File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... All rats, except for those in the control group were injected with a hormone (ACTH, cortisol, LH, TRH, testosterone or TSH) on a daily basis for two weeks, sacrificed humanely and autopsied. Organ weights were measured at autopsy. Using your predictions of hormone effects and the autopsy data, match ...
... All rats, except for those in the control group were injected with a hormone (ACTH, cortisol, LH, TRH, testosterone or TSH) on a daily basis for two weeks, sacrificed humanely and autopsied. Organ weights were measured at autopsy. Using your predictions of hormone effects and the autopsy data, match ...
detailed lecture outline
... prohormones—inactive molecules that are converted to active hormones either before or after they are secreted. ...
... prohormones—inactive molecules that are converted to active hormones either before or after they are secreted. ...
The Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
... What do the parathyroid glands do? The parathyroid glands release a hormone called parathyroid hormone. This hormone helps to control the levels of three minerals in the body: calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. Parathyroid hormone has a number of effects in the body: It causes the release of calcium ...
... What do the parathyroid glands do? The parathyroid glands release a hormone called parathyroid hormone. This hormone helps to control the levels of three minerals in the body: calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. Parathyroid hormone has a number of effects in the body: It causes the release of calcium ...
Chapter 18 The Central Endocrine Glands
... Plasma concentration of each hormone is normally controlled by regulated changes in rate of hormone secretion Direct regulatory inputs that influence secretory output of endocrine cells – Neural input – Input from another hormone Effective plasma concentration also influenced by – Rate of removal fr ...
... Plasma concentration of each hormone is normally controlled by regulated changes in rate of hormone secretion Direct regulatory inputs that influence secretory output of endocrine cells – Neural input – Input from another hormone Effective plasma concentration also influenced by – Rate of removal fr ...
Chapter 1 A Perspective on Human Genetics
... pituitary stimulates thyroid hormone secretion by thyroid gland ...
... pituitary stimulates thyroid hormone secretion by thyroid gland ...
The Endocrine System
... Endocrine Glands vs. Exocrine Glands: There are two basic types of glands in the body, called endocrine glands and exocrine glands. The main difference between the two is that exocrine glands produce things like sweat, saliva, or digestive hormones, and deliver them to other parts of the body via du ...
... Endocrine Glands vs. Exocrine Glands: There are two basic types of glands in the body, called endocrine glands and exocrine glands. The main difference between the two is that exocrine glands produce things like sweat, saliva, or digestive hormones, and deliver them to other parts of the body via du ...
Chapter 1 A Perspective on Human Genetics
... • The effective plasma concentration of a hormone is normally regulated by changes in its rate of secretion. • The effective plasma concentration of a hormone is influenced by its transport, metabolism, and excretion. • Endocrine disorders result from hormone excess or deficiency or decreased target ...
... • The effective plasma concentration of a hormone is normally regulated by changes in its rate of secretion. • The effective plasma concentration of a hormone is influenced by its transport, metabolism, and excretion. • Endocrine disorders result from hormone excess or deficiency or decreased target ...
- ISpatula
... blood vessels and improves blood flow. B)When secreted by certain white blood cells, NO stimulates the reproduction of some bacteria and cancer cells. C)NO decreases the blood flow into the penis, producing an erection. D)In the nervous system, NO serves as a cell surface receptor. E)All of the list ...
... blood vessels and improves blood flow. B)When secreted by certain white blood cells, NO stimulates the reproduction of some bacteria and cancer cells. C)NO decreases the blood flow into the penis, producing an erection. D)In the nervous system, NO serves as a cell surface receptor. E)All of the list ...
Regulating Plasma Hormone Levels
... Why Regulate Peptide Hormone Release? • Allows for large, rapid changes in peptide hormone levels. • Allows for the release of peptide hormones at a greater rate than the hormone is synthesized. - peptide can be accumulated in secretory granules, and rapidly released when necessary ...
... Why Regulate Peptide Hormone Release? • Allows for large, rapid changes in peptide hormone levels. • Allows for the release of peptide hormones at a greater rate than the hormone is synthesized. - peptide can be accumulated in secretory granules, and rapidly released when necessary ...
File
... parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands • Hypothalamus is Neuroendocrine organ • Some have exocrine and endocrine functions – Pancreas, gonads, placenta ...
... parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands • Hypothalamus is Neuroendocrine organ • Some have exocrine and endocrine functions – Pancreas, gonads, placenta ...
ch16_wcr
... Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands (on dorsal aspect of thyroid gland) Thymus ...
... Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands (on dorsal aspect of thyroid gland) Thymus ...
Hipofizer hastal*klar
... most common presenting symptom in this age group, possibly with an associated delay in tooth development. Hypoglycemia, although less frequent, can also be a presenting sign of hypopituitarism in older infants and children. Patients with acquired or milder forms of gonadotropin deficiency who do not ...
... most common presenting symptom in this age group, possibly with an associated delay in tooth development. Hypoglycemia, although less frequent, can also be a presenting sign of hypopituitarism in older infants and children. Patients with acquired or milder forms of gonadotropin deficiency who do not ...
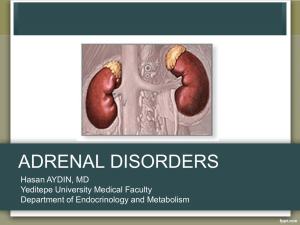
Adrenal disorders - University of Yeditepe Faculty of Medicine, 2011
... • Found on work up for another cause, not on cancer workup – US 0.1% – CT 0.4 to 4.4% – MRI ...
... • Found on work up for another cause, not on cancer workup – US 0.1% – CT 0.4 to 4.4% – MRI ...
Pathology of Hypophysis
... Why bitemporal hemianopsia usually is NOT perfectly symmetrical. Because pituitary tumors are under no law to grow perfectly midline. ...
... Why bitemporal hemianopsia usually is NOT perfectly symmetrical. Because pituitary tumors are under no law to grow perfectly midline. ...
Pituitary Disorders - Endocrinology
... Which pharmacologic option to choose depends on type of tumor: • Dopamine agonists: bromocriptine, cabergoline- most useful for prolactinomas, less useful for GH secreting adenomas ...
... Which pharmacologic option to choose depends on type of tumor: • Dopamine agonists: bromocriptine, cabergoline- most useful for prolactinomas, less useful for GH secreting adenomas ...
Unit P: Endocrine System
... 3. If not treated, excess glucose in blood (hyperglycemia) and secreted in urine (glycosuria) 4. If too much insulin given, blood sugar can get too low (hypoglycemia) and person can develop insulin shock 5. Type II diabetes is not insulin-dependent – most common, usually familial, occurs later in li ...
... 3. If not treated, excess glucose in blood (hyperglycemia) and secreted in urine (glycosuria) 4. If too much insulin given, blood sugar can get too low (hypoglycemia) and person can develop insulin shock 5. Type II diabetes is not insulin-dependent – most common, usually familial, occurs later in li ...
21 Endocrine
... body that are endocrine glands. • An endocrine gland secretes endocrine hormones. • Endocrine hormones are hormones that are secreted into the blood. • Hormones are substances that are secreted by one group of cells that affects the physiology of another group of cells (organs). The endocrine system ...
... body that are endocrine glands. • An endocrine gland secretes endocrine hormones. • Endocrine hormones are hormones that are secreted into the blood. • Hormones are substances that are secreted by one group of cells that affects the physiology of another group of cells (organs). The endocrine system ...
Chapter 18 The Central Endocrine Glands
... Plasma concentration of each hormone is normally controlled by regulated changes in rate of hormone secretion Direct regulatory inputs that influence secretory output of endocrine cells – Neural input – Input from another hormone Effective plasma concentration also influenced by – Rate of removal fr ...
... Plasma concentration of each hormone is normally controlled by regulated changes in rate of hormone secretion Direct regulatory inputs that influence secretory output of endocrine cells – Neural input – Input from another hormone Effective plasma concentration also influenced by – Rate of removal fr ...
Endocrine Ch 16-Fall 2016-PPT-Student
... the presence or absence of other ___________ When ion or nutrient concentrations in the blood stimulate hormone release, the stimulus is humoral Neural stimuli of referred to as ___________ . ________ endocrine glands occur when nerve impulses stimulate hormone release directly. ...
... the presence or absence of other ___________ When ion or nutrient concentrations in the blood stimulate hormone release, the stimulus is humoral Neural stimuli of referred to as ___________ . ________ endocrine glands occur when nerve impulses stimulate hormone release directly. ...
The Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
... What are the thyroid and parathyroid glands? Both the thyroid and parathyroid glands are endocrine glands. This means they make and secrete (release) hormones. Hormones are chemicals which can be released into the bloodstream. They act as messengers, affecting cells and tissues in distant parts of y ...
... What are the thyroid and parathyroid glands? Both the thyroid and parathyroid glands are endocrine glands. This means they make and secrete (release) hormones. Hormones are chemicals which can be released into the bloodstream. They act as messengers, affecting cells and tissues in distant parts of y ...
Endocrine disease
... ACTH Underscretion Primary hypothyroidism where the thyroid gland is unable to make sufficient thyroid hormone despite continued stimulation by TSH Failure of hormone responsiveness Pseudohypoparathyroidism where pt become hypocalcemic despite elevated plasma PTH concentration because target organs ...
... ACTH Underscretion Primary hypothyroidism where the thyroid gland is unable to make sufficient thyroid hormone despite continued stimulation by TSH Failure of hormone responsiveness Pseudohypoparathyroidism where pt become hypocalcemic despite elevated plasma PTH concentration because target organs ...
1- What are trophic hormones? Hormones secreted by the anterior
... 1- What are trophic hormones? Hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary, which influence hormone secretion by other endocrine glands such as thyroid, adrenal cortex, etc., are termed trophic hormones. The trophic hormones are, in turn, controlled by the hypothalamus which synthesizes regulator ...
... 1- What are trophic hormones? Hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary, which influence hormone secretion by other endocrine glands such as thyroid, adrenal cortex, etc., are termed trophic hormones. The trophic hormones are, in turn, controlled by the hypothalamus which synthesizes regulator ...
Quick Review of Feedback Systems
... • At this point, do NOT memorize the preceding lists of hormone sources and functions. • DO understand the following information on hormone structure…. ...
... • At this point, do NOT memorize the preceding lists of hormone sources and functions. • DO understand the following information on hormone structure…. ...
SECOND HORMONE(s)
... 22. All of the following glands listed below are endocrine glands, except? Answer not given. . . You should be able to figure out from the choices given. 23. Characteristics of Exocrine Glands include all of the following, except? a. non-hormonal material secreted through ducts b. holocrine, merocri ...
... 22. All of the following glands listed below are endocrine glands, except? Answer not given. . . You should be able to figure out from the choices given. 23. Characteristics of Exocrine Glands include all of the following, except? a. non-hormonal material secreted through ducts b. holocrine, merocri ...
Neuroendocrine tumor

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. Many are benign, while some are malignant. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung and the rest of the body.Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, such as looking similar, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones.