactin levels as well as other pituitary function tests – MRI or CT & visual field tests to determine size and position of the adenoma. – Bone scan ...
... – Prolactin levels as well as other pituitary function tests – MRI or CT & visual field tests to determine size and position of the adenoma. – Bone scan ...
Chapter 13: The Endocrine System
... Chemical messengers that influence or control the activities of other tissues or organs Most are transported to areas of the body far from their release site Two classes o Steroids (from the adrenal cortex and sex glands) o Proteins (all other hormones) Hormone Targets Each hormone only bind ...
... Chemical messengers that influence or control the activities of other tissues or organs Most are transported to areas of the body far from their release site Two classes o Steroids (from the adrenal cortex and sex glands) o Proteins (all other hormones) Hormone Targets Each hormone only bind ...
ENDOCRINOLOGY Pituitary Diseases (secondary) Pituitary Tumor
... 2º (secondary) adrenal insufficiency- pit. Problem (not enough ACTH) a. MCC- long steroid use body therefore won’t produce it’s own endogenous steroids (HPA suppression) b. c. Sx: salt craving, N/V/D, weight loss, dehydration d. Dx: normal cosyntropin test (b/c ACTH problem not adrenal problem) e. ...
... 2º (secondary) adrenal insufficiency- pit. Problem (not enough ACTH) a. MCC- long steroid use body therefore won’t produce it’s own endogenous steroids (HPA suppression) b. c. Sx: salt craving, N/V/D, weight loss, dehydration d. Dx: normal cosyntropin test (b/c ACTH problem not adrenal problem) e. ...
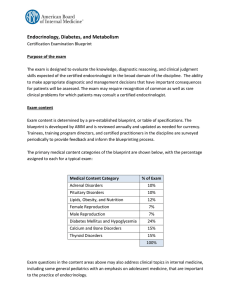
Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism
... Hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes Hypoglycemia due to oral agents and insulin management Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes Additional types of diabetes mellitus Monogenic diabetes Ketosis-prone diabetes (KPD) New-onset diabetes after transplant (NODAT) [post-transplant diabetes mellitus (PTDM)] Pancrea ...
... Hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes Hypoglycemia due to oral agents and insulin management Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes Additional types of diabetes mellitus Monogenic diabetes Ketosis-prone diabetes (KPD) New-onset diabetes after transplant (NODAT) [post-transplant diabetes mellitus (PTDM)] Pancrea ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction Growth and development Mobilization of body defenses Maintenance of much of homeostasis Regulation of metabolism ...
... Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction Growth and development Mobilization of body defenses Maintenance of much of homeostasis Regulation of metabolism ...
Chapter 14
... secrete hormones. The kidney, for example, contains scattered cells that secrete erythropoietin, a hormone essential for production of red blood cells. Even the heart contains cells that produce atrial naturetic hormone, which is important in sodium and water balance. ...
... secrete hormones. The kidney, for example, contains scattered cells that secrete erythropoietin, a hormone essential for production of red blood cells. Even the heart contains cells that produce atrial naturetic hormone, which is important in sodium and water balance. ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Stephen G
... 6. How do hormones bring about their effects on cells? What are five ways a hormone may produce a change? 7. There are two major mechanisms by which hormone-receptor binding places intracellular machinery into action. One uses G-proteins and ________________, and the other involves steroid hormones ...
... 6. How do hormones bring about their effects on cells? What are five ways a hormone may produce a change? 7. There are two major mechanisms by which hormone-receptor binding places intracellular machinery into action. One uses G-proteins and ________________, and the other involves steroid hormones ...
Option D.5 Hormones and metabolism
... • Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream • Steroid hormones bind to receptors proteins in the cytoplasm of the target cell to form a receptor-hormone complex • The receptor-hormone complex promotes the transcription of specific genes • Peptide hormones bind to receptors in t ...
... • Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream • Steroid hormones bind to receptors proteins in the cytoplasm of the target cell to form a receptor-hormone complex • The receptor-hormone complex promotes the transcription of specific genes • Peptide hormones bind to receptors in t ...
No Slide Title - People Server at UNCW
... B. Review of structure and function 1. Pituitary gland a. Controlled by the hypothalamus b. Infundibulum c. ...
... B. Review of structure and function 1. Pituitary gland a. Controlled by the hypothalamus b. Infundibulum c. ...
File - Mr. Downing Biology 30
... chemical messengers – called hormones Endocrine glands are different from exocrine glands in that they release hormones and secrete these substances directly into the blood Exocrine glands produce secretions released via tubular ducts (ex: mammary glands secrete milk through ducts and therefore they ...
... chemical messengers – called hormones Endocrine glands are different from exocrine glands in that they release hormones and secrete these substances directly into the blood Exocrine glands produce secretions released via tubular ducts (ex: mammary glands secrete milk through ducts and therefore they ...
Neuroendocrine tumor

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. Many are benign, while some are malignant. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung and the rest of the body.Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones.